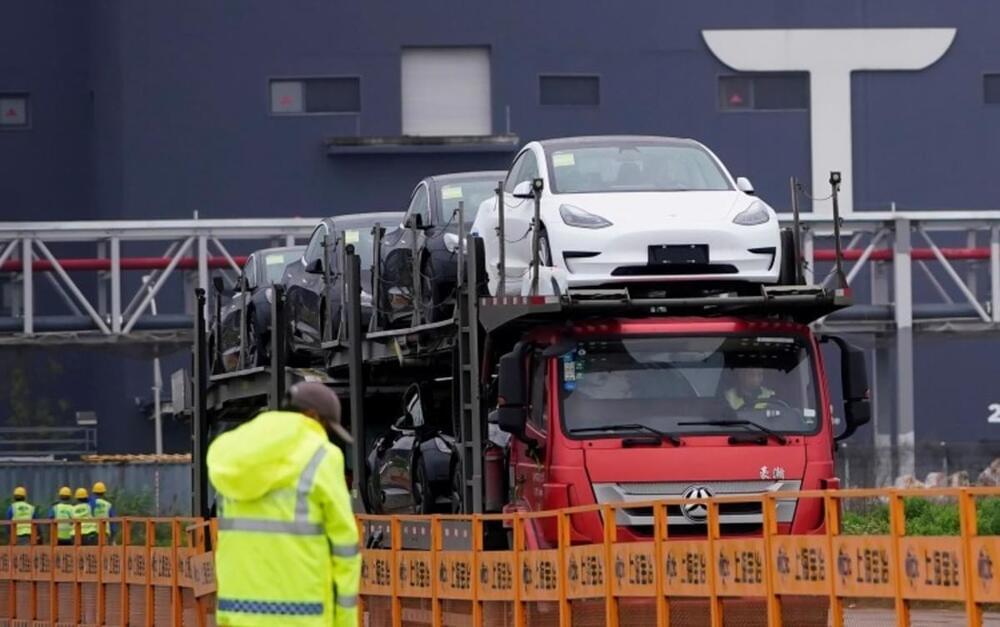
Whether it’s photovoltaics or fusion, sooner or later, human civilization must turn to renewable energies. This is deemed inevitable, considering the ever-growing energy demands of humanity and the finite nature of fossil fuels. Much research has been pursued in order to develop alternative sources of energy, most of which use electricity as the main energy carrier. The extensive R&D in renewables has been accompanied by gradual societal changes as the world adopted new products and devices running on renewables. The most striking change has been the rapid adoption of electric vehicles. While they were rarely seen on the roads even 10 years ago, now, millions of electric cars are being sold annually. The electric car market is one of the most rapidly growing sectors.
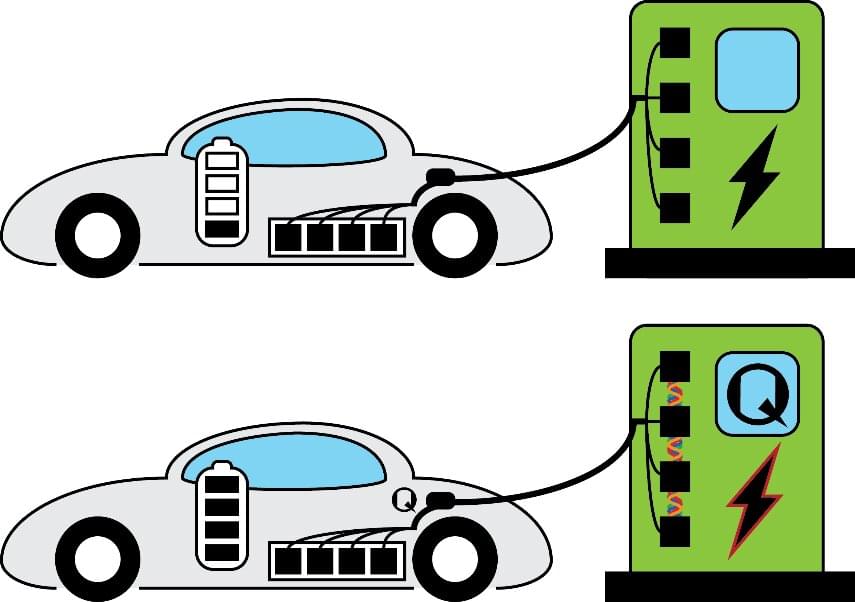
Unlike traditional cars, which derive energy from the combustion of hydrocarbon fuels, electric vehicles rely on batteries as the storage medium for their energy. For a long time, batteries had far lower energy density than those offered by hydrocarbons, which resulted in very low ranges of early electric vehicles. However, gradual improvement in battery technologies eventually allowed the drive ranges of electric cars to be within acceptable levels in comparison to gasoline-burning cars. It is no understatement that the improvement in battery storage technology was one of the main technical bottlenecks that had to be solved in order to kickstart the current electric vehicle revolution.
However, despite the vast improvements in battery technology, today’s consumers of electric vehicles face another difficulty: slow battery charging speed. Currently, cars take about 10 hours to fully recharge at home. Even the fastest superchargers at the charging stations require up to 20 to 40 minutes to fully recharge the vehicles. This creates additional costs and inconvenience to the customers.