Category: space – Page 863


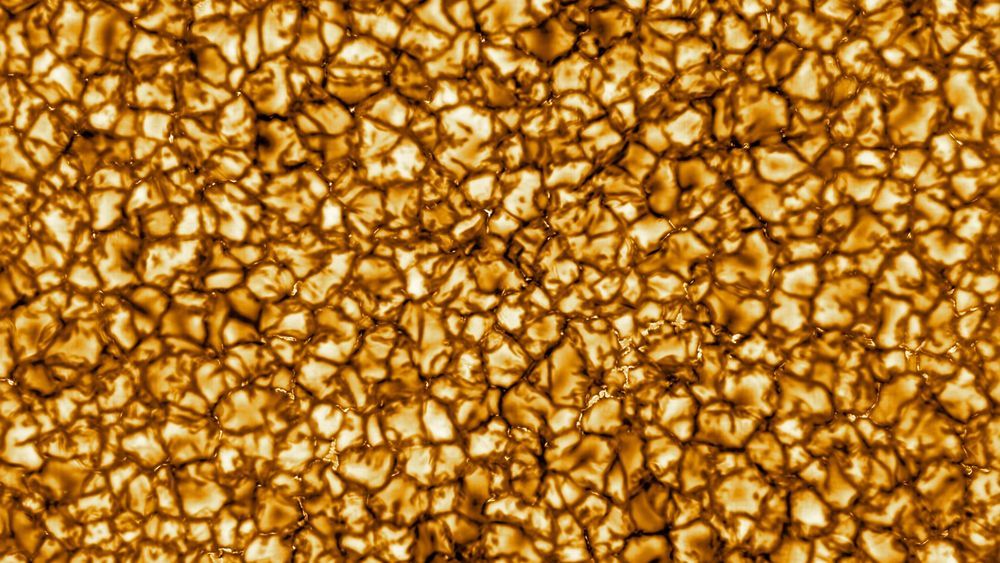
This is the highest-resolution photo of the sun ever taken
There’s a good reason why we need to take a closer look at the sun. When the solar atmosphere releases its magnetic energy, it results in explosive phenomena like solar flares that hurl ultra-energized particles through the solar system in all directions, including ours. This […] can wreak havoc on things like GPS and electrical grids. Learning more about solar activity could give us more notice of when hazardous space weather is due to hit.
You can see structures on the surface as small as 18.5 miles in size.
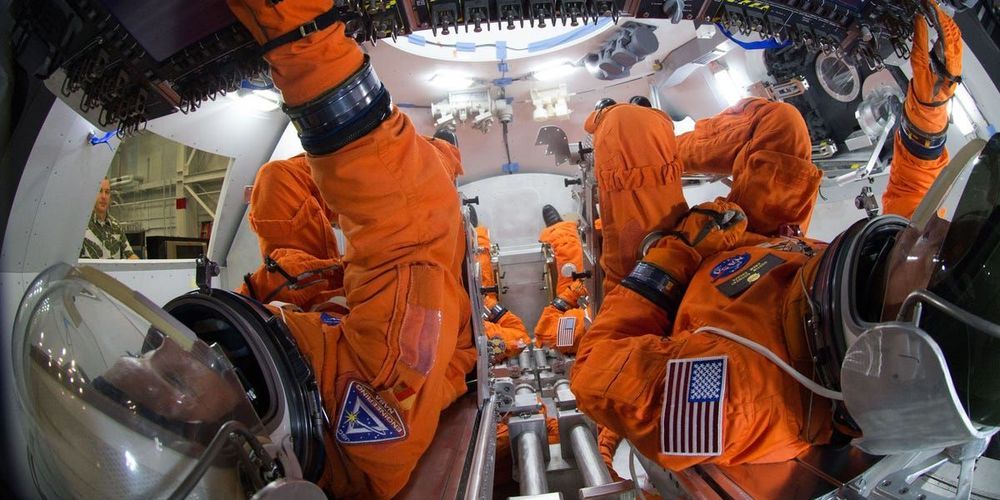

9 Everyday Things Astronauts Can’t do in Space
- Some everyday things are near-impossible for astronauts to do in space.
- Common items like salt and bread are banned from the International Space Station due to fears that they’ll send floating pieces everywhere and potentially damage space equipment or accidentally get inhaled by astronauts.
- Basic eating, sleeping, and showering habits must also be modified.
Astronauts make a lot of sacrifices when they venture off of Earth.
Besides the dangers of space travel and time away from family, microgravity comes with a whole new set of rules that dictates many facets of everyday life.
Taiwan Is Opening A Giant AI-Focused Business Park
Taiwan has been the world’s hardware hub for decades, so the shift toward AI makes the most of the existing inexpensive engineering talent. A refocus on AI, however, reduces reliance on hardware, which can easily be made somewhere else, such as China, at lower costs. Multinational tech companies have already shown interest in tapping Taiwan’s talent in software, including AI.
To move things along further, the government of Hsinchu County, near Taipei, will open a 126,000-square-meter (about 1.3 million square feet) AI business park near one of Taiwan’s major all-purpose high-tech zones and two top universities.
