The absence of piezoelectricity in silicon makes direct electromechanical applications of this mainstream semiconductor impossible. Integrated electrical control of the silicon mechanics, however, would open up new perspectives for on-chip actuorics. Here, we combine wafer-scale nanoporosity in single-crystalline silicon with polymerization of an artificial muscle material inside pore space to synthesize a composite that shows macroscopic electrostrain in aqueous electrolyte. The voltage-strain coupling is three orders of magnitude larger than the best-performing ceramics in terms of piezoelectric actuation. We trace this huge electroactuation to the concerted action of 100 billions of nanopores per square centimeter cross section and to potential-dependent pressures of up to 150 atmospheres at the single-pore scale. The exceptionally small operation voltages (0.4 to 0.9 volts), along with the sustainable and biocompatible base materials, make this hybrid promising for bioactuator applications.
An electrochemical change in the oxidation state of polypyrrole (PPy) can increase or decrease the number of delocalized charges in its polymer backbone (1). Immersed in an electrolyte, this is also accompanied by a reversible counter-ion uptake or expulsion and thus with a marcroscopic contraction or swelling under electrical potential control, making PPy one of the most used artificial muscle materials (1–5).
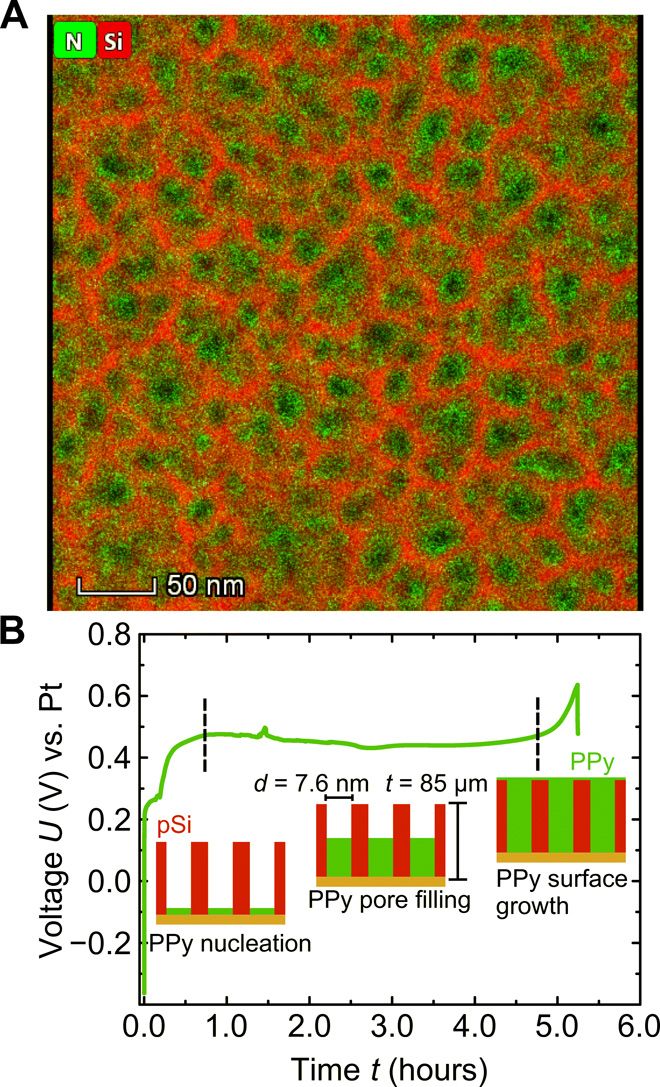
Here, we combine this actuator polymer with the three-dimensional (3D) scaffold structure of nanoporous silicon (6–8) to design, similarly as found in many multiscale biological composites in nature (9), a material with embedded electrochemical actuation that consists of a few light and abundant elemental constituents (i.e., H, C, N, O, Si, and Cl).