Researchers demonstrate a loss-tolerant method for so-called quantum steering, a phenomenon that could give quantum communication networks complete security.



Hive Social, a social media platform that has seen meteoric growth since Elon Musk took over Twitter, abruptly shut down its service on Wednesday after a security advisory warned the site was riddled with vulnerabilities that exposed all data stored in user accounts.
“The issues we reported allow any attacker to access all data, including private posts, private messages, shared media and even deleted direct messages,” the advisory, published on Wednesday by Berlin-based security collective Zerforschung, claimed. “This also includes private email addresses and phone numbers entered during login.”
The post went on to say that after the researchers privately reported the vulnerabilities last Saturday, many of the flaws they reported remained unpatched. They headlined their post “Warning: do not use Hive Social.”

Google’s Threat Analysis Group (TAG) has linked an exploit framework that targets now-patched vulnerabilities in the Chrome and Firefox web browsers and the Microsoft Defender security app to a Spanish software company.
While TAG is Google’s team of security experts focused on protecting Google users from state-sponsored attacks, it also keeps track of dozens of companies that enable governments to spy on dissidents, journalists, and political opponents using surveillance tools.
The search giant says the Barcelona-based software firm is one of these commercial surveillance vendors and not just a provider of custom security solutions as it officially claims.
Dr. Svitlana Volkova, Ph.D. (https://www.pnnl.gov/people/svitlana-volkova) is Chief Scientist, Decision Intelligence and Analytics, National Security Directorate, Pacific Northwest National Laboratory (PNNL), which is one of the United States Department of Energy national laboratories, managed by the Department of Energy’s (DOE) Office of Science.
Dr. Volkova is a recognized leader in the field of computational social science and computational linguistics and her scientific contributions and publication profile cover a range of topics on applied machine learning, deep learning, natural language processing, and social media analytics.
Dr. Volkova’s research focuses on understanding, predicting, and explaining human behavior, interactions, and real-world events from open-source social data and her approaches help advance effective decision making and reasoning about extreme volumes of dynamic, multilingual, multimodal, and diverse real-world unstructured data.
Dr. Volkova has a Ph.D. in Computer Science from Johns Hopkins University, Center for Language and Speech Processing, and an M.S. in Computer Science, from Kansas State University.

Someone else posted about this, but this is from LLNL. I love what they do, and Twitter reminded me of the many Photonics shares I have. This is cool, and Ill post more links.
November 7, 2022
A record high-laser-energy NIF target shot on Sept. 19 produced about 1.2 million joules of fusion energy yield. Compared with the groundbreaking 1.35-megajoule (MJ) experiment of Aug. 8, 2021, this experiment used higher laser energy and a modified experimental design.
The NIF and Photon Science Directorate at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory conducts cutting-edge research in the fields of laser inertial confinement fusion, high energy density physics, and advanced photonics for the advancement of national security, energy security, discovery science, and national competitiveness.

