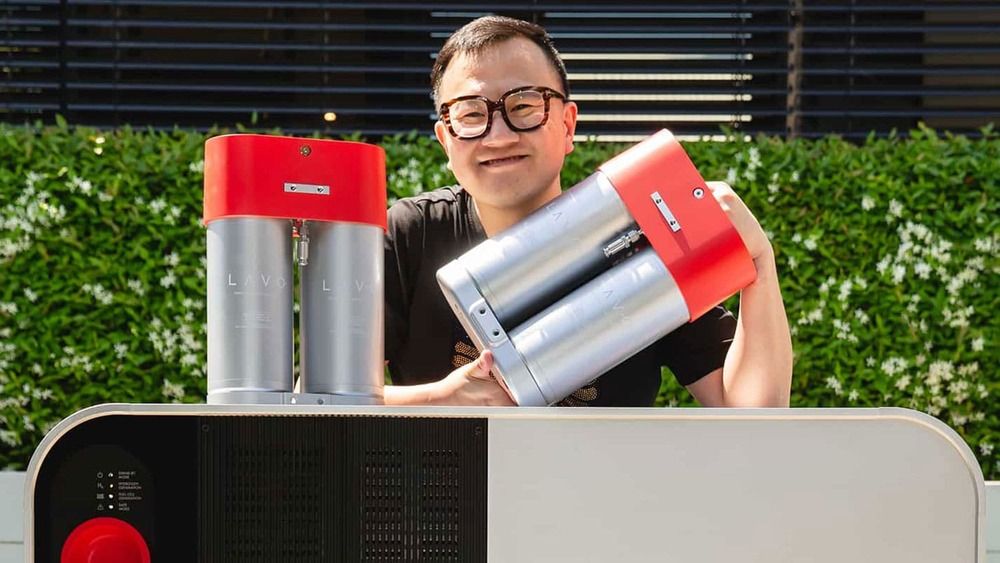
The Australian company LAVO has developed a hydrogen storage system for domestic solar systems. It is the world’s first integrated hybrid hydrogen battery that combines with rooftop solar to deliver sustainable, reliable, and renewable green energy to your home and business. Developed in partnership with UNSW, Sydney, Australia, and Design + Industry, the Hydrogen Battery System from LAVO consists of an electrolysis system, hydrogen storage array, and fuel cell power system rolled into one attractive cabinet. When the electricity from the solar system on the roof is not needed, it is stored in the form of hydrogen. This then serves as fuel for the fuel cell when the solar system is not supplying electricity.
However, LAVO’s hydrogen hybrid battery delivers a continuous output of 5 kW and stores over 40kWh of electricity – enough to power the average Australian home for two days on a single charge. The system is designed to easily integrate with existing solar panels, creating a significant opportunity for LAVO to have an immediate and notable impact. There are Wi-Fi connectivity and a phone app for monitoring and control, and businesses with higher power needs can run several in parallel to form an intelligent virtual power plant.
Hydrogen is often incorrectly seen as an unsafe fuel, usually due to the 1937 Hindenburg disaster. However, the company says any leaks will disperse quickly, though, making it inherently no more dangerous than other conventional fuels such as gasoline or natural gas. This innovation has a lifespan of approximately 30 years, which is three times longer than that of lithium batteries, thanks to its reliance on hydrogen gas rather than the chemicals in a conventional battery.
According to the manufacturer, LAVO’s hydrogen storage should be ready for installation by the middle of this year. It costs AU$34750 (US$26900) for the first 2500 units and will require a fully refundable deposit to secure your LAVO pre-order. In the coming year, the price is expected to drop to AU$29450 (US$22800).