Superconductivity and quantum computing are two fields that have seeped from theoretical circles into popular consciousness. The 2025 Nobel Prize in physics was awarded for work in superconducting quantum circuits that could drive ultra-powerful computers. But what may be less well known is that these promising technologies are often possible only at cryogenic temperatures—near absolute zero. Unfortunately, few materials can handle such extremes. Their cherished physical properties disappear when the chill is on.
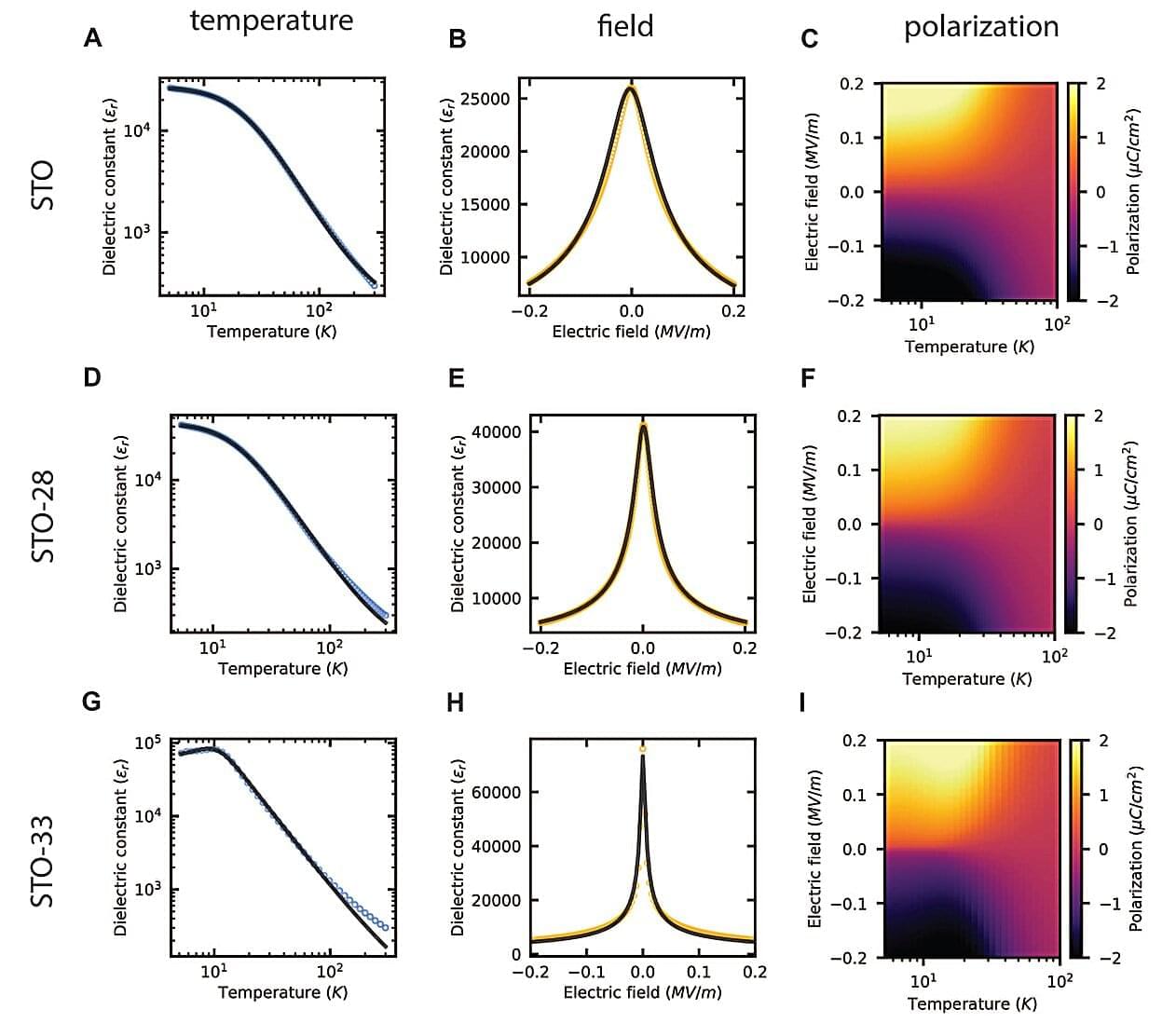
In a new paper published in Science, however, a team of engineers at Stanford University spotlights a promising material—strontium titanate, or STO for short—where the optical and mechanical characteristics do not decline at extreme low temperatures, but actually get significantly better, outperforming existing materials by a wide margin.
They believe these findings suggest that STO could become the building block for new light-based and mechanical cryogenic devices that push quantum computing, space exploration, and other fields to the next level.