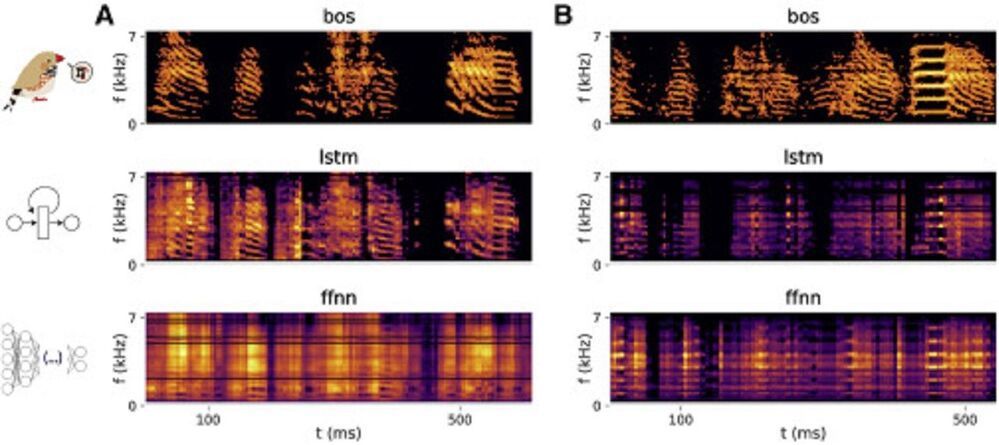
Scientists used AI to predict birdsong in real time from brain activity. This could go a long way towards establishing a BCI link for human communication. property= description.
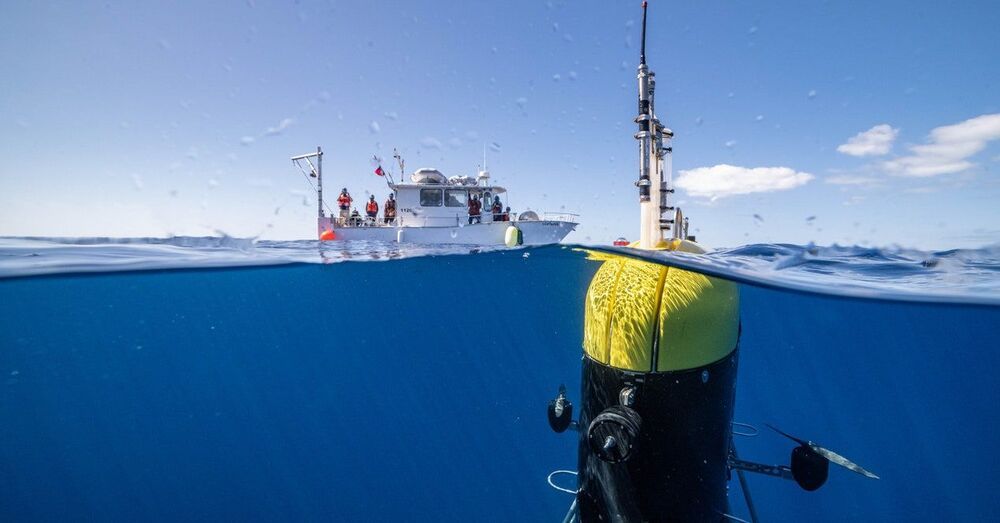


But now a spy swims among them: Mesobot. Today in the journal Science Robotics, a team of engineers and oceanographers describes how they got a new autonomous underwater vehicle to lock onto movements of organisms and follow them around the ocean’s “twilight zone,” a chronically understudied band between 650 feet and 3200 feet deep, which scientists also refer to as mid-water. Thanks to some clever engineering, the researchers did so without flustering these highly sensitive animals, making Mesobot a groundbreaking new tool for oceanographers.
“It’s super cool from an engineering standpoint,” says Northeastern University roboticist Hanumant Singh, who develops ocean robots but wasn’t involved in this research. “It’s really an amazing piece of work, in terms of looking at an area that’s unexplored in the ocean.”
Mesobot looks like a giant yellow-and-black AirPods case, only it’s rather more waterproof and weighs 550 pounds. It can operate with a fiber-optic tether attached to a research vessel at the surface, or it can swim around freely.

Observing the secrets of the universe’s “Dark Ages” will require capturing ultra-long radio wavelengths—and we can’t do that on Earth.
