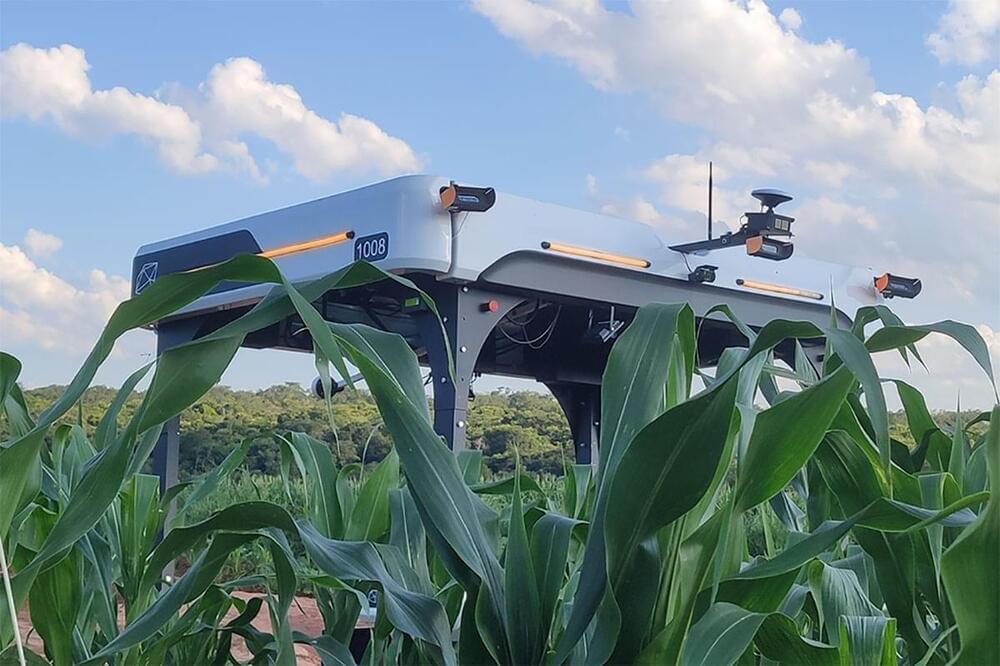
Canadian agri-tech company Solinftec has announced that it will expand the launch of its new cutting-edge AgTech robotic platform, Solix Ag Robotics, into Canada in partnership with Stone Farms and the University of Saskatchewan. The new robot is state-of-art technology built to scan and monitor fields providing detailed real-time data.
Solinftec’s new technology aims to provide farmers and agronomists with a new level of information to increase yields, improve the usage of inputs, lower environmental impact, and support the global demand for food supply. The robot should be commercially available for use in wheat crops in time for next year’s growing season.
Solinftec’s Solix Ag Robot will autonomously move back and forth through farmers’ fields on four wheels. It will use onboard cameras and other sensors – along with AI-based software – to check the health of plants and assess their nutritional content. Solix Ag is integrated with the company’s artificial intelligence platform, ALICE A.I. Programmed with a neurological network featuring a complex detection algorithm, the new in-field robotic device has the ability not only to scan for crop health and nutrition, insects, and weeds but is built to monitor the entire field ecosystem and provide real-time insights.