Huawei, ZTE, Hytera Communications Corp., Hikvision, and Dahua have made it to the list.
United States has prohibited selling and importing new Huawei and ZTE telecommunications devices due to “national security concerns.”
The Federal Communications Commission (FCC) approved new regulations that forbade the sale and import of new Huawei and ZTE, according to the documents released by the agency on Friday.
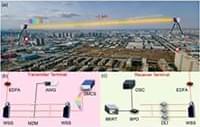
Large-capacity wireless data transmission systems are demanded along with the development of multimedia services, video-based interactions, and cloud computing in the era of big data. Compared with radio-frequency communication systems, free-space optical (FSO) signal transmission technology has the merits of high data rate, great flexibility, less power consumption, high security, and large license-free bandwidths [1– 3], which has been widely applied in terrestrial transmission [4], last mile solutions [5], ground-to-satellite optical communication [6], disaster recovery [7], and so on. To date, up to 10 Gbit/s FSO communication system has been realized for transmission distance over 1,000 km of star-ground or inter-star communications [8], and 208 Gbit/s terrestrial communication is also reported at 55 m transmission distance [9]. Wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) technology is commonly employed to improve data transmission capacity in fiber communication systems, which would be more effective in FSO communication systems benefitting from very weak non-linear cross talk between different frequency channels in free space. Based on a simulation platform, a WDM FSO communication system could boost the signal transmission capacity to 1.28 Tbit/s by modulating 32 optical channels with dual-polarization 16 quadrature amplitude modulation signals [10]. To date, beyond 10 Tbit/s FSO communication systems have been experimentally demonstrated recently using WDM technology [11,12]. However, a WDM communication system becomes power-hungry and bulky with the increase of transmission channels while traditional distributed feedback lasers are used as optical carriers. In addition, more rigorous requirement is imposed on the frequency tolerance of carrier lasers to avoid channel overlap with the decrease of channel frequency interval.
The invention of microresonator-based optical frequency combs provides novel integrated optical laser sources with the natural characteristic of equi-spaced frequency intervals which can overcome the challenge of massive parallel carrier generation [13 – 19]. In particular, the spontaneously organized solitons in continuous-wave (CW)-driven microresonators provide a route to low-noise ultra-short pulses with a repetition rate from 10 GHz to beyond terahertz. Soliton microcombs (SMCs) are typical stable laser sources where the double balances of non-linearity and dispersion as well as dissipation and gain are reached in microcavities. Meanwhile, the linewidth of the comb lines is similar with the pump laser, which enables low power consumption and costs multiwavelength narrow-linewidth carriers for a wide range of applications. Through designing the scale of microresonators, the repetition rate of SMCs could be compatible with dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM) communication standard. To date, several experiments have demonstrated the potential capacity for ultra-high-speed fiber communication systems using SMCs as multiwavelength laser sources [20 – 30]. For instance, a coherent fiber communication system has improved the transmission capacity up to 55 Tbit/s using single bright SMCs as optical carriers and a local oscillator [20]. And dark solitons and soliton crystals are also employed as multiwavelength laser sources for WDM communication systems [27 – 30]. However, few studies have carried out massive parallel FSO communication systems using the integrated SMCs as laser sources.
In this paper, we experimentally demonstrate a massive parallel FSO communication system using an SMC as a multiple optical carrier generator. 102 comb lines are modulated by 10 Gbit/s differential phase shift keying (DPSK) signals to boost the FSO transmission rate up to beyond 1 Tbit/s. The transmitter and receiver terminals are installed in two buildings at a distance of ∼1 km, respectively. Using a CW laser as reference, the influence of optical signal-to-noise ratios (OSNRs) on the bit error rate (BER) performance is experimentally analyzed. Our results show an effective solution for large-capacity spatial signal transmission using an integrated SMC source which has potential applications in future satellite-to-ground communication systems.