The universe is constantly beaming its history to us. For instance: Information about what happened long, long ago, contained in the long-length radio waves that are ubiquitous throughout the universe, likely hold the details about how the first stars and black holes were formed. There’s a problem, though. Because of our atmosphere and noisy radio signals generated by modern society, we can’t read them from Earth.
That’s why NASA is in the early stages of planning what it would take to build an automated research telescope on the far side of the moon. One of the most ambitious proposals would build the Lunar Crater Radio Telescope, the largest (by a lot) filled-aperture radio telescope dish in the universe. Another duo of projects, called FarSide and FarView, would connect a vast array of antennas—eventually over 100000, many built on the moon itself and made out of its surface material—to pick up the signals. The projects are all part of NASA’s Institute for Advanced Concepts (NIAC) program, which awards innovators and entrepreneurs with funding to advance radical ideas in hopes of creating breakthrough aerospace concepts. While they are still hypothetical, and years away from reality, the findings from these projects could reshape our cosmological model of the universe.
“With our telescopes on the moon, we can reverse-engineer the radio spectra that we record, and infer for the first time the properties of the very first stars,” said Jack Burns, a cosmologist at the University of Colorado Boulder and the co-investigator and science lead for both FarSide and FarView. “We care about those first stars because we care about our own origins—I mean, where did we come from? Where did the Sun come from? Where did the Earth come from? The Milky Way?”
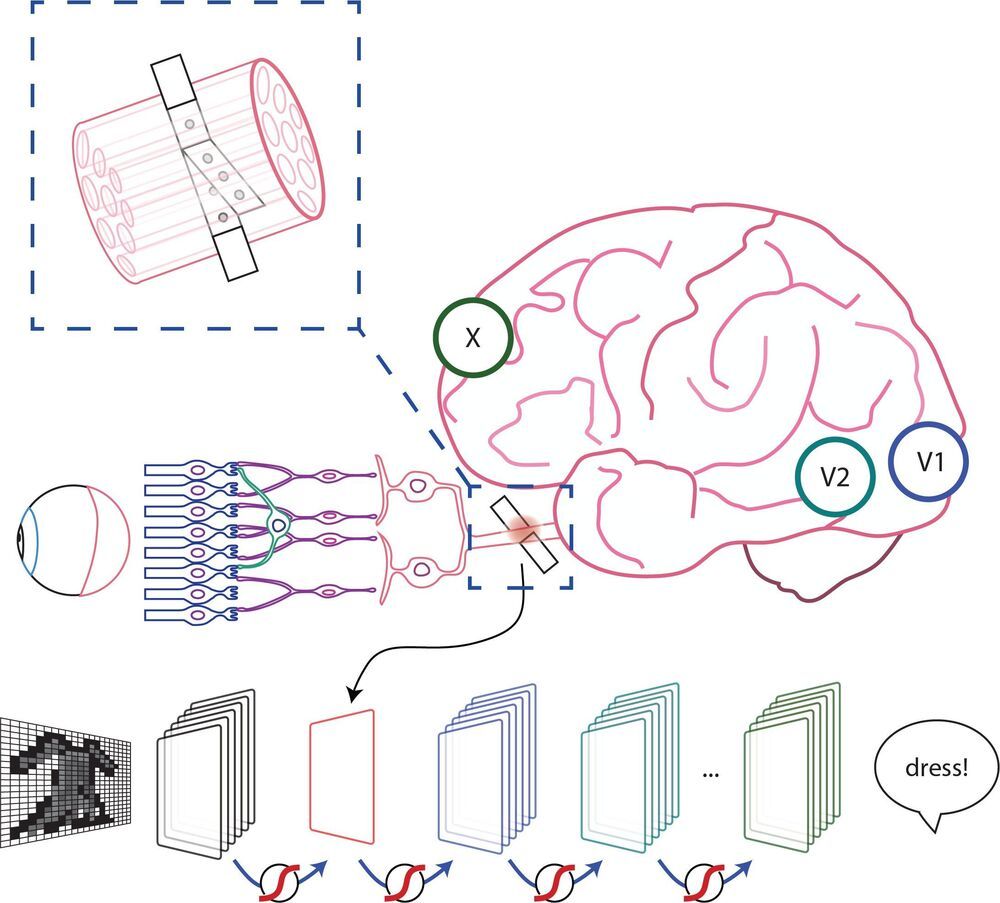
Stimulation of the nervous system with neurotechnology has opened up new avenues for treating human disorders, such as prosthetic arms and legs that restore the sense of touch in amputees, prosthetic fingertips that provide detailed sensory feedback with varying touch resolution, and intraneural stimulation to help the blind by giving sensations of sight.
Scientists in a European collaboration have shown that optic nerve stimulation is a promising neurotechnology to help the blind, with the constraint that current technology has the capacity of providing only simple visual signals.
Nevertheless, the scientists’ vision (no pun intended) is to design these simple visual signals to be meaningful in assisting the blind with daily living. Optic nerve stimulation also avoids invasive procedures like directly stimulating the brain’s visual cortex. But how does one go about optimizing stimulation of the optic nerve to produce consistent and meaningful visual sensations?
Now, the results of a collaboration between EPFL, Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna and Scuola Internazionale Superiore di Studi Avanzati, published today in Patterns, show that a new stimulation protocol of the optic nerve is a promising way for developing personalized visual signals to help the blind–that also take into account signals from the visual cortex. The protocol has been tested for the moment on artificial neural networks known to simulate the entire visual system, called convolutional neural networks (CNN) usually used in computer vision for detecting and classifying objects. The scientists also performed psychophysical tests on ten healthy subjects that imitate what one would see from optic nerve stimulation, showing that successful object identification is compatible with results obtained from the CNN.
“We are not just trying to stimulate the optic nerve to elicit a visual perception,” explains Simone Romeni, EPFL scientist and first author of the study. “We are developing a way to optimize stimulation protocols that takes into account how the entire visual system responds to optic nerve stimulation.”
“The research shows that you can optimize optic nerve stimulation using machine learning approaches. It shows more generally the full potential of machine learning to optimize stimulation protocols for neuroprosthetic devices,” continues Silvestro Micera, EPFL Bertarelli Foundation Chair in Translational Neural Engineering and Professor of Bioelectronics at the Scuola Superiore Sant’Anna.

Hugh Herr is building the next generation of bionic limbs, robotic prosthetics inspired by nature’s own designs. Herr lost both legs in a climbing accident 30 years ago; now, as the head of the MIT Media Lab’s Biomechatronics group, he shows his incredible technology with the help of ballroom dancer Adrianne Haslet-Davis, who lost her left leg in the 2013 Boston Marathon bombing.

A supply-chain component lays open camera feeds to remote attackers thanks to a critical security vulnerability.
Millions of connected security and home cameras contain a critical software vulnerability that can allow remote attackers to tap into video feeds, according to a warning from the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA).
The bug (CVE-2021–32934, with a CVSS v3 base score of 9.1) has been introduced via a supply-chain component from ThroughTek that’s used by several original equipment manufacturers (OEMs) of security cameras – along with makers of IoT devices like baby-and pet-monitoring cameras, and robotic and battery devices.
AI has finally come full circle.
A new suite of algorithms by Google Brain can now design computer chips —those specifically tailored for running AI software —that vastly outperform those designed by human experts. And the system works in just a few hours, dramatically slashing the weeks-or months-long process that normally gums up digital innovation.
At the heart of these robotic chip designers is a type of machine learning called deep reinforcement learning. This family of algorithms, loosely based on the human brain’s workings, has triumphed over its biological neural inspirations in games such as Chess, Go, and nearly the entire Atari catalog.
✅ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/pro_robots.
You are on the Pro Robot channel and today we are going to talk about the soldiers of the future. Exoskeletons, ballistic helmets, military suits, chips and more are already being introduced into the armaments of different countries. In this issue we will find out what the super-soldier of the future will be like and what developments are being conducted in the military industry. Watch the video to the end and write your opinion in the comments: will robots replace humans in military service?
0:00 In this video.
0:30 Combat glasses.
2:26 Devtac Ronin Kevlar ballistic helmet.
3:00 STILE smart fabric.
3:42 Stealth Cloak.
4:10 Future Soldier System Full Suit.
5:15 Sotnik Suit.
5:55 Exoskeleton Military.
6:32 PowerWalk current generator exoskeletons.
7:00 Human Universal Load Carrier exoskeleton with hydraulic drive.
7:24 A Flying Suit for Military.
7:48 Jetpack.
8:09 Invasive chips and genetic engineering.
9:02 Man-Made Lightning.
More interesting and useful content:
✅ Elon Musk Innovation https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLcyYMmVvkTuQ-8LO6CwGWbSCpWI2jJqCQ
✅Future Technologies Reviews https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLcyYMmVvkTuTgL98RdT8-z-9a2CGeoBQF
✅ Technology news.
#prorobots #technology #roboticsnews.
By employing a neural network, the company says its numbers will be more accurate—and allow it to offer to buy more homes.