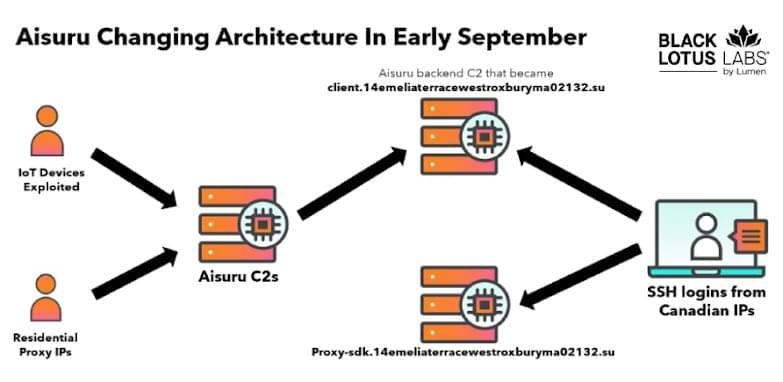
AI security risks are shifting from models to workflows after malicious extensions stole chat data from 900,000 users & prompt injections abused AI to

Scientific theories of consciousness should be falsifiable and non-trivial. Recent research has given us formal tools to analyze these requirements of falsifiability and non-triviality for theories of consciousness. Surprisingly, many contemporary theories of consciousness fail to pass this bar, including theories based on causal structure but also (as I demonstrate) theories based on function. Herein I show these requirements of falsifiability and non-triviality especially constrain the potential consciousness of contemporary Large Language Models (LLMs) because of their proximity to systems that are equivalent to LLMs in terms of input/output function; yet, for these functionally equivalent systems, there cannot be any falsifiable and non-trivial theory of consciousness that judges them conscious. This forms the basis of a disproof of contemporary LLM consciousness. I then show a positive result, which is that theories of consciousness based on (or requiring) continual learning do satisfy the stringent formal constraints for a theory of consciousness in humans. Intriguingly, this work supports a hypothesis: If continual learning is linked to consciousness in humans, the current limitations of LLMs (which do not continually learn) are intimately tied to their lack of consciousness.
The idea never died, progress is still being made.
Nanotechnology was once imagined as the next great technological revolution—atom-by-atom manufacturing, machines as small as cells, and materials we can only dream of today. Instead, it stalled. While AI, robotics, and nuclear surged ahead, nanotech faded into the background, reduced to buzzwords and sci-fi aesthetics.
But the idea never died.
We can manipulate matter at the atomic scale. We can design perfect materials. We can build molecular machines. What’s been missing isn’t physics—it’s ambition, investment, and the will to push beyond today’s tools.
In this interview with futurist J. Storrs Hall, we explore what nanotechnology really is, why it drifted off course, and why its future may finally be on the horizon. If AI was a “blue-sky fantasy” until suddenly it wasn’t, what happens when someone decides nanotech deserves the same surge of talent, money, and imagination?
SpaceX is well-positioned to dominate the future of space AI due to its innovative technologies, scalable satellite production, and strategic partnerships, which will enable it to efficiently deploy and operate a massive network of satellites with advanced computing capabilities ## ## Questions to inspire discussion.
Launch Economics & Infrastructure.
🚀 Q: Why is Starship essential for space AI data centers? A: Starship enables 100-1000x more satellites than Falcon 9, making orbital AI economically viable through massive scaling and lower launch costs, while Falcon 9 remains too expensive for commercial viability at scale.
🛰️ Q: What is SpaceX’s deployment plan for AI satellites? A: SpaceX plans Starlink version 3 satellites with 100 Nvidia chips each, deploying 5,000 satellites via 100 Starship launches at 50 satellites per flight to create a gigawatt-scale AI constellation by early 2030s.
📈 Q: What launch cadence gives SpaceX its advantage? A: SpaceX plans 10,000 annual launches and produces satellites at 10-100x the level of competitors, creating a monopoly on launch and manufacturing that positions them as the gatekeeper to space AI success.
Energy & Power Systems.