The information security landscape is rapidly changing in response to quantum computing technology, which is capable of cracking modern encryption techniques in minutes, but a promising US government encryption algorithm for the post-quantum world was just cracked in less than an hour thanks to a decades-old math theorem.
In July 2022, the US National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) chose a set of encryption algorithms that it hoped would stand up to the encryption-cracking power of quantum computers and tasked researchers with probing them for vulnerabilities, offering a $50,000 prize for anyone who was able to break the encryption.
High-Risk, High-Payoff Bio-Research For National Security Challenges — Dr. David A. Markowitz, Ph.D., IARPA
Dr. David A. Markowitz, Ph.D. (https://www.markowitz.bio/) is a Program Manager at the Intelligence Advanced Research Projects Activity (IARPA — https://www.iarpa.gov/) which is an organization that invests in high-risk, high-payoff research programs to tackle some of the most difficult challenges of the agencies and disciplines in the U.S. Intelligence Community (IC).
IARPA’s mission is to push the boundaries of science to develop solutions that empower the U.S. IC to do its work better and more efficiently for national security. IARPA does not have an operational mission and does not deploy technologies directly to the field, but instead, they facilitate the transition of research results to IC customers for operational application.
Currently, Dr. Markowitz leads three research programs at the intersection between biology, engineering, and computing. These programs are: FELIX, which is revolutionizing the field of bio-surveillance with new experimental and computational tools for detecting genetic engineering in complex biological samples; MIST, which is developing compact and inexpensive DNA data storage devices to address rapidly growing enterprise storage needs; and MICrONS, which is guiding the development of next-generation machine learning algorithms by reverse-engineering the computations performed by mammalian neocortex.
Previously, as a researcher in neuroscience, Dr. Markowitz published first-author papers on neural computation, the neural circuit basis of cognition in primates, and neural decoding strategies for brain-machine interfaces.
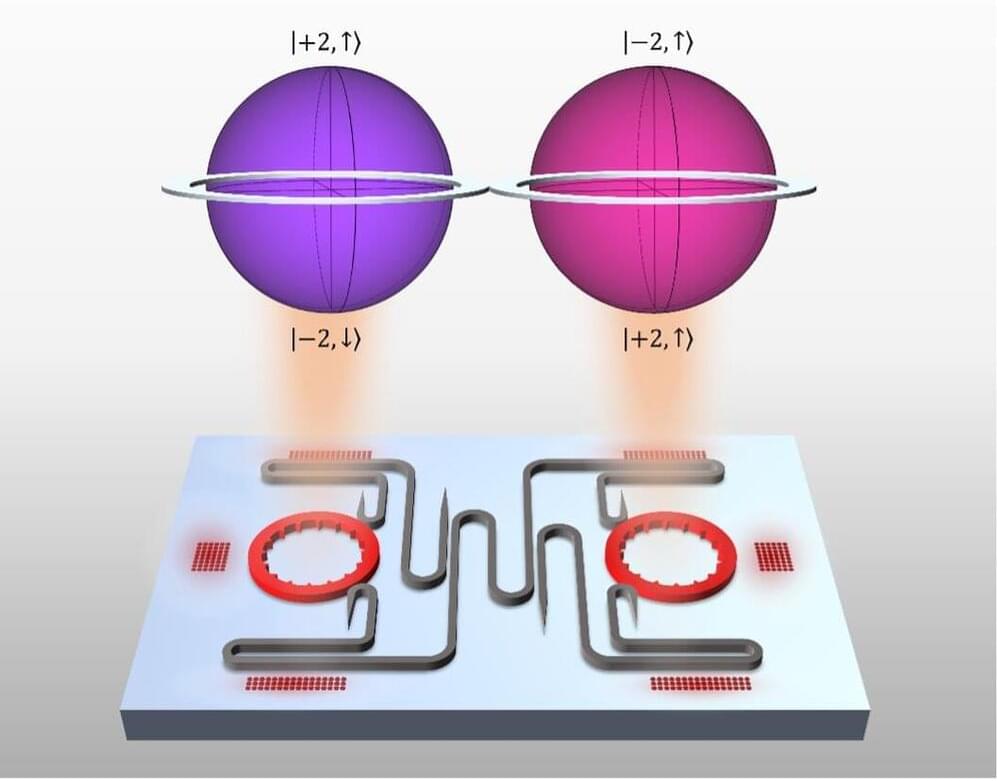
Researchers at Penn Engineering have created a chip that outstrips the security and robustness of existing quantum communications hardware. Their technology communicates in “qudits,” doubling the quantum information space of any previous on-chip laser.
Liang Feng, Professor in the Departments of Materials Science and Engineering (MSE) and Electrical Systems and Engineering (ESE), along with MSE postdoctoral fellow Zhifeng Zhang and ESE Ph.D. student Haoqi Zhao, debuted the technology in a recent study published in Nature. The group worked in collaboration with scientists from the Polytechnic University of Milan, the Institute for Cross-Disciplinary Physics and Complex Systems, Duke University and the City University of New York (CUNY).