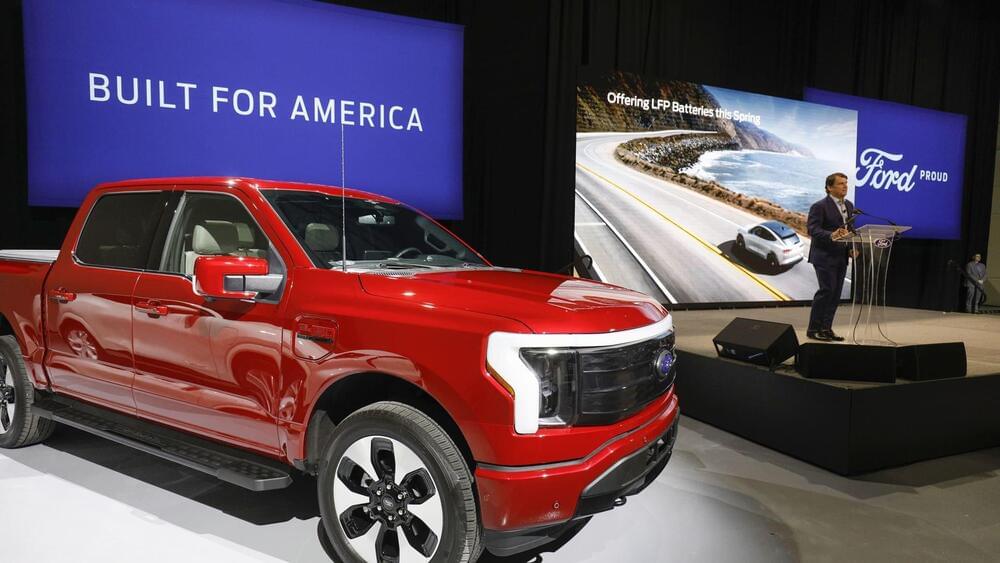
Ford said Tuesday it is cutting production capacity by roughly 43% to 20 gigawatt hours per year and reducing expected employment from 2,500 jobs to 1,700 jobs. The company declined to disclose how much less it would invest in the plant. Based on the reduced capacity, it would still be about a $2 billion investment.
The decision adds to a recent retreat from EVs by automakers globally. Demand for the vehicles is lower than expected due to higher costs and challenges with supply chains and battery technologies, among other issues.
Reductions at the Marshall, Michigan, plant are part of Ford’s plans announced last month to cut or delay about $12 billion in previously announced EV investments. The company will also postpone construction of another electric vehicle battery plant in Kentucky.