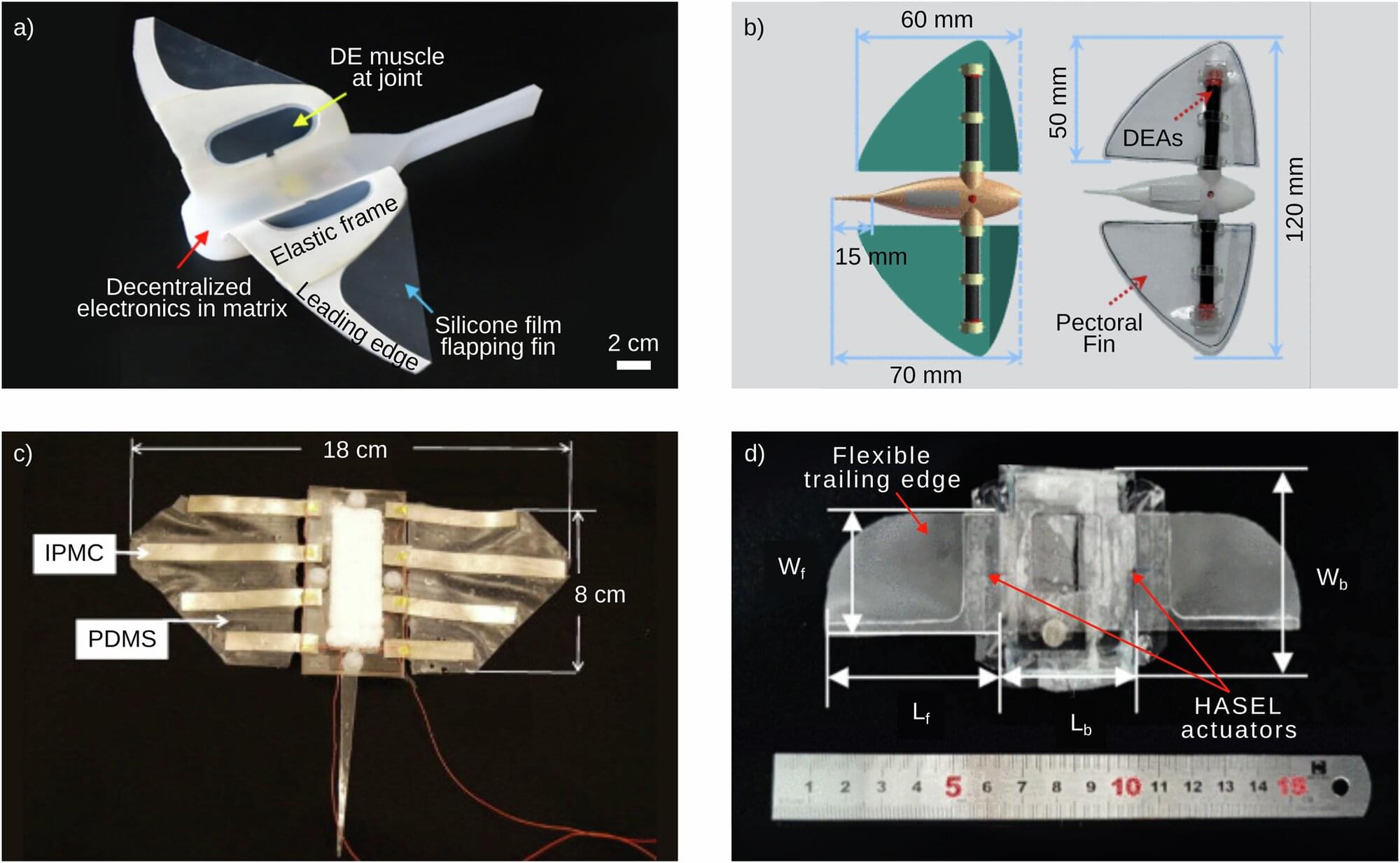
Underwater robots face many challenges before they can truly master the deep, such as stability in choppy currents. A new paper published in the journal npj Robotics provides a comprehensive update of where the technology stands today, including significant progress inspired by the movement of rays.
Underwater robots are not a gimmick. We need them to help us explore the roughly 74% of the ocean floor that still remains a mystery. While satellites, buoys and imaging technology can map the surface and the upper reaches of the ocean, we need underwater drones to explore and gather data from the hidden depths.
