Category: robotics/AI – Page 1,894



Big Tech is replacing human artists with AI
I wish I had some sort of different response to give than this, but this summary is totally clear-eyed about the coming Semantic Apocalypse.
Artistic corpocracy
It’s actually even worse (in a way aptly not noticed by the Google employee). Because as we discussed, in the future advanced versions of this sort of AI will be solely owned and developed by Big Tech due the scaling laws around how they’re trained and run. The immediate licensing of GPT-3 by Microsoft was an augury of this. Indeed, the rights to interact with these AIs will be some of the most valuable licenses on the planet in the next decade. Consumers, even academic AI researchers, will communicate with company-owned trillion-parameter AIs solely via oracles, getting nowhere near the source code. The future of this technology belongs to huge corporations with major resources. So it’s not really that “AI is automating art”—no, corporations are automating art. And writing. And translation. And illustration. And music. And the thousand other human forms of creativity that give life meaning. They are now the province of Big Tech.

Department of Commerce establishes National Artificial Intelligence Advisory Committee
US Secretary of Commerce Gina Raimondo has announced that the Commerce Department has established a high-level committee to advise the President and other federal agencies on a range of issues related to artificial intelligence (AI). Working with the National AI Initiative Office (NAIIO) in the White House Office of Science and Technology Policy (OSTP), the Department is now seeking to recruit top-level candidates to serve on the committee.
A formal notice describing the National Artificial Intelligence Advisory Committee (NAIAC) and the call for nominations for the committee and its Subcommittee on Artificial Intelligence and Law Enforcement appears in the Federal Register published today.
“AI presents an enormous opportunity to tackle the biggest issues of our time, strengthen our technological competitiveness, and be an engine for growth in nearly every sector of the economy,” said Secretary Raimondo. “But we must be thoughtful, creative, and wise in how we address the challenges that accompany these new technologies. That includes, but is not limited to, ensuring that President Biden’s comprehensive commitment to advancing equity and racial justice extends to our development and use of AI technology. This committee will help the federal government to do that by providing insights into a full range of issues raised by AI.”

Artificial brain networks simulated with new quantum materials
Isaac Newton’s groundbreaking scientific productivity while isolated from the spread of bubonic plague is legendary. University of California San Diego physicists can now claim a stake in the annals of pandemic-driven science.
A team of UC San Diego researchers and colleagues at Purdue University have now simulated the foundation of new types of artificial intelligence computing devices that mimic brain functions, an achievement that resulted from the COVID-19 pandemic lockdown. By combining new supercomputing materials with specialized oxides, the researchers successfully demonstrated the backbone of networks of circuits and devices that mirror the connectivity of neurons and synapses in biologically based neural networks.
The simulations are described in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS).
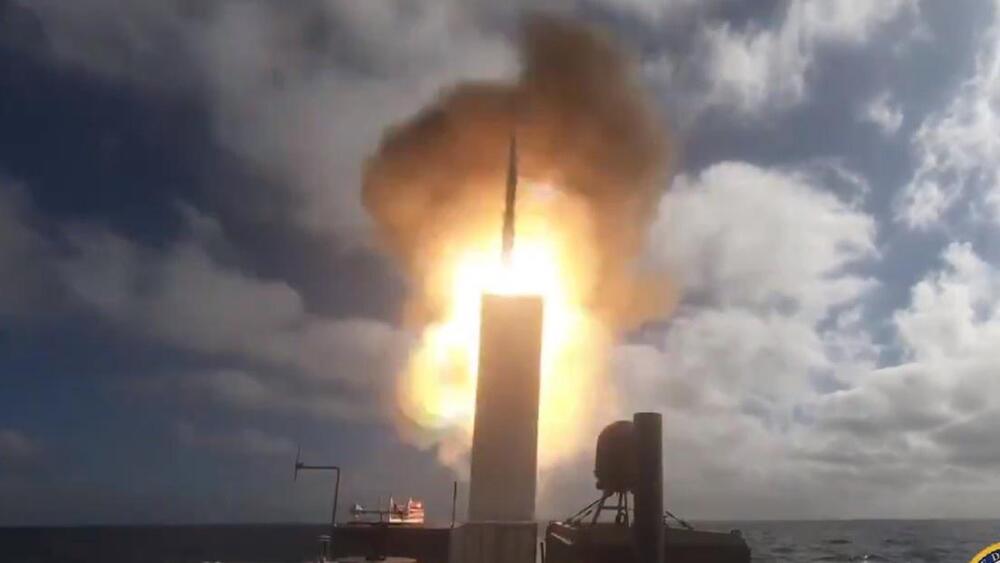


