The revolution in artificial intelligence may soon require more electricity than all electric vehicles combined.


One of the early opportunities for Optimus to which Elon has alluded.
Disrupting prostitution, OnlyFans and the female profiteering off men’s emotional and sexual needs.
. Our guest, Mo Gawdat, former chief business officer for Google X, brings a stark warning from the forefront of technology. Having shaped the tech landscape through his work with IBM, Microsoft, and Google, Mo unflinchingly declares AI as a greater threat to humanity than global warming. The AI revolution is upon us, reshaping our future, irrespective of our stance. This episode delves into the startling implications of a world intertwined with sex robots. Could such artificial companionship eclipse our inherent need for human connection?
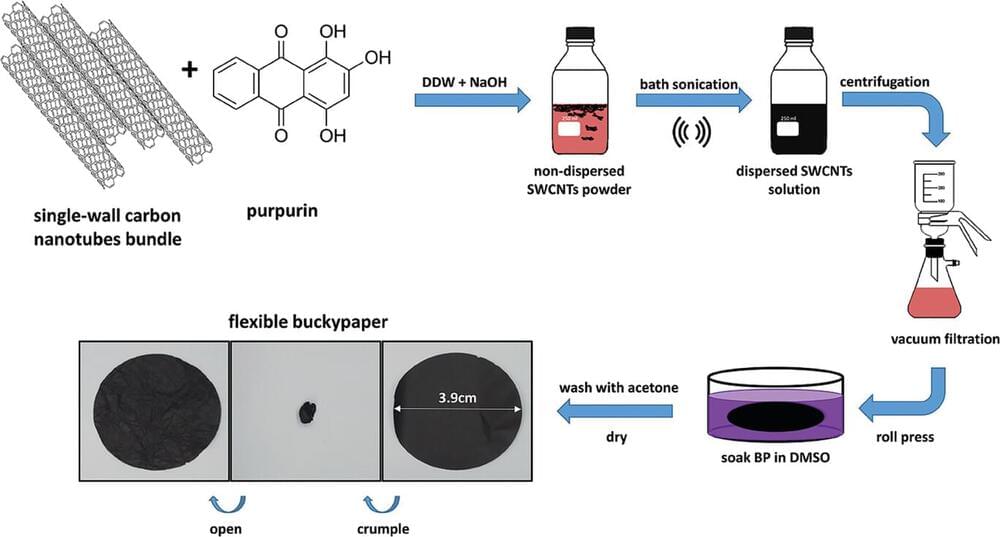
Carbon nanotubes have long tantalized researchers with their extraordinary mechanical and electronic properties. As one-dimensional nanostructures with remarkable mechanical strength and electrical conductivity, CNTs have been eyed for next-generation composites, energy storage devices, sensors and more. Yet realizing their promise has proven an enduring challenge.
CNTs have ultra-high surface energy and readily form large bundles rather than remaining as individualized tubes, severely compromising resultant material properties. Exfoliating these bundles, particularly in solution, has remained an immense difficulty despite intense R&D efforts over 30+ years employing covalent and noncovalent functionalization strategies.
Covalent approaches disrupt the CNTs’ pristine sp2 carbon networks, damaging their intrinsic properties. Noncovalent methods like surfactants and polymers have had limited success in debundling smaller diameter single-wall CNTs (SWCNTs), especially longer high aspect ratio tubes preferred for optimal conductivity and strength. And virtually all tactics have struggled to exfoliate specific SWCNT types, hindering enrichment in metallic SWCNTs boasting far higher conductance than their semiconducting counterparts.
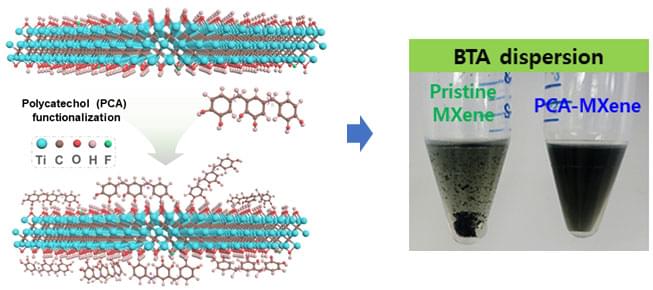
A research team led by Professor Jong-min Choi of the Department of Energy Engineering has developed a technology that can significantly improve the efficiency of quantum dot photovoltaic cells by introducing organic solvent dispersible MXene.
The findings were published in Advanced Energy Materials (“Organic solvent dispersible MXene integrated colloidal quantum dot photovoltaics”).
Comparison of the dispersibility of quantum dot solar cell ink organic solvent according to surface modification of MXene. (Image: DGIST)
Immigration to and living on Mars have often been themes in science fiction. Before these dreams can become reality, humanity faces significant challenges, such as the scarcity of vital resources like oxygen needed for long-term survival on the Red Planet. Yet, recent discoveries of water activity on Mars have sparked new hope for overcoming these obstacles.
Scientists are now exploring the possibility of decomposing water to produce oxygen through electrochemical water oxidation driven by solar power with the help of oxygen evolution reaction (OER) catalysts. The challenge is to find a way to synthesize these catalysts in situ using materials on Mars, instead of transporting them from the Earth, which is of high cost.

This was suggested by Gustave Fechner and other philosophers.
How about planets? Can they have minds? This idea, that planets are also conscious beings, seems to be at the heart of a new theory put forth by astrobiologists. The premise of this thought experiment is that bacteria and plants working together have altered planets like Earth, giving them a new lease on life.
This research, published in the International Journal of Astrobiology, provides a scale by which planets’ intelligence can be evaluated. It’s shocking to consider an extraterrestrial organism intelligent rather than a sentient animal like a human. But in a way, a planet can have a “green mind”; this paradigm suggests novel approaches to coping with climate change, technological upheaval, and other emergencies.
Planetary intelligence was characterised by the researchers as “cognitive activity” and knowledge functioning on a global scale. We understand that the concept of intelligence may be applied to everything from an individual to a community or even the peculiar actions of a virus or mould. For example, fungi’s webs of mycelium beneath the forest floor are its own breath; together, they make up a living system that can detect and adapt to shifting climates. All of Earth’s conditions will be drastically altered by these factors.
The Limiting Factor joins Rebellionaire to talk about the latest wild news about the Tesla Megapacks. Rebellionaires check out www.Rebellionaire.com Rebellionaire is a brand of Halter Ferguson Financial. www.hffinancial.com/disclaimer

Advanced infrared mirrors enhance climate and biofuel research via precision trace gas sensing.
An international team of researchers from the United States, Austria, and Switzerland has demonstrated the first true supermirrors in the mid-infrared spectral region. These mirrors are key for many applications, such as optical spectroscopy for environmental sensing, as well as laser cutting and welding for manufacturing.
Achieving Near-Perfect Reflectivity
Developed at NTU Singapore, a new device can quickly rejuvenate and extend the life of old and new solar panels using heat and light.
Through an innovative use of heat and light, a new device developed at NTU Singapore can restore and extend the life of old and new solar panels.
These new wind turbine replacements could soon become Instagram celebrities, just like those Dyson fans.
Glasgow’s Katrick Technologies introduces Wind Panel, their bladeless gadget designed to replace wind turbines with efficiency and innovation.