As revenues and research output soar in the field of AI, global competition between the United States, China and Europe heats up.

There’s a multibillion-dollar race going on to build the first complete map of the brain, something scientists are calling the “connectome.” It involves slicing the brain into thousands of pieces, and then digitally stitching them back together using a powerful AI algorithm.
Presented by Polestar.
#HelloWorld #Science #BloombergQuicktake.
About Hello World:
Meet the exotic, colorful, and endlessly entertaining characters that make up the technology industry beyond big tech. Watch Bloomberg’s Ashlee Vance in a journey around the world to find the inventors, scientists and technologists shaping our future: https://youtube.com/playlist?list=PLqq4LnWs3olU-bP2R9uD8YXbt02JjocOk.
——-
Whoever controls AI controls the world
“Most Valuable AI unicorn” goes for IPO.
“In 2019, SenseTime became one of the first Chinese companies to be placed on the US Entity List, a trade blacklist that restricts it from gaining access to certain technologies originating from the US. The White House under Donald Trump claimed that the company was ”implicated in human rights violations and abuses in the implementation of China’s campaign of repression, mass arbitrary detention, and high-technology surveillance” against the Uyghur population, a mostly Muslim ethnic group in the Xinjiang region.
SenseTime – a Chinese artificial intelligence (AI) company – has been approved to list on the Hong Kong Stock Exchange.
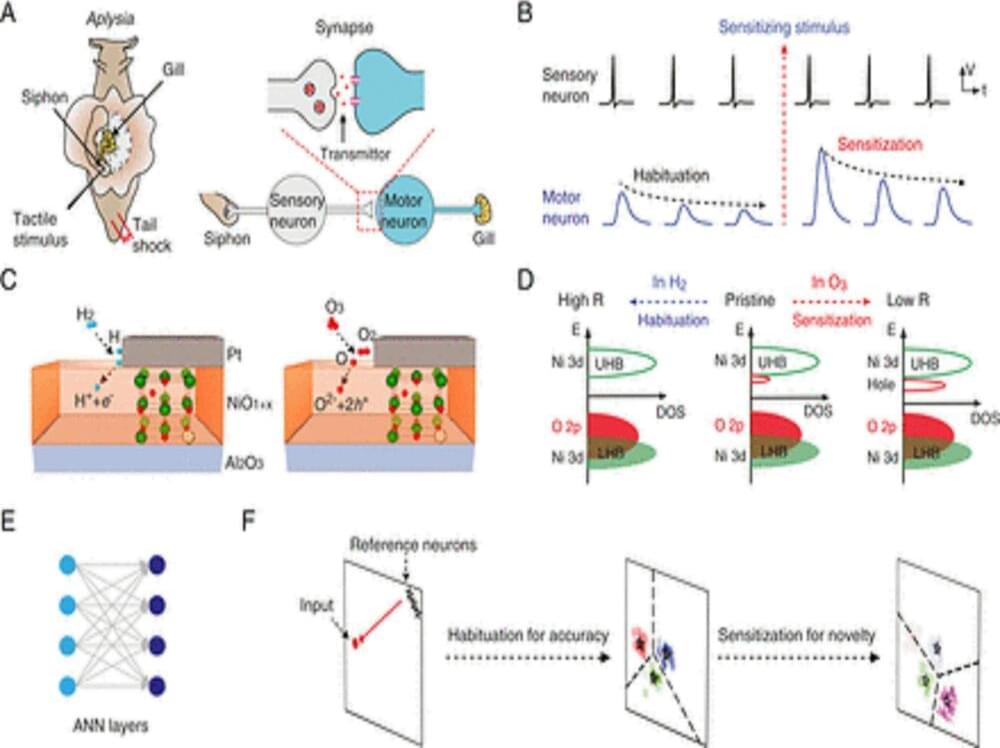
Rutgers researchers and their collaborators have found that learning — a universal feature of intelligence in living beings — can be mimicked in synthetic matter, a discovery that in turn could inspire new algorithms for artificial intelligence (AI).
The study appears in the journal PNAS.
One of the fundamental characteristics of humans is the ability to continuously learn from and adapt to changing environments. But until recently, AI has been narrowly focused on emulating human logic. Now, researchers are looking to mimic human cognition in devices that can learn, remember and make decisions the way a human brain does.
No, it’s not from a science fiction movie or from an episode of a popular kid’s television show. It’s real life. Researchers, in a proof-of-concept study, have made fish-shaped microrobots that are guided with magnets to cancer cells, where a pH change triggers them to open their mouths and release their chemotherapy cargo.
Scientists have previously made microscale (smaller than 100 µm) robots that can manipulate tiny objects, but most can’t change their shapes to perform complex tasks, such as releasing drugs. Some groups have made 4D-printed objects (3D-printed devices that change shape in response to certain stimuli), but they typically perform only simple actions, and their motion can’t be controlled remotely.
In a step toward biomedical applications for these devices, Jiawen Li, Li Zhang, Dong Wu and colleagues wanted to develop shape-morphing microrobots that could be guided by magnets to specific sites to deliver treatments. Because tumors exist in acidic microenvironments, the team decided to make the microrobots change shape in response to lowered pH.
This series looks at concepts such as Artificial Intelligence, Transhumanism, Cybernetics, Androids, Robots, and Augmenting the human or animal mind.
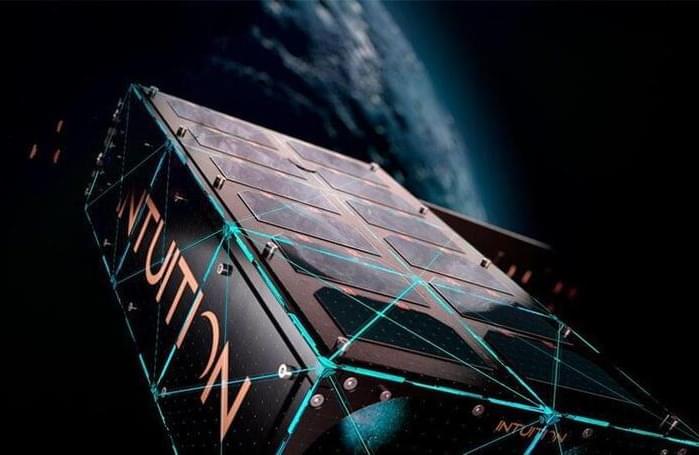

A new European satellite will use machine learning to provide rapid, low-cost information on soil conditions to enable smarter agriculture. The project is a model for what novel sensors and artificial intelligence technology can do in a vehicle no bigger than a shoebox.
Edge computing is a fashionable buzz-phrase for the technique of shifting the processing power away from the server farms of the internet and out to where the data is being collected. According to some, edge computing is the next great tech revolution, and in the case of satellites, where communications bandwidth is severely limited, it could be transformational.
The Intuition-1 satellite program will provide soil data to drive European precision agriculture projects, which involve applying fertilizer only when and where needed rather than treating an entire field. Precision agriculture is both more economical and easier on the environment — the catch is that it requires detailed information about soil conditions on a small scale. At present, establishing levels of soil nutrients in sufficient detail involves taking samples from multiple locations and sending them to a laboratory for analysis. This typically takes about three weeks.

There are billions of people around the world whose online experience has been shaped by algorithms that utilize artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML). Some form of AI and ML is employed