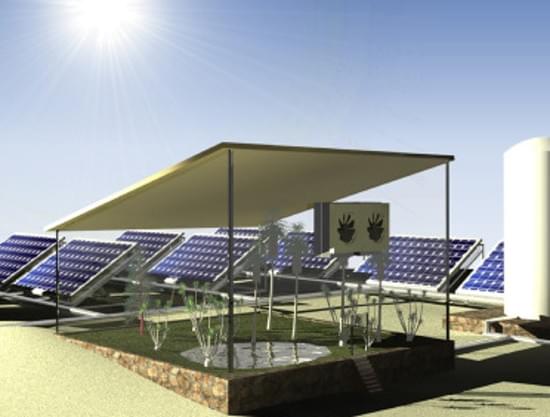
Developed at King Abdullah University of Science and Technology, it combines solar panels and a hydrogel underlayer.
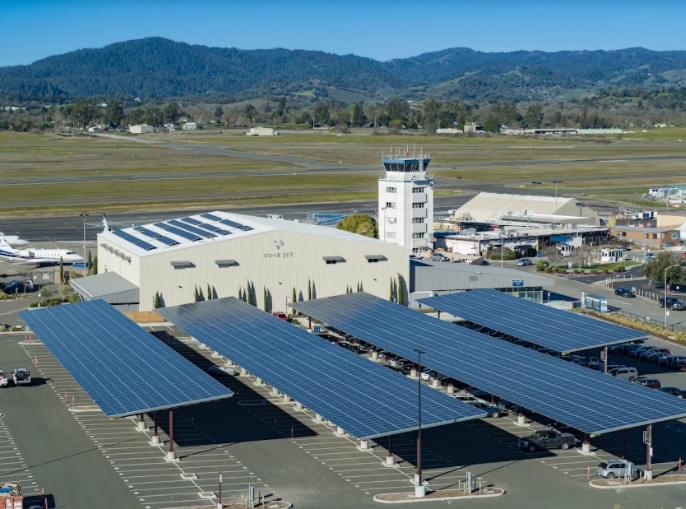



The Charles M. Schulz Sonoma County Airport had two solar power systems installed onsite and made them live in February. Over the course of their electricity-generating life spans, they will offset thousands of tons of CO2 emissions and potentially save millions of dollars.
Sonoma County has been hit particularly hard by wildfires in the last several years. These natural disasters occur with some regularity on their own, but many believe the latest ones are connected to the effects of climate change. The county has been experiencing higher temperatures and droughts as well. As a result of these challenges, Sonoma County’s government set a goal for the county to be carbon neutral by 2030. The airport solar power installations fit within the carbon-free plan. (The California state government has a goal for California to be operating on clean, carbon-free electricity by 2045.)
Jon Stout, the Sonoma Airport Manager, and Rachel McLaughlin, ForeFront Power’s Vice President of Sales & Marketing, provided some insights to CleanTechnica about the new solar power systems. (The last three answers are from ForeFront.)
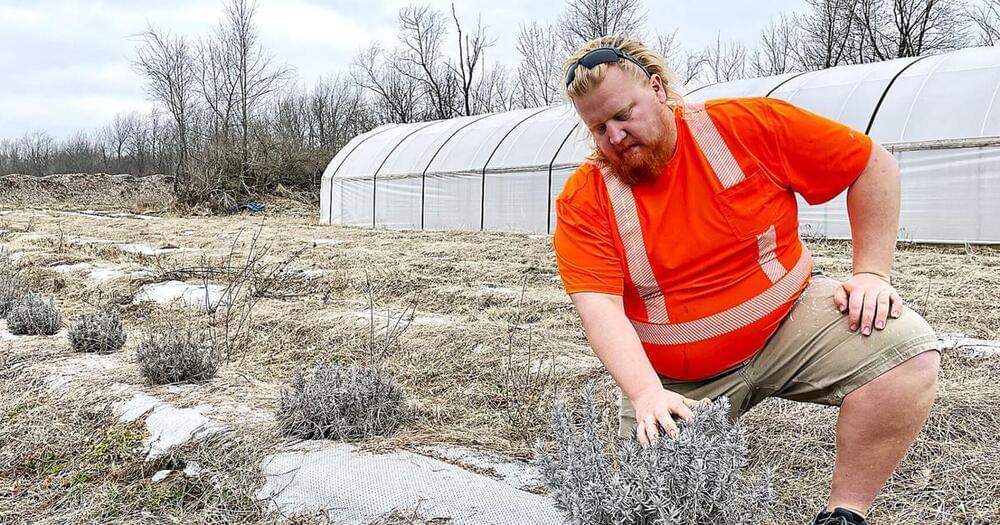

