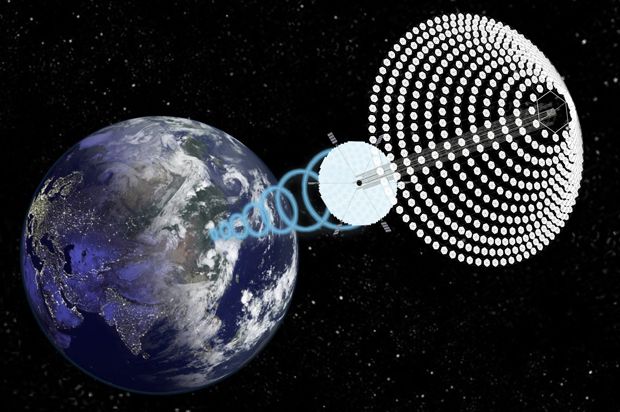
Yes, renewable energy technologies exist. But solar power, the one with arguably the most promise for significant, scalable deployment, is intermittent. Although the sun provides more energy in one hour than humans consume in a year, we can only tap into this power when the sun is shining. At least, that’s been the predominant school of thought.
But since the 1960s, a group of researchers from NASA and the Pentagon have been thinking outside the box — or in this case, outside the atmosphere. Solar power captured in outer space would not be limited by nighttime hours or cloud cover. And — unlike 23 percent of current incoming solar energy — it wouldn’t be absorbed by water vapor, dust and ozone before reaching us. Finally, because space solar is constant, it wouldn’t need to be stored, which can lead to energy losses of up to 50 percent. In other words, taking our solar panels from the ground to the cosmos could be a great deal more efficient. It may also be key to humanity’s survival.
“In countries right now where they’re trying to deal with poverty, water scarcity, poor health, lack of education and political instability — these are all things you need energy in order to fight,” Paul Jaffe, PhD, spacecraft engineer at the U.S. Naval Research Laboratory, said in a recent TakeApart story. Or, as John C. Mankins, founder of Mankins Space Technology and author of “The Case for Space Based Solar,” told Salon, “In the long run, renewable large-scale energy sources such as space solar power are essential to sustaining industrial civilization, and the long and increasingly high quality of lives that we enjoy.”