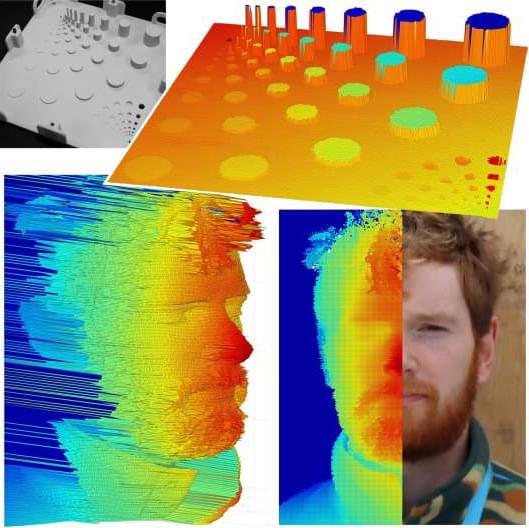
Researchers have designed a single-photon time-of-flight LiDAR system that can acquire a high-resolution 3D image of an object or scene up to 1 kilometer away. The new system could help enhance security, monitoring, and remote sensing by enabling detailed imaging even in challenging environmental conditions or when objects are obscured by foliage or camouflage netting.
“Our system uses a single-photon detector approximately twice as efficient as detectors deployed in similar LiDAR systems reported by other research groups and has a system timing resolution at least 10 times better,” said research team member Aongus McCarthy, from Heriot-Watt University in the UK.
“These improvements allow the imaging system to collect more scattered photons from the target and achieve a much higher spatial resolution.”