Meta Platforms on Friday said it will invest $600 billion in U.S. infrastructure and jobs over the next three years, including artificial intelligence data centers, as the social media giant races to build infrastructure to power its AI ambitions.



The last decade has seen incredible progress in machine learning (ML), primarily driven by powerful neural network architectures and the algorithms used to train them. However, despite the success of large language models (LLMs), a few fundamental challenges persist, especially around continual learning, the ability for a model to actively acquire new knowledge and skills over time without forgetting old ones.
When it comes to continual learning and self-improvement, the human brain is the gold standard. It adapts through neuroplasticity — the remarkable capacity to change its structure in response to new experiences, memories, and learning. Without this ability, a person is limited to immediate context (like anterograde amnesia). We see a similar limitation in current LLMs: their knowledge is confined to either the immediate context of their input window or the static information that they learn during pre-training.
The simple approach, continually updating a model’s parameters with new data, often leads to “catastrophic forgetting” (CF), where learning new tasks sacrifices proficiency on old tasks. Researchers traditionally combat CF through architectural tweaks or better optimization rules. However, for too long, we have treated the model’s architecture (the network structure) and the optimization algorithm (the training rule) as two separate things, which prevents us from achieving a truly unified, efficient learning system.
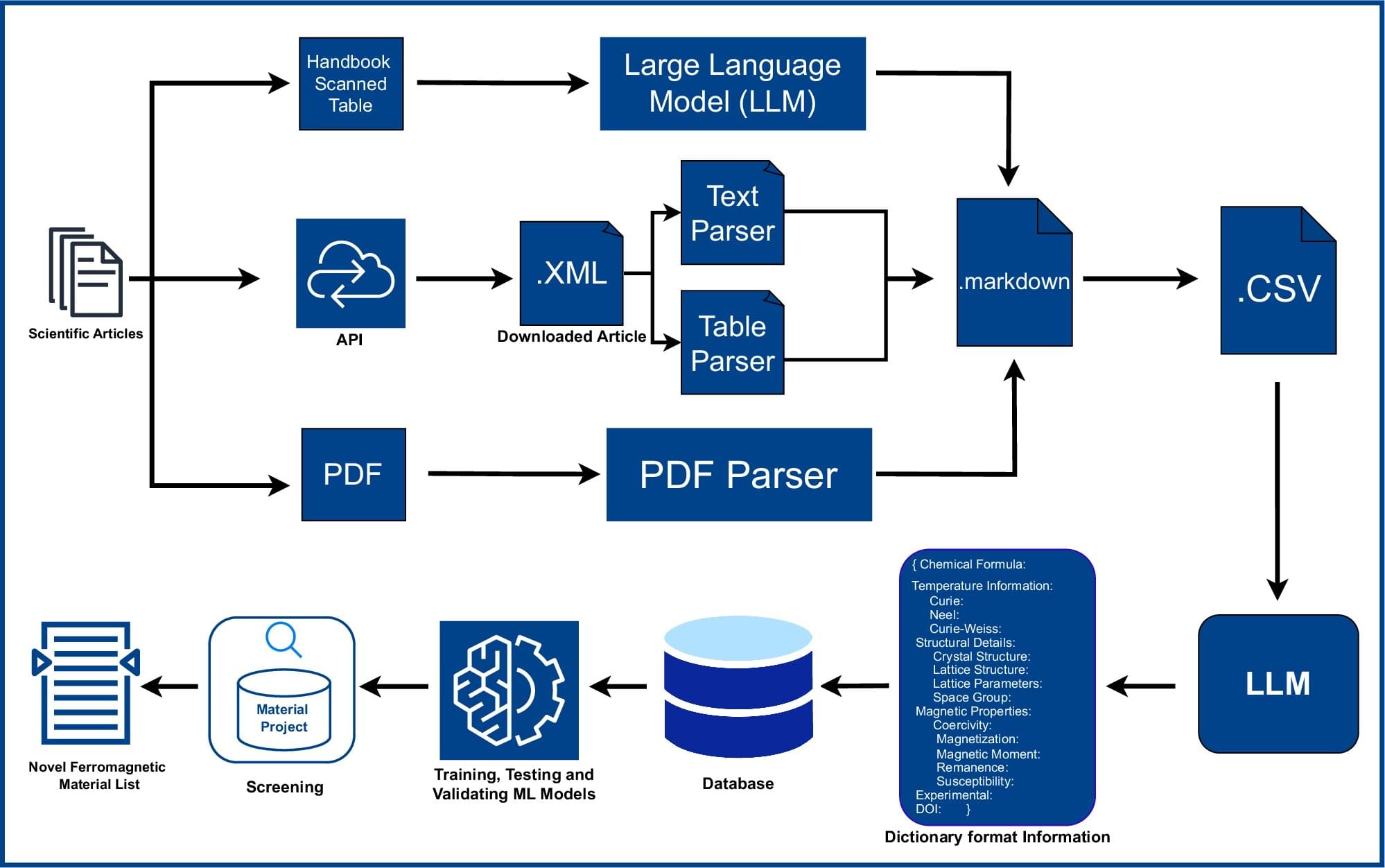
Researchers at the University of New Hampshire have harnessed artificial intelligence to accelerate the discovery of new functional magnetic materials, creating a searchable database of 67,573 magnetic materials, including 25 previously unrecognized compounds that remain magnetic even at high temperatures.
“By accelerating the discovery of sustainable magnetic materials, we can reduce dependence on rare earth elements, lower the cost of electric vehicles and renewable-energy systems, and strengthen the U.S. manufacturing base,” said Suman Itani, lead author and a doctoral student in physics.
The newly created database, named the Northeast Materials Database, helps to more easily explore all the magnetic materials which play a major role in the technology that powers our world: smartphones, medical devices, power generators, electric vehicles and more. But these magnets rely on expensive, imported, and increasingly difficult to obtain rare earth elements, and no new permanent magnet has been discovered from the many magnetic compounds we know exist.
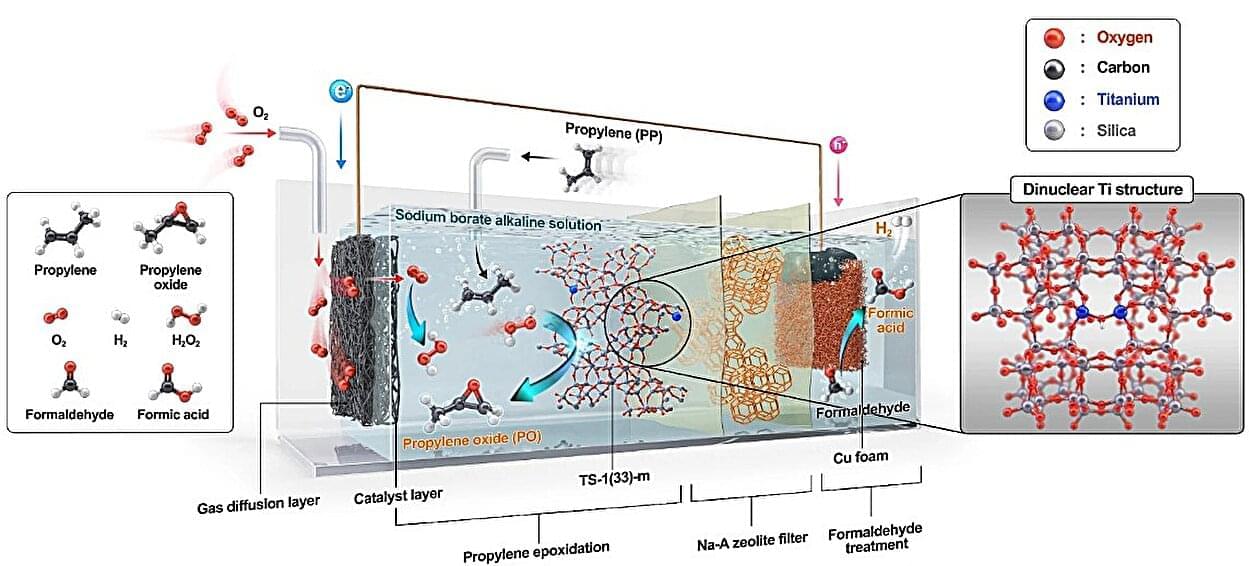
An eco-friendly system capable of producing propylene oxide (PO) without external electricity or sunlight has been developed. PO is a vital raw material used in manufacturing household items such as polyurethane for sofas and mattresses, as well as polyester for textiles and water bottles.
