The ESA’s Trace Gas Orbiter (part of the ExoMars 2020 mission) has revealed images of the Perseverance rover and where it landed.
A little over a week ago (February 18th, 2021), NASA’s Perseverance rover landed in the Jezero crater on the surface of Mars. In what was truly a media circus, people from all over the world tuned to watch the live coverage of the rover landing. When Perseverance touched down, it wasn’t just the mission controllers at NASA who triumphantly jumped to their feet to cheer and applaud.
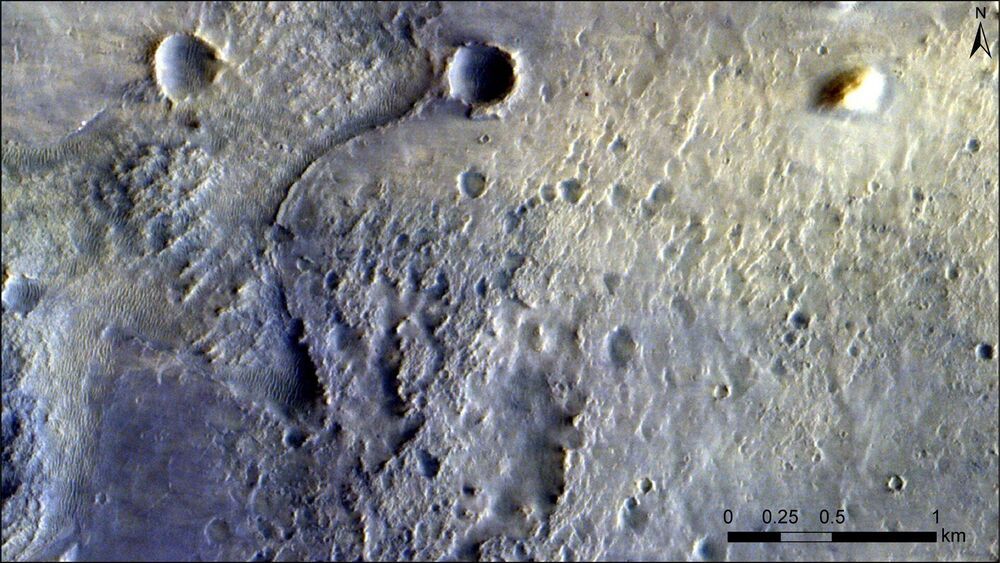
In the days that followed, the world was treated to all kinds of media that showed the surface of Mars and the descent. The most recent comes from the Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO), which is part of the ESA-Roscosmos ExoMars program. From its vantage point, high above the Martian skies, the TGO caught sight of Perseverance in the Jezero crater and acquired images that show the rover and other elements of its landing vehicle.