ANDERSON — For Sam Johnson, organic farming isn’t only a practical way of protecting the environment. It’s also a vital part of a healthy lifestyle.
“My main reason for doing it is just to get away from all these problems we’re having with herbicide and pesticide resistance,” Johnson said. “We’re just getting back to the natural ways our bodies process food.”
Organic farming is becoming undeniably more mainstream in the U.S. agriculture industry. According to an analysis of data in the USDA’s 2019 Survey of Organic Agriculture by Commodity.com, the number of organic farms in the U.S. rose by more than 50% in the last decade. The country’s estimated 16,500 organic farms now cover about 5.5 million acres, a 38% increase from 2008.



States seeking electric vehicle charging station funds can calculate job creation.
With the sale of electric vehicles on the rise, the race is on to build a network of convenient, affordable electric vehicle charging stations to keep the cars running.
There are currently about 47,000 public charging stations across the country. As the administration rolls out its plan to build a network of 500,000 electric charging stations across the nation by the end of the decade, the number of charging stations will increase significantly — and quickly.
With both homelessness rates and the cost of housing continuing to climb in the U.S., one startup described as the “IKEA of houses” is determined to make beautifully-designed, energy efficient homes more affordable for everyone.
The founders of NODE believe that access to affordable housing should be a fundamental right. They’re working toward a sustainable solution to the current housing crisis, and it’s one that goes above and beyond the status quo.
What if you could build a carbon negative home for a fraction of the cost of a traditional home? What if you could do so in just two weeks? These ambitious objectives are exactly what NODE has set out to accomplish.

As the world struggles to improve the efficiency of cars and other vehicles in order to curb greenhouse gas emissions and improve the range of electric vehicles, the search is on for ever-lighter materials that are strong enough to be used in the bodies of cars.
Lightweight materials made from carbon fiber, similar to the material used for some tennis rackets and bicycles, combine exceptional strength with low weight, but these have been more expensive to produce than comparable structural elements made of steel or aluminum. Now, researchers at MIT and elsewhere have come up with a way of making these lightweight fibers out of an ultracheap feedstock: the heavy, gloppy waste material left over from the refining of petroleum, material that refineries today supply for low-value applications such as asphalt, or eventually treat as waste.
Not only is the new carbon fiber cheap to make, but it offers advantages over the traditional carbon fiber materials because it can have compressional strength, meaning it could be used for load-bearing applications. The new process is described in the journal Science Advances, in a paper by graduate student Asmita Jana, research scientist Nicola Ferralis, professor Jeffrey Grossman, and five others at MIT, Western Research Institute in Wyoming, and Oak Ridge National Laboratory in Tennessee.
Quantum computers are getting bigger, but there are still few practical ways to take advantage of their extra computing power. To get over this hurdle, researchers are designing algorithms to ease the transition from classical to quantum computers. In a new study in Nature, researchers unveil an algorithm that reduces the statistical errors, or noise, produced by quantum bits, or qubits, in crunching chemistry equations.
Developed by Columbia chemistry professor David Reichman and postdoc Joonho Lee with researchers at Google Quantum AI, the algorithm uses up to 16 qubits on Sycamore, Google’s 53-qubit computer, to calculate ground state energy, the lowest energy state of a molecule. “These are the largest quantum chemistry calculations that have ever been done on a real quantum device,” Reichman said.
The ability to accurately calculate ground state energy, will enable chemists to develop new materials, said Lee, who is also a visiting researcher at Google Quantum AI. The algorithm could be used to design materials to speed up nitrogen fixation for farming and hydrolysis for making clean energy, among other sustainability goals, he said.