Picus Security explains why relying on LLM-generated attack scripts is risky and how an agentic approach maps real threat intel to safe, validated TTPs. Their breakdown shows how teams can turn headline threats into reliable defense checks without unsafe automation.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 77

Malicious VSCode extensions on Microsoft’s registry drop infostealers
Two malicious extensions on Microsoft’s Visual Studio Code Marketplace infect developers’ machines with information-stealing malware that can take screenshots, steal credentials, crypto wallets, and hijack browser sessions.
The marketplace hosts extensions for the popular VSCode integrated development environment (IDE) to extend functionality or add customization options.
The two malicious extensions, called Bitcoin Black and Codo AI, masquerade as a color theme and an AI assistant, respectively, and were published under the developer name ‘BigBlack.’

Google Chrome adds new security layer for Gemini AI agentic browsing
Google is introducing in the Chrome browser a new defense layer called ‘User Alignment Critic’ to protect upcoming agentic AI browsing features powered by Gemini.
Agentic browsing is an emerging mode in which an AI agent is configured to autonomously perform for the user multi-step tasks on the web, including navigating sites, reading their content, clicking buttons, filling forms, and carrying out a sequence of actions.
User Alignment Critic is a separate LLM model isolated from untrusted content that acts as a “high-trust system component.”

Revolutionary AI System Achieves 600x Speed Breakthrough in the Search for Signals from Space
In a significant advance for astronomy, researchers from the Breakthrough Listen initiative, working in collaboration with NVIDIA and utilizing their system on the SETI Institute’s Allen Telescope Array (ATA) in California, have improved the process for detecting Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs). Their newly developed artificial intelligence system outperforms existing methods, operating hundreds of times faster than current pipelines while maintaining accuracy.
Detailed in the peer-reviewed journal Astronomy & Astrophysics, the new system operates on NVIDIA’s Holoscan platform, designed to process massive streaming datasets in real-time. Traditionally, FRB detection requires “dedispersion” — searching through thousands of possible signal parameters to correct for frequency-dependent time delays. The new end-to-end AI architecture eliminates that bottleneck, analyzing signals in real time and transforming how astronomers search for transient and potentially artificial signals from space.
The performance gains are notable. At the ATA, the state-of-the-art pipeline currently takes approximately 59 seconds to process 16.3 seconds of observational data — nearly four times slower than real-time. The new AI-driven system performs the same task 600 times faster, operating over 160 times faster than real-time.

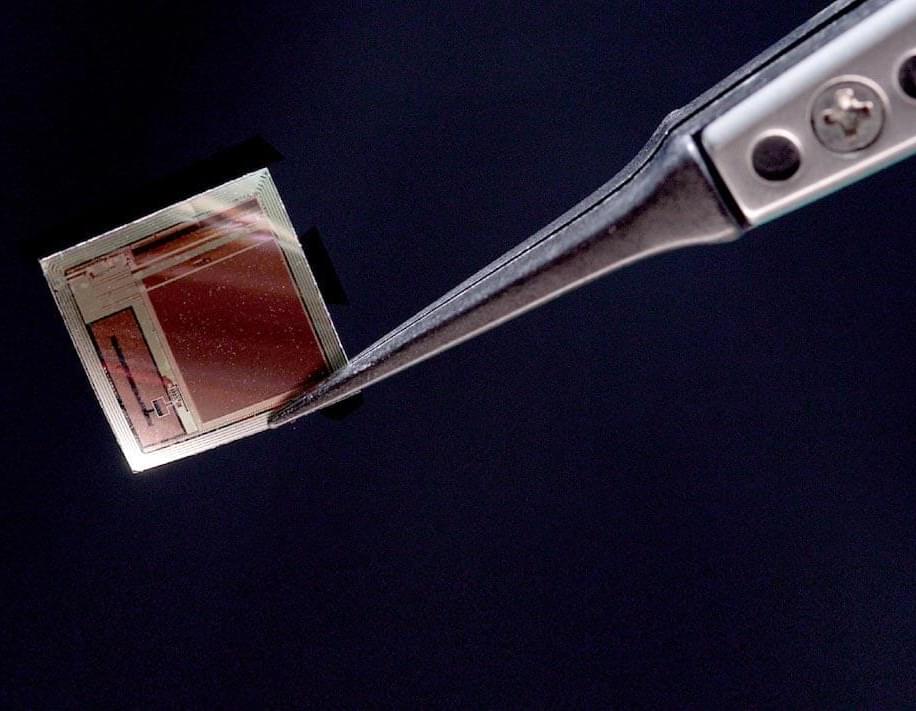
New Paper-Thin Brain Implant Could Transform How Humans Connect With AI
A radically miniaturized brain implant called BISC is redefining what’s possible in human–computer interaction, offering a paper-thin, wireless, high-bandwidth link directly to the brain.
With over 65,000 electrodes and unprecedented data throughput, it enables advanced AI decoding of thoughts, intentions, and sensory experiences while remaining minimally invasive.

After losing more than $70 billion, Mark Zuckerberg seems to have finally admitted that his biggest bet is ‘not working’
The TOI Tech Desk is a dedicated team of journalists committed to delivering the latest and most relevant news from the world of technology to readers of The Times of India. TOI Tech Desk’s news coverage spans a wide spectrum across gadget launches, gadget reviews, trends, in-depth analysis, exclusive reports and breaking stories that impact technology and the digital universe. Be it how-tos or the latest happenings in AI, cybersecurity, personal gadgets, platforms like WhatsApp, Instagram, Facebook and more; TOI Tech Desk brings the news with accuracy and authenticity.
AI Expert: We Have 2 Years Before Everything Changes! We Need To Start Protesting! — Tristan Harris
For example: “If you’re worried about immigration, you should be way more concerned about AI” — for the impact on jobs, cultural stability, and social predictability.
Ex-Google Insider and AI Expert TRISTAN HARRIS reveals how ChatGPT, China, and Elon Musk are racing to build uncontrollable AI, and warns it will blackmail humans, hack democracy, and threaten jobs…by 2027.
Tristan Harris is a former Google design ethicist and leading voice from Netflix’s The Social Dilemma. He is also co-founder of the Center for Humane Technology, where he advises policymakers, tech leaders, and the public on the risks of AI, algorithmic manipulation, and the global race toward AGI.
Please consider sharing this episode widely. Using this link to share the episode will earn you points for every referral, and you’ll unlock prizes as you earn more points: https://doac-perks.com/
He explains:
Neuralink Patient Controls a Robotic Arm Telepathically! (Interview w/ Nick Wray)
Follow Nick on X: https://twitter.com/Telepath_8
Pre-order linkaChart for free: https://linkaChart.ai/?utm_term=ryan2
Generate AI voice audio via ElevenLabs: https://try.elevenlabs.io/xe894d3yv35h.
Neura Pod is a series covering topics related to Neuralink, Inc. Topics such as brain-machine interfaces, brain injuries, and artificial intelligence will be explored. Host Ryan Tanaka synthesizes information, shares the latest updates, and conducts interviews to easily learn about Neuralink and its future.
Sign up for Neuralink’s Patient Registry: https://neuralink.com/trials/
Join the Neuralink team: https://neuralink.com/careers/