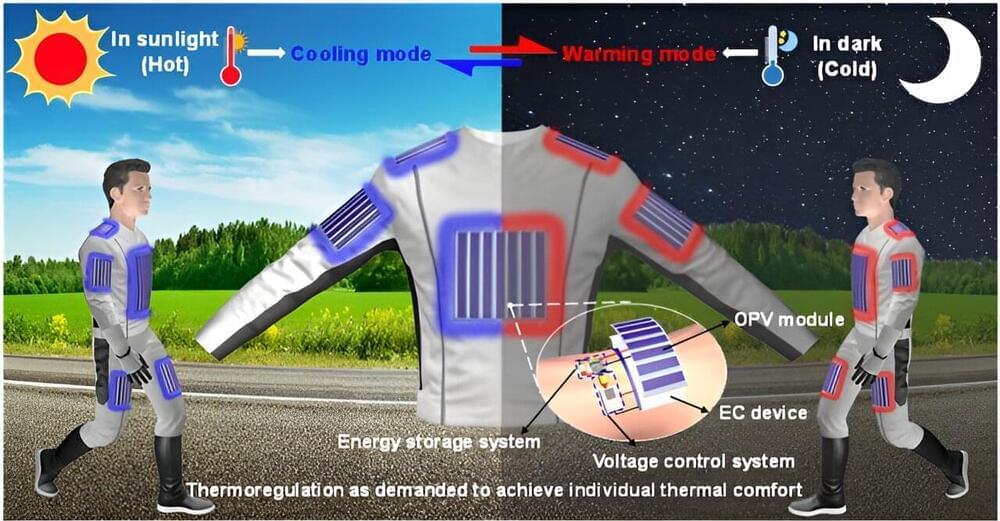
A team of engineers, materials scientists and chemists at Nankai University, in China, has developed a microfiber-based meta-fabric that provides full-day thermoregulation of body temperature during periods of changing external temperatures.
In their paper published in the journal Science, the group describes how they developed their fabrics, how they work and how well they performed when tested. Xingyi Huang and Pengli, both with Shanghai Jiao Tong University, in China, have published a Perspective piece in the same journal issue outlining the work done by the team.
As the researchers note, clothing keeps people warm when it is cold, and in some cases, can help people stay cool in hot temperatures. Prior research efforts have attempted to extend the capabilities of clothing by adding heating or cooling elements, but thus far, most such products have proven to be too bulky for general use.