Year 2019 face_with_colon_three
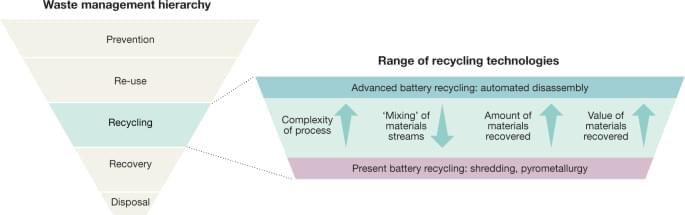
For high-cobalt cathodes such as lithium cobalt oxide (LCO) conventional pyrometallurgical (see section ‘Pyrometallurgical recovery’) or hydrometallurgical (see section ‘Hydrometallurgical recovery’) recycling processes can recover around 70% of the cathode value11. However, for other cathode chemistries that are not as cobalt-rich, this figure drops notably11. A 2019 648-lb Nissan Leaf battery, for example, costs US$6,500–8,500 new, but the value of the pure metals in the cathode material is less than US$400 and the cost of the equivalent amount of NMC (an alternative cathode material) is in the region of US$4,000. It is important, therefore, to appreciate that cathode material must be directly recycled (or upcycled) to recover sufficient value. As direct recycling avoids lengthy and expensive purification steps, it could be particularly advantageous for lower-value cathodes such as LiMn2O4 and LiFePO4, where manufacturing of the cathode oxides is the major contributor to cathode costs, embedded energy and carbon dioxide footprint95.
Direct recycling also has the advantage that, in principle, all battery components20 can be recovered and re-used after further processing (with the exclusion of separators). Although there is substantial literature regarding the recycling of the cathode component from spent LIBs, research on recycling of the graphitic anode is limited, owing to its lower recovery value. Nevertheless, the successful re-use of mechanically separated graphite anodes from spent batteries has been demonstrated, with similar properties to that of pristine graphite96.
Despite the potential advantages of direct recycling, however, considerable obstacles remain to be overcome before it can become a practical reality. The efficiency of direct recycling processes is correlated with the state of health of the battery and may not be advantageous where the state of charge is low97. There are also potential issues with the flexibility of these routes to handle metal oxides of different compositions. For maximum efficiency, direct recycling processes must be tailored to specific cathode formulations, necessitating different processes for different cathode materials97. The ten or so years spent in a vehicle—followed, perhaps, by a few more in a second-use application—therefore present a challenge in an industry where battery formulations are evolving at a rapid pace. Direct recycling may struggle to accommodate feedstocks of unknown or poorly characterized provenance, and there will be commercial reluctance to re-use material if product quality is affected.