The weight from the additional battery cells required to match the range of gas cars would slow the car down and make it less efficient, Musk said.



Tesla’s Fremont Factory could have its production capacity increased, according to CEO Elon Musk. Tesla is “considering expanding [Fremont] significantly,” Musk said in a Tweet last night.
Following Musk’s heavily publicized jab at President Joe Biden on Tuesday night for not mentioning Tesla in the State of the Union Speech with the likes of Ford and GM, who received Biden’s praise for electric vehicle projects resulting in employment opportunities. While Biden commended Ford for $11 billion invested and 11,000 new jobs and GM for $7 billion and 4,000 new employment opportunities in Michigan, Musk hit back with a valid point.
“Tesla has created over 50,000 US jobs building electric vehicles & is investing more than double GM + Ford combined,” he said, alerting “the person running this account” to give Tesla more credit.
Space worms.
Two young worms are the first offspring in a Mars soil experiment at Wageningen University & Research. Biologist Wieger Wamelink found them in a Mars soil simulant that he obtained from NASA. At the start he only added adult worms. The experiments are crucial in the study that aims to determine whether people can keep themselves alive at the red planet by growing their own crops on Mars soils.
To feed future humans on Mars a sustainable closed agricultural ecosystem is a necessity. Worms will play a crucial role in this system as they break down and recycle dead organic matter. The poop and pee of the (human) Martian will also have to be used to fertilise the soil, but for practical and safety reasons we are presently using pig slurry. We have since been observing the growth of rucola (rocket) in Mars soil simulant provided by NASA to which worms and slurry have been added. ‘Clearly the manure stimulated growth, especially in the Mars soil simulant, and we saw that the worms were active. However, the best surprise came at the end of the experiment when we found two young worms in the Mars soil simulant’, said Wieger Wamelink of Wageningen University & Research.
‘The positive effect of adding manure was not unexpected’, added Wamelink, ‘but we were surprised that it makes Mars soil simulant outperform Earth silver sand’. We added organic matter from earlier experiments to both sands. We added the manure to a sample of the pots and then, after germination of the rucola, we added the worms. We therefore ended up with pots with all possible combinations with the exception of organic matter which was added to all of the pots.

