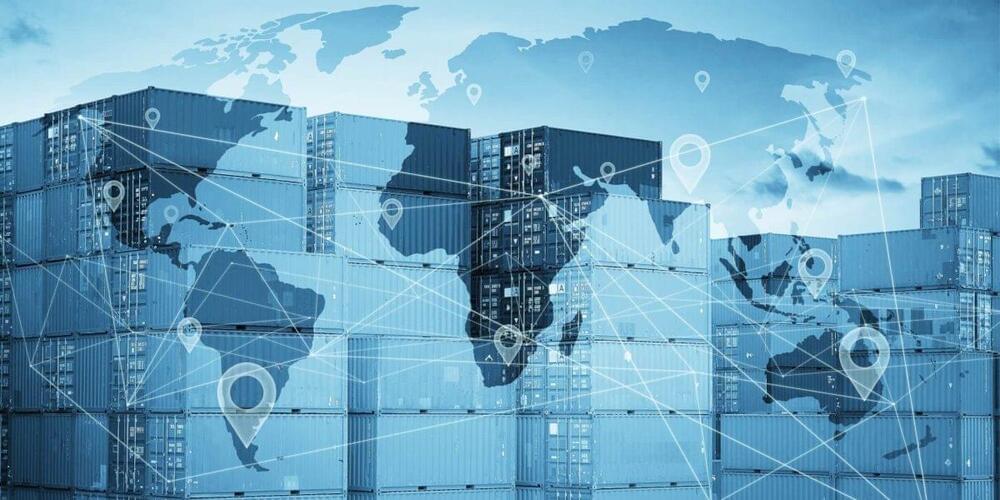
Altana AI, a startup building a database for global supply chain networks, today announced that it raised $15 million in a series A funding round led by GV with participation from Floating Point, Ridgeline Partners, Amadeus Capital Partners, and Schematic Ventures. The proceeds, which bring the company’s total raised to $22 million to date, will be used to further develop Altana’s data and AI systems and launch new machine learning and network analysis tools, according to CEO Evan Smith.
Trade wars, the rise of ecommerce, pandemic supply chain shocks, and sustainability concerns are driving fundamental changes to supply chain networks and global trade flows. Nearly 75% of companies report supply chain disruptions in some capacity due to pandemic-related transportation restrictions. And in a recent IBM survey, 40% of executives stressed the need for spare capacity to weather future crises.
Altana’s product aims to solve these challenges with a platform that connects and learns from billions of supply chain data points. It answers questions about products, shipments, companies, and networks, filtering out illicit trade and targeting bad actors and security threats across global commerce networks.