A research team led by Professors Ja Hun Kwak and Ji-Wook Jang from the School of Energy and Chemical Engineering at UNIST, in collaboration with Professor Sung June Cho of Chonnam National University, has successfully created a self-driven PO production system utilizing in-situ generated hydrogen peroxide (H₂O₂).
The research is published in Nature Communications.

Six of the most influential minds in artificial intelligence joined FT Live for an exclusive conversation on how their breakthroughs and the current state of AI are shaping our world.
On 6 November, Jensen Huang, Yoshua Bengio, Geoffrey Hinton, Fei-Fei Li, Yann LeCun, and Bill Dally spoke with the FT’s AI editor, Madhumita Murgia at the FT Future of AI Summit in London. Together, they reflected on decades of pioneering work — from neural networks to generative AI and discuss the ethical, social, and economic implications of the technology they helped to create.
All six, along with Professor John Hopfield, are recipients of the 2025 Queen Elizabeth Prize for Engineering for their foundational contributions to machine learning and AI.
👉 For more exclusive interviews and agenda-setting conversations with global AI leaders, visit our website: https://ai.live.ft.com/
#ArtificialIntelligence #JensenHuang #GeoffreyHinton #AI #MachineLearning #FTLive #FutureofAI

Seoul National University College of Engineering announced that a research team led by Professor Hyun Oh Song from the Department of Computer Science and Engineering has developed a new AI technology called KVzip that intelligently compresses the conversation memory of large language model (LLM)-based chatbots used in long-context tasks such as extended dialog and document summarization. The study is published on the arXiv preprint server.
The term conversation memory refers to the temporary storage of sentences, questions, and responses that a chatbot maintains during interaction, which it uses to generate contextually coherent replies. Using KVzip, a chatbot can compress this memory by eliminating redundant or unnecessary information that is not essential for reconstructing context. The technique allows the chatbot to retain accuracy while reducing memory size and speeding up response generation—a major step forward in efficient, scalable AI dialog systems.