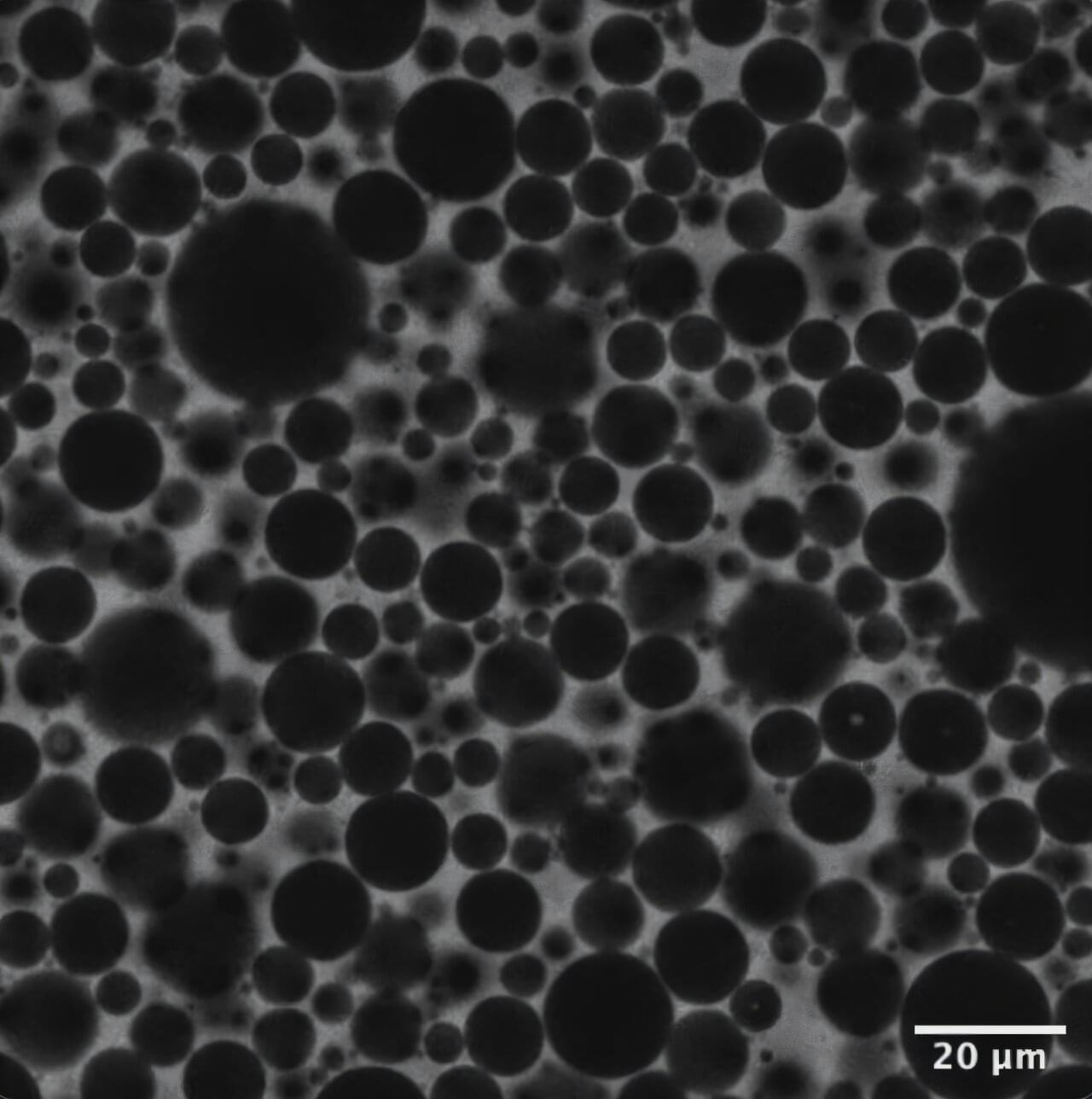
Foams are everywhere: soap suds, shaving cream, whipped toppings and food emulsions like mayonnaise. For decades, scientists believed that foams behave like glass, their microscopic components trapped in static, disordered configurations.
Now, engineers at the University of Pennsylvania have found that foams actually flow ceaselessly inside while holding their external shape. More strangely, from a mathematical perspective, this internal motion resembles the process of deep learning, the method typically used to train modern AI systems.
The discovery could hint that learning, in a broad mathematical sense, may be a common organizing principle across physical, biological and computational systems, and provide a conceptual foundation for future efforts to design adaptive materials. The insight could also shed new light on biological structures that continuously rearrange themselves, like the scaffolding in living cells.

The AI-generated Ghost Player system appears to be an evolution of the PS5 Game Help system, which was launched alongside the PlayStation [11,413 articles] href=https://www.videogameschronicle.com/platforms/playstation/ PlayStation fans who enjoy hunting trophies, due to the convenience of not having to call up a separate guide on another screen, such as a phone.
It is worth noting that there is no evidence that Sony has plans to use this technology in future hardware, and that patents like this have been filed by the firm, and many others, for years without any intention for use.