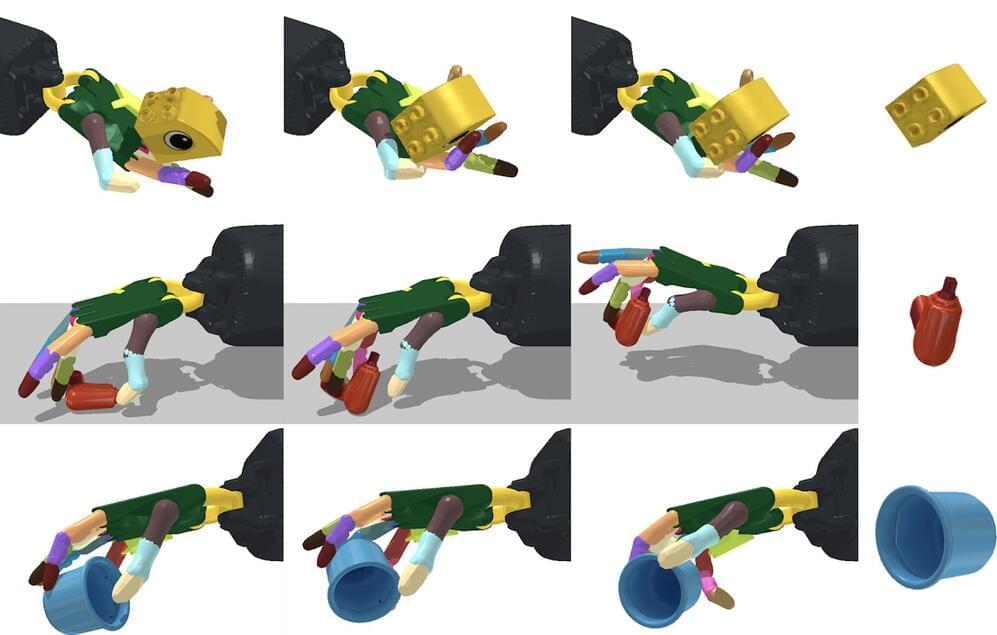
When most of us pick up an object, we don’t have to think about how to orient it in our hand. It’s something that comes naturally to us as we learn to navigate the world. That’s something that allows young children to be more deft with their hands than even the most advanced robots available today.
But that could quickly change. A team of scientists from MIT’s has developed a system that could one day give robots that same kind of dexterity. Using a AI algorithm, they created a simulated, anthropomorphic hand that could manipulate more than 2,000 objects. What’s more, the system didn’t need to know what it was about to pick up to find a way to move it around in its hand.
The system isn’t ready for real-world use just yet. To start, the team needs to transfer it to an actual robot. That might not be as much of a roadblock as you might think. At the start of the year, we saw researchers from Zhejiang University and the University of Edinburgh successfully transfer an AI reinforcement approach to their robot dog. The system allowed the robot to learn how to walk and recover from falls on its own.