Russia’s attacks on Ukraine continue to take lives and destroy infrastructure as the country invades. This infrastructure damage has disrupted internet access in Ukraine, leading a government official to publicly request Starlink satellite internet access for the country from SpaceX CEO Elon Musk. Musk obliged, activating Starlink service in Ukraine and sending additional hardware. But with continued attacks on infrastructure, how will Ukraine stay connected?
Fedorov brings up an important point: Even though Starlink operates without the need for traditional internet infrastructure, the Earth-bound hardware still needs power. And, as Russian attacks bombard the country, Ukraine’s internet access will continue to be threatened.
Fedorov’s statement publicly reached out for help acquiring generators to keep Starlink online for Ukrainians. But Musk responded with an alternative suggestion.
“Solar panels + battery pack better than generator, as no heat signature or smoke & doesn’t run out of fuel,” Musk wrote in response on Twitter.
Elon Musk has some ideas.
Ford this morning said it’s separating its electric vehicle and internal combustion businesses into separate units. Why it matters: The creation of distinct business lines — called “Model e” and “Ford Blue” — underscores how auto giants are reorienting around EV development. Get market news worthy of your time with Axios Markets. Subscribe for free. How it works: Ford said the two units would be “strategically interdependent” and share relevant tech. Together with the Ford Pro commercial services line launched last year, Ford said the three units will begin to separately report profits and losses in 2023.
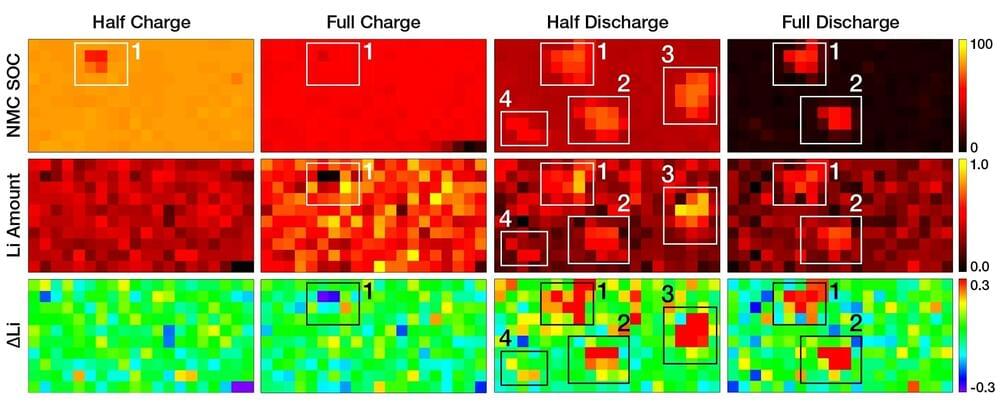
Pure lithium metal is a promising replacement for the graphite-based anodes currently used in electric vehicle batteries. It could tremendously reduce battery weights and dramatically extend the driving range of electric vehicles relative to existing technologies. But before lithium metal batteries can be used in cars, scientists must first figure out how to extend their lifetimes.
A new study led by Peter Khalifah—a chemist at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Brookhaven National Laboratory and Stony Brook University—tracked lithium metal deposition and removal from a battery anode while it was cycling to find clues as to how failure occurs. The work is published in a special issue of the Journal of the Electrochemical Society honoring the contributions of Nobel Prize-winning battery researcher John Goodenough, who like Khalifah is a member of the Battery 500 Consortium research team.
“In a good battery, the rate of lithium plating (deposition) and stripping (removal) will be the same at all positions on the surface of electrodes,” Khalifah said. “Our results show that it’s harder to remove lithium at certain places, which means there are problems there. By identifying the cause of the problems, we can figure out how to get rid of them and make better batteries with higher capacities and longer lifetimes.”
A new study challenges the conventional approach to designing soft robotics and a class of materials called metamaterials by utilizing the power of computer algorithms. Researchers from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign and Technical University of Denmark can now build multimaterial structures without dependence on human intuition or trial-and-error to produce highly efficient actuators and energy absorbers that mimic designs found in nature.
The study, led by Illinois civil and environmental engineering professor Shelly Zhang, uses optimization theory and an algorithm-based design process called topology optimization. Also known as digital synthesis, the design process builds composite structures that can precisely achieve complex prescribed mechanical responses.
The study results are published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
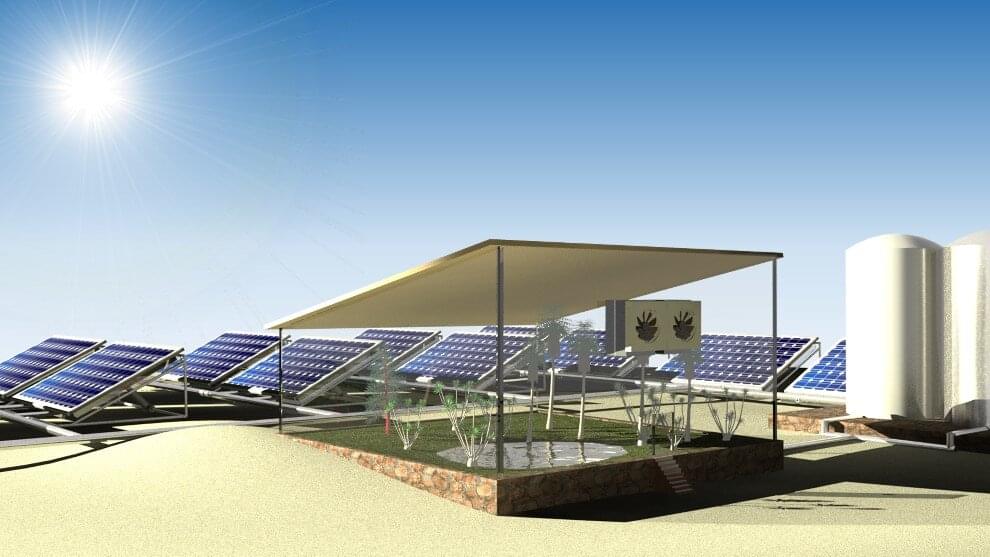

Using a unique hydrogel, scientists in Saudi Arabia created a solar-driven system that successfully grows spinach by using water drawn from the air while producing electricity. The proof-of-concept design, described March 1 in the journal Cell Reports Physical Science, offers a sustainable, low-cost strategy to improve food and water security for people living in dry-climate regions.
“A fraction of the world’s population still doesn’t have access to clean water or green power, and many of them live in rural areas with arid or semi-arid climate,” says senior author Peng Wang, a professor of environmental science and engineering at the King Abdullah University of Science and Technology (KAUST). “Our design makes water out of air using clean energy that would’ve been wasted and is suitable for decentralized, small-scale farms in remote places like deserts and oceanic islands.”
The system, called WEC2P, is composed of a solar photovoltaic panel placed atop a layer of hydrogel, which is mounted on top of a large metal box to condense and collect water. Wang and his team developed the hydrogel in their prior research, and the material can effectively absorb water vapor from ambient air and release the water content when heated.