“[The park] will not just help [promote] industry-academia cooperation, but also let AI-oriented startups and companies have a demo space to verify AI product services,” says Shirley Tsai, a research manager with IDC Taiwan’s enterprise solution group. “It will be helpful as well to attract the companies who are interested in the AI field and then accelerating the AI ecosystem.”
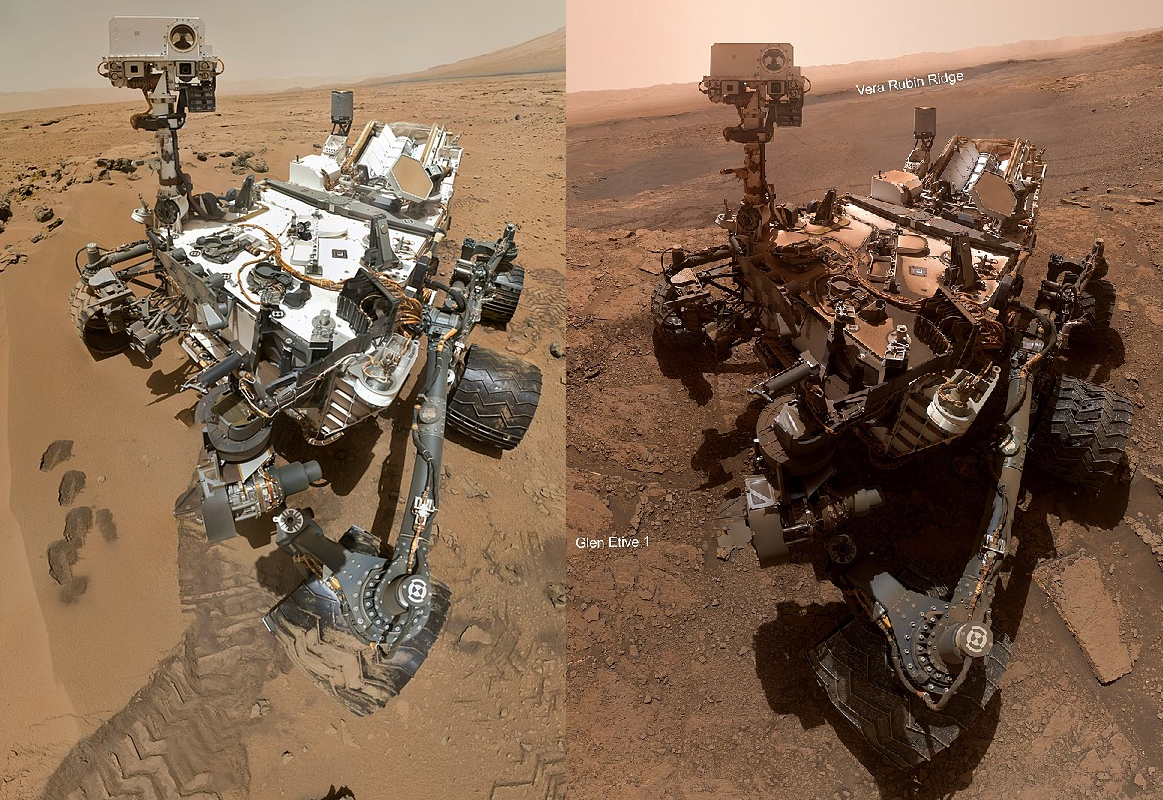
NASA selects Axiom Space to build commercial space station segment
NASA has announced that they have selected Axiom Space, an American company headquartered in Houston, Texas, to design, build and launch three large pressurized modules and a large Earth observation window to the International Space Station (ISS).
This partnership between NASA and Axiom is issued under Appendix I of NASA Next Space Technologies for Exploration Partnerships 2 (NextSTEP-2) public-private partnership program witch the agency hopes will help stimulate commercial development of deep space exploration capabilities.
Appendix I of NextSTEP-2 was originally issued on June 7th 2019 and called for private companies to bid to develop habitable commercial modules, to be built and launched to the International Space Station, and then attached to the forward end of the station as part of NASA’s long term plan to open up the ISS to large amounts of commercial opportunities.
We’re All Going to Live in Mushroom Houses on Mars
NASA is sharing information about its myco-architecture program, in which experimental fungus-based building technologies could be the feasible future of Mars habitats. “Science fiction often imagines our future on Mars and other planets as run by machines, with metallic cities and flying cars rising above dunes of red sand,” NASA says. “But the reality may be even stranger.”
The myco-architecture (myco is the prefix meaning “fungus”) NASA is excited about isn’t only a new way to make furniture, although it can do that, the agency says. Mushroom House—not its real name—is an integrated habitat with layers. The tough, complex fibers made by fungal mycelia are building blocks of furniture, interior walls, and the innermost layer of the outer shell.
Happy Lunar New Year from Hubble
Hubble welcomes the Year of the Rat with a view of its own favorite rodents, NGC 4676A and B, and highlights the planetary origins of the Chinese zodiac’s 12-year timetable.
For more information, visit https://nasa.gov/hubble.
Credit: NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center Bradley A Hague (GSFC intern): Producer / Editor.