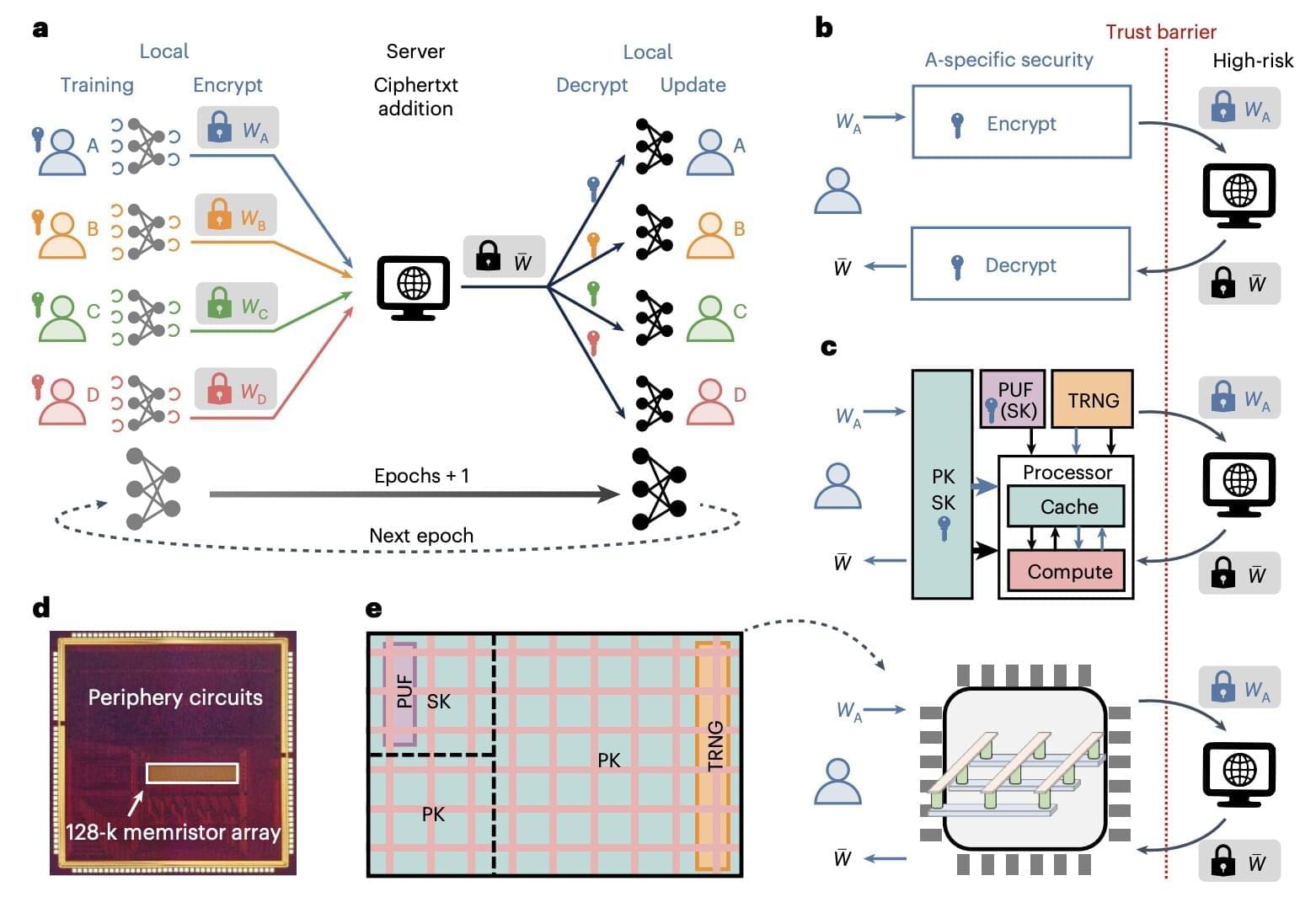
The Canadian government has ordered Hikvision’s subsidiary in the country to cease all operations following a review that determined them to pose a national security risk.
The order was forwarded to Hikvision last Friday, and the matter was made public over the weekend by Mélanie Joly, Canada’s Minister of Innovation, Science and Industry.
“Following a National Security Review under the Investment Canada Act, the Government of Canada has ordered Hikvision Canada Inc. to cease all operations in Canada and close its Canadian business,” reads the announcement.