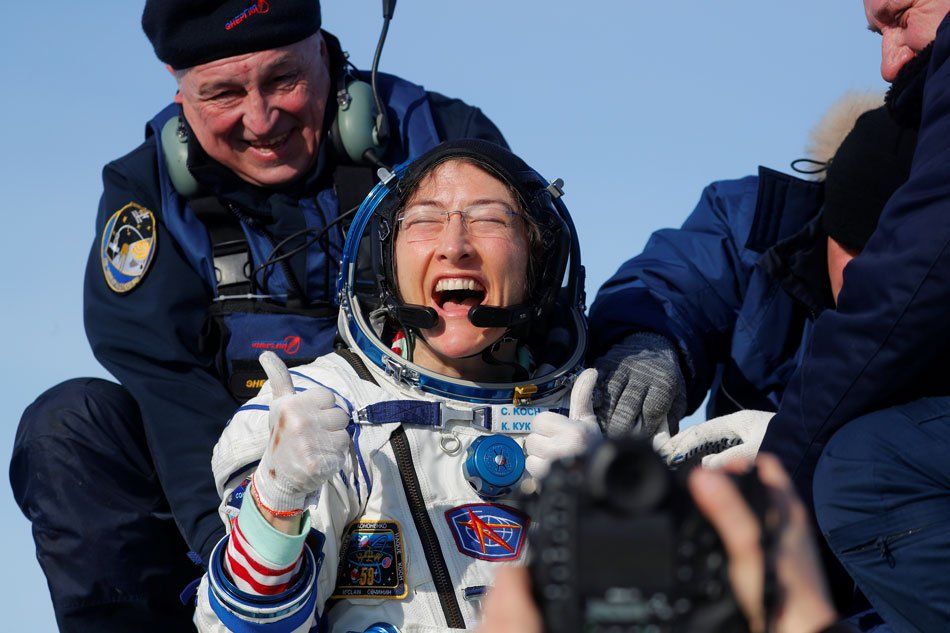
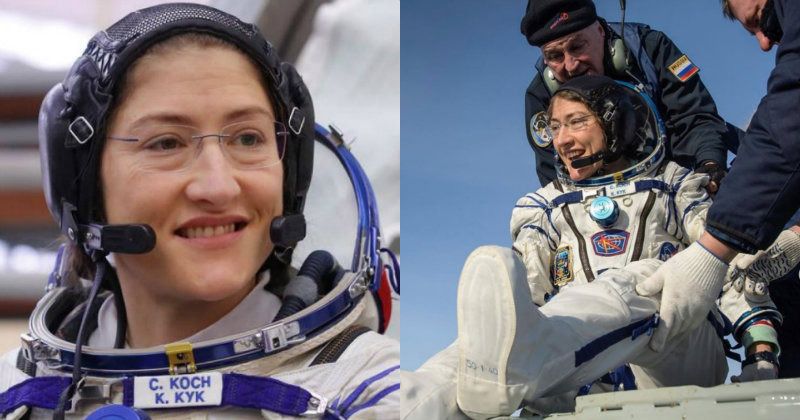
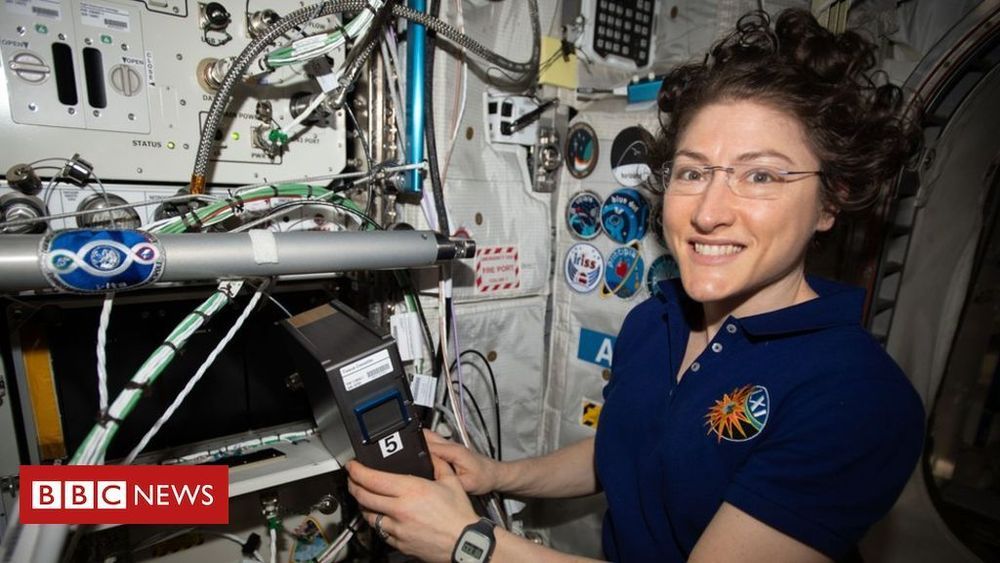
NASA’s Christina Koch returned to Earth safely on Thursday after shattering the spaceflight record for female astronauts with a stay of almost 11 months aboard the International Space Station.
Koch touched down at 0912 GMT on the Kazakh steppe after 328 days in space, along with Luca Parmitano of the European Space Agency and Alexander Skvortsov of the Russian space agency.
Koch was shown seated and smiling broadly after being extracted from the Soyuz descent module in the Roscosmos space agency’s video footage from the landing site.