Hydrogen, the lightest element on the periodic table, is a master of escaping almost any container it’s stored in. Its extremely small size allows it to squeeze through atomic-scale gaps in the storage materials, which is one of the major issues hindering hydrogen energy from becoming mainstream.
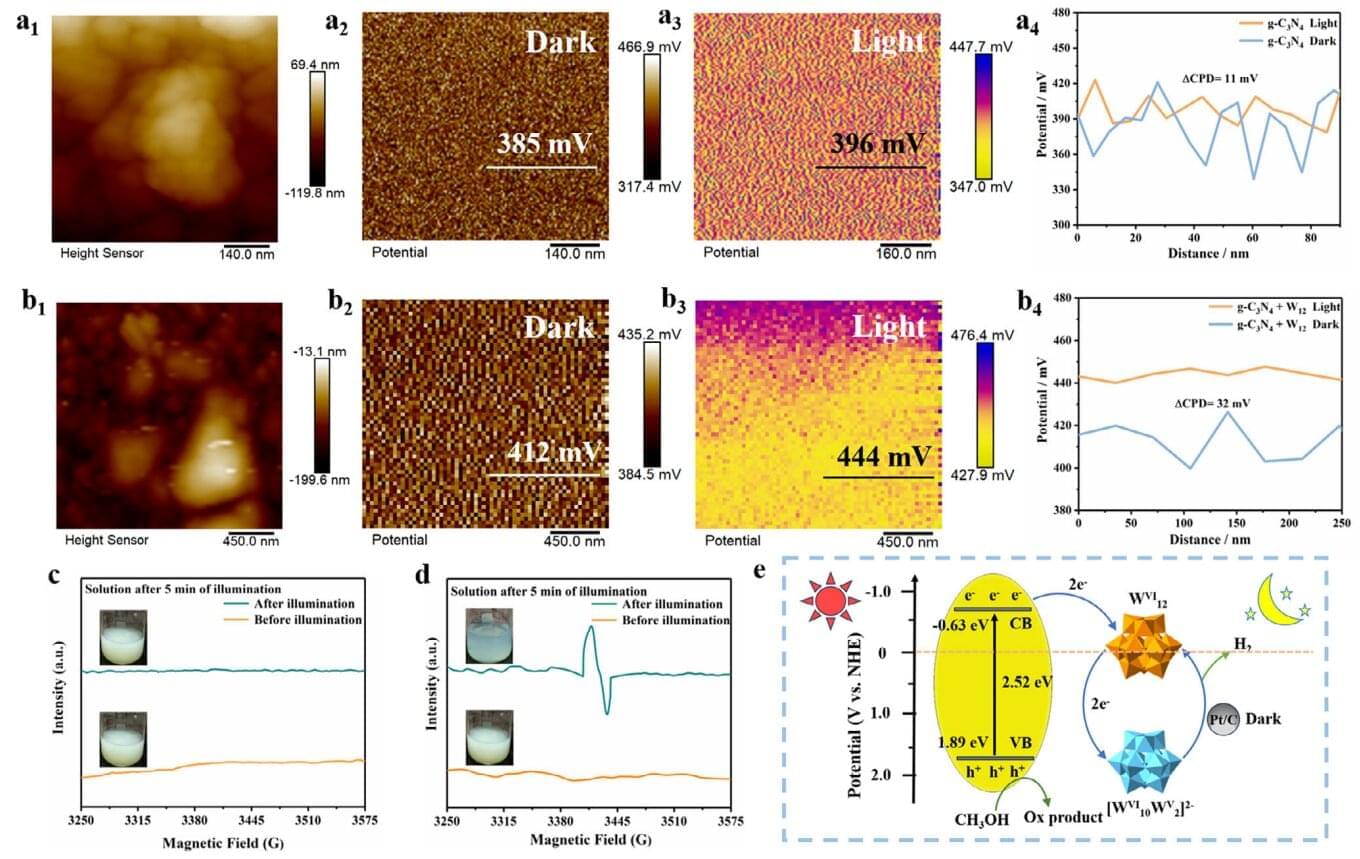
A team of Chinese researchers has solved the issue of containment with on-demand hydrogen production. They developed a simple chemical system containing commercial ammonium metatungstate (W12) and graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) in a liquid suspension. This system captures solar energy and, rather than converting it into electricity, uses it to produce hydrogen fuel on demand—even in darkness.
The new system provided twofold benefits: it made solar energy available even when the sun isn’t shining, and it eliminated the need to transport hydrogen in dangerous, high-pressure tanks.