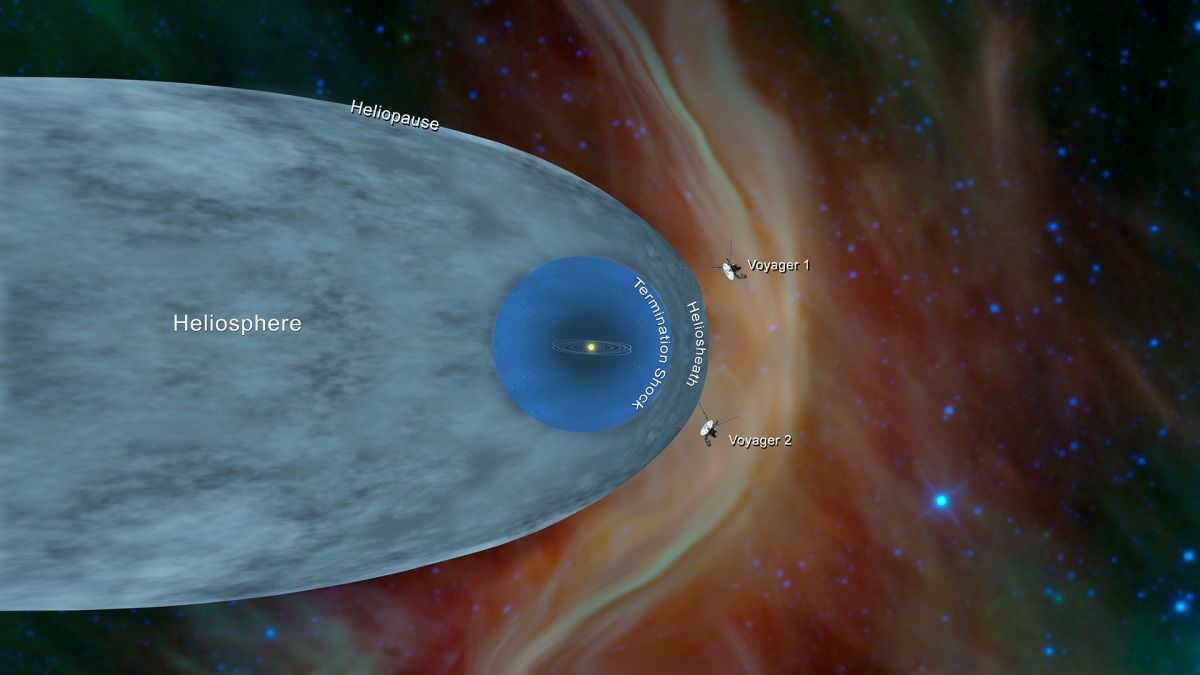
It’s pretty cool how NASA knows the spacecraft is in interstellar space.
It’s only the second object made by humans to ever reach this distance, following Voyager 1 in 2012.
The long journey: Since launching more than 40 years ago back in 1977, the probe has traveled 11 billion miles to get to cross into interstellar space. While it launched before Voyager 1, its flight path put Voyager 2 on a slower path to reach this milestone.
What does that mean? No, Voyager 2 hasn’t left the solar system. Our solar system is huge and goes way beyond its last planet. Instead, it means Voyager 2 has left the heliosphere, the pocket of particles and magnetic fields created by our closest star. Solar wind, the charged plasma particles that come out from the sun, generates this bubble.