Modern LLM chatbots perform tasks such as dialog, coding, and question answering using enormous contexts that can span hundreds or even thousands of pages. As conversations grow longer, however, the accumulated conversation memory increases computational cost and slows down response time.
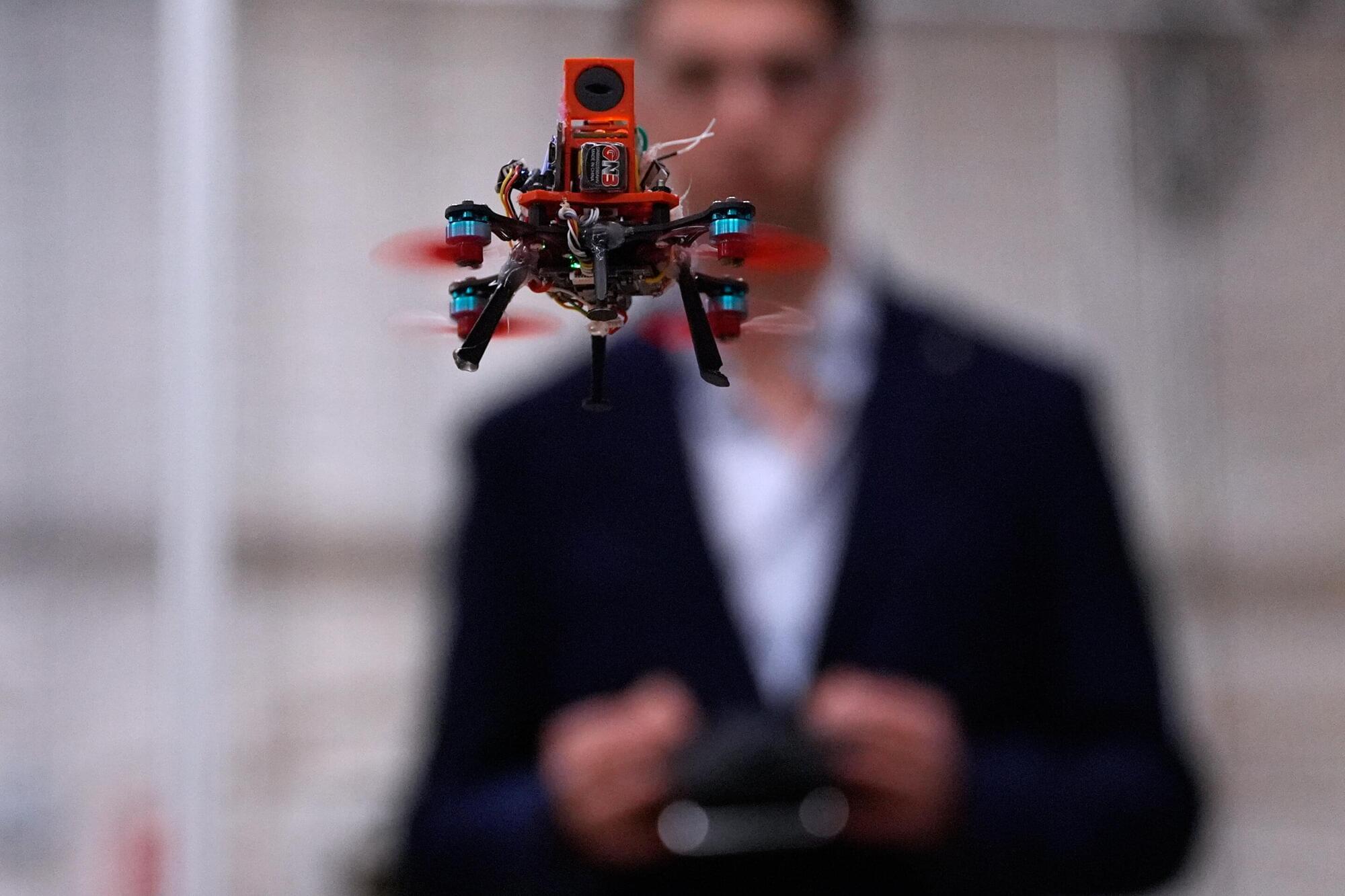

Don’t be fooled by the fog machine, spooky lights and fake bats: the robotics lab at Worcester Polytechnic Institute lab isn’t hosting a Halloween party.
Instead, it’s a testing ground for tiny drones that can be deployed in search and rescue missions even in dark, smoky or stormy conditions.
“We all know that when there’s an earthquake or a tsunami, the first thing that goes down is power lines. A lot of times, it’s at night, and you’re not going to wait until the next morning to go and rescue survivors,” said Nitin Sanket, assistant professor of robotics engineering. “So we started looking at nature. Is there a creature in the world which can actually do this?”

The human brain comprises hundreds of interconnected regions that drive our thoughts, emotions, and behaviours. Existing brain atlases can identify major structures in MRI scans – such as the hippocampus, which supports memory and learning – but their finer sub-regions remain hard to detect. These distinctions matter because sub-regions of areas like the hippocampus, for example, are affected differently during Alzheimer’s disease progression.
Examining the brain at the cellular level is achievable using microscopy (histology), but cannot be done in living individuals, limiting its potential for understanding how the human brain changes during development, ageing and disease.
Published in Nature, the new study introduces NextBrain, an atlas of the entire adult human brain that can be used to analyse MRI scans of living patients in a matter of minutes and at a level of detail not possible until now.
The creators of the atlas, which is freely available, hope it will ultimately help to accelerate discovery in brain science and its translation into better diagnosis and treatment of conditions such as Alzheimer’s.
&