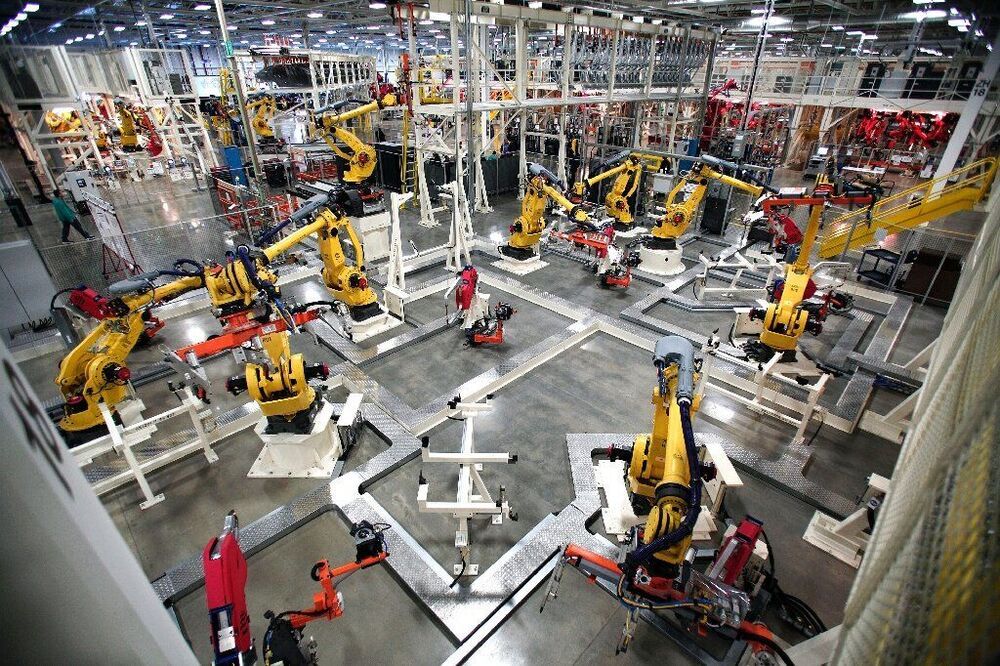
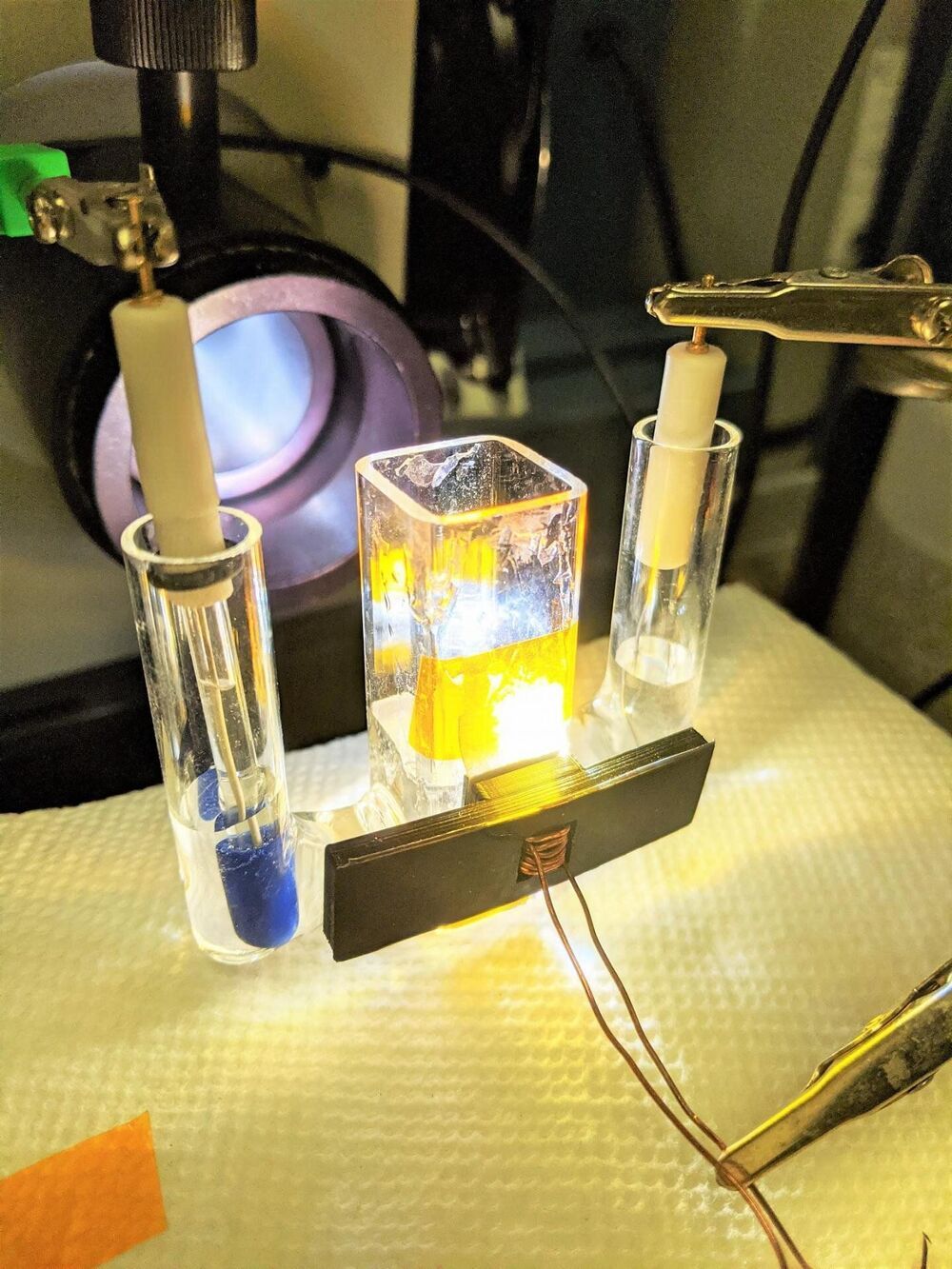
As renewable forms of power like wind and solar continue to gain prominence, there will be a need for creative solutions when it comes to storing energy from sources that are intermittent by nature. One potential solution is known as a molten salt battery, which offers advantages that lithium batteries do not, but have their share of kinks to iron out, too. Scientists at Sandia National Laboratories have come up with a new design that addresses a number of these shortcomings, and demonstrated a working molten salt battery that can be constructed far more cheaply, while storing more energy, than currently available versions.
Storing vast amounts of energy in a cheap and efficient manner is the name of the game when it comes to powering whole cities with renewable energy, and despite its many strengths, this is where expensive lithium battery technology falls short. Molten salt batteries shape as a more cost-effective solution, which use electrodes kept in a molten state with the help of high temperatures. This is something that the Sandia scientists have been working to change.
“We’ve been working to bring the operating temperature of molten sodium batteries down as low as physically possible,” says Leo Small, the lead researcher on the project. “There’s a whole cascading cost savings that comes along with lowering the battery temperature. You can use less expensive materials. The batteries need less insulation and the wiring that connects all the batteries can be a lot thinner.”