The image tagging system that went viral on social media was part of artist Trevor Paglen and AI researcher Kate Crawford’s attempts to publicize how prejudiced technology can be.


After debuting just shy of two years ago, Boston Dynamics has finally made its Spot robotic dog available for sale, but don’t expect to find a great Black Friday deal on this bot at Best Buy come Thanksgiving. The company hasn’t made them available to the average consumer just yet—only businesses that can promise an interesting application for the technology.
A new twist on robotics.
New twist on robotics: Boston Dynamics showcases Atlas’ agility with gymnastics routine.
“Her” is one of the top 20 artificial intelligence films — in pictures for The…
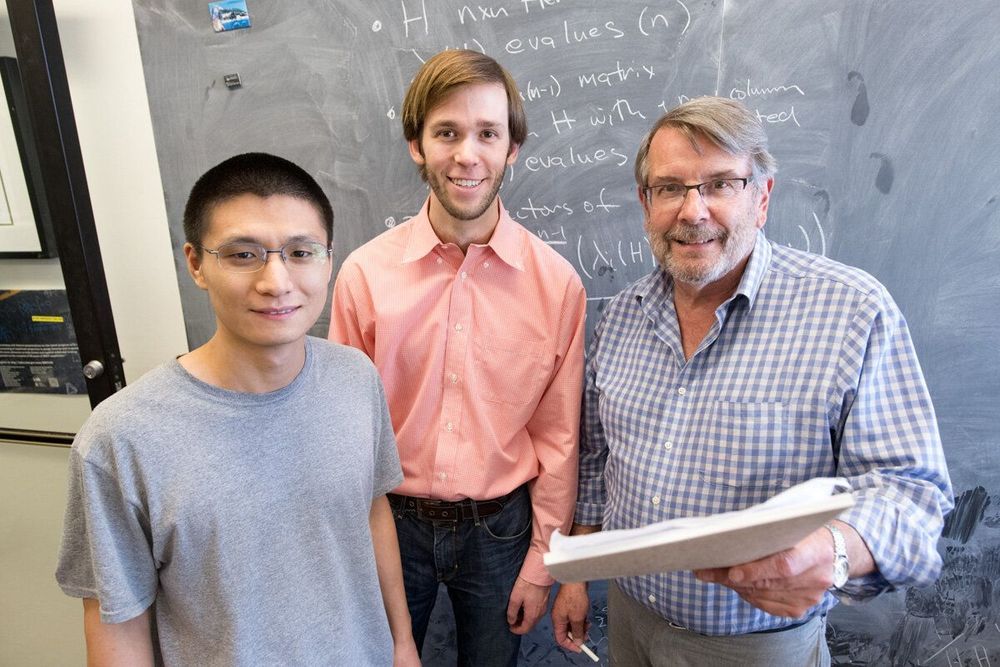
Linear algebra is a field of mathematics that has been thoroughly investigated for many centuries, providing invaluable tools used not only in mathematics, but also across physics and engineering as well as many other fields. For years physicists have used important theorems in linear algebra to quickly calculate solutions to the most complicated problems.
This August, three theoretical physicists—Peter Denton, a scientist at Brookhaven National Laboratory and a scholar at Fermilab’s Neutrino Physics Center; Stephen Parke, theoretical physicist at Fermilab; and Xining Zhang, a University of Chicago graduate student working under Parke—turned the tables and, in the context of particle physics, discovered a fundamental identity in linear algebra.
The identity relates eigenvectors and eigenvalues in a direct way that hadn’t been previously recognized. Eigenvectors and eigenvalues are two important ways of reducing the properties of a matrix to their most basic components and have applications in many math, physics and real-world contexts, such as in analyzing vibrating systems and facial recognition programs. The eigenvectors identify the directions in which a transformation occurs, and the eigenvalues specify the amount of stretching or compressing that occurs.
Boston Dynamics is announcing this morning that Spot, its versatile quadruped robot, is now for sale. The machine’s animal-like behavior regularly electrifies crowds at tech conferences, and like other Boston Dynamics’ robots, Spot is a YouTube sensation whose videos amass millions of views.
Now anyone interested in buying a Spot—or a pack of them—can go to the company’s website and submit an order form. But don’t pull out your credit card just yet. Spot may cost as much as a luxury car, and it is not really available to consumers. The initial sale, described as an “early adopter program,” is targeting businesses. Boston Dynamics wants to find customers in select industries and help them deploy Spots in real-world scenarios.
Watch this robot do gymnastics 🤖.
Making the world more epic, one giant robot at a time.
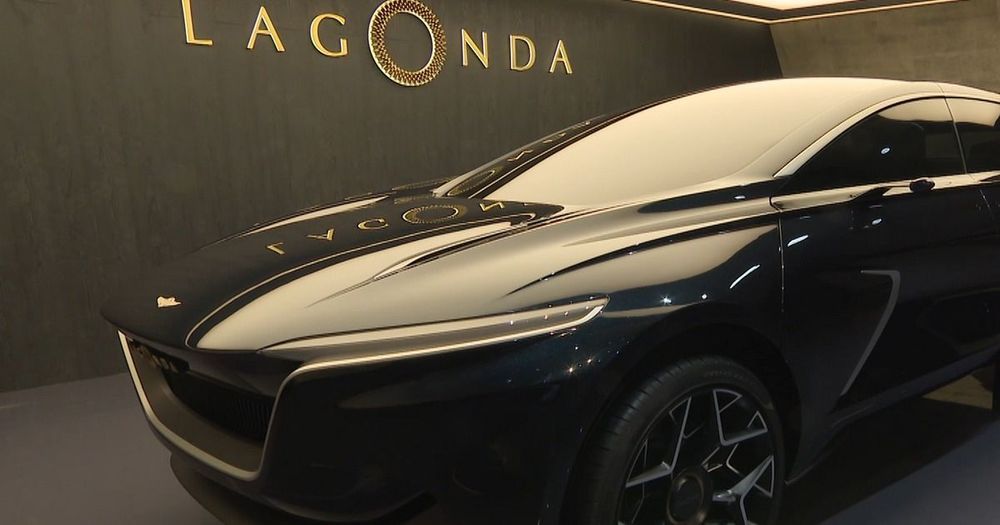

The brand claims it’s the first luxury battery electric vehicle promising both autonomous and zero-emissions driving, with an opulent touch.
The car will be powered by two electric motors, which will be mounted on its floor, one on each axle, freeing up a considerable amount of space in the shell for the occupant to enjoy.
The concept features gesture and voice control systems, a levitating key, which will work as the driver’s own personal assistant, rotating seats and premium materials.
Boston Dynamics is putting Spot to work. The company has announced a new leasing program for its Spot robot (formerly SpotMini), which is aimed at construction, entertainment, and other automation-friendly industries. But is the world ready for this semi-autonomous quadruped?
Subscribe: http://goo.gl/G5RXGs
Like The Verge on Facebook: https://goo.gl/2P1aGc
Follow on Twitter: https://goo.gl/XTWX61
Follow on Instagram: https://goo.gl/7ZeLvX
Why’d You Push That Button Podcast: https://pod.link/1295289748
The Vergecast Podcast: https://pod.link/430333725
More about our podcasts: https://www.theverge.com/podcasts
Community guidelines: http://bit.ly/2D0hlAv
Wallpapers from The Verge: https://bit.ly/2xQXYJr