The Pentagon’s Robot Warship Just Fired Its First Missile
One of the U.S. Defense Department’s two prototype robot warships just fired its first missile.
The military on Friday hailed the test-launch of an SM-6 missile from the Unmanned Surface Vessel Ranger, sailing off the California coast, as “game-changing.”
It’s one thing for an unmanned vessel to launch a missile, however. It’s quite another for the same vessel autonomously to find and fix targets.
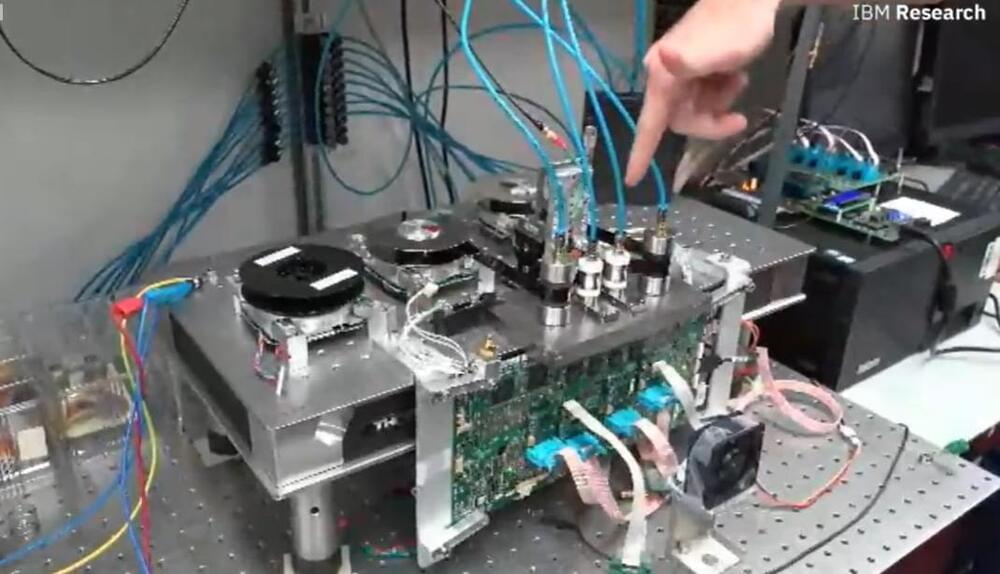

Big Blue Shines A Light On The Future Of Tape Storage
Circa 2020
IBM knows how to adapt to an ever-changing enterprise tech landscape. The venerable company more almost 20 years ago shed its PC business – selling it to Lenovo – understanding that that systems were quickly becoming commodity devices and the market was going to stumble. A decade later IBM sold its X86-based server business to Lenovo for $2.3 billion and in the intervening years has put a keen focus on hybrid clouds and artificial intelligence, buying Red Hat for $34 billion and continuing to invest its Watson portfolio.
However, that hasn’t meant throwing out product lines simply because they’ve been around for a while. IBM has continued to upgrade its mainframe systems to keep up with modern workloads and the bet has paid off. In the last quarter 2,019 the company saw mainframe revenue – driven by its System z15 mainframe in September 2019 – jump 63 percent, a number followed the next quarter by a 59 percent increase.
Tape storage is a similar story. The company rolled out its first tape storage device in 1,952 the 726 Tape Unit, which had a capacity of 2MB. Five decades later, the company is still innovating its tape storage technology and this week said that, as part of a 15-year partnership with Fujifilm, has set a record with a prototype system of 317 gigabits-per-square-inch (GB/in2) in areal density, 27 times more than the areal density of current top-performance tape drives. The record, reached with the help of a new tape material called Strontium Ferrite (SrFe), is an indication that magnetic tape fits nicely in a data storage world of flash, SSDs and NVMe and a rising demand for cloud-based storage.
Stretching the capacity of flexible energy storage
Some electronics can bend, twist and stretch in wearable displays, biomedical applications and soft robots. While these devices’ circuits have become increasingly pliable, the batteries and supercapacitors that power them are still rigid. Now, researchers in ACS’ Nano Letters report a flexible supercapacitor with electrodes made of wrinkled titanium carbide — a type of MXene nanomaterial — that maintained its ability to store and release electronic charges after repetitive stretching.
One major challenge stretchable electronics must overcome is the stiff and inflexible nature of their energy storage components, batteries and supercapacitors. Supercapacitors that use electrodes made from transitional metal carbides, carbonitrides or nitrides, called MXenes, have desirable electrical properties for portable flexible devices, such as rapid charging and discharging. And the way that 2D MXenes can form multi-layered nanosheets provides a large surface area for energy storage when they’re used in electrodes. However, previous researchers have had to incorporate polymers and other nanomaterials to keep these types of electrodes from breaking when bent, which decreases their electrical storage capacity. So, Desheng Kong and colleagues wanted to see if deforming a pristine titanium carbide MXene film into accordion-like ridges would maintain the electrode’s electrical properties while adding flexibility and stretchability to a supercapacitor.
The researchers disintegrated titanium aluminum carbide powder into flakes with hydrofluoric acid and captured the layers of pure titanium carbide nanosheets as a roughly textured film on a filter. Then they placed the film on a piece of pre-stretched acrylic elastomer that was 800% its relaxed size. When the researchers released the polymer, it shrank to its original state, and the adhered nanosheets crumpled into accordion-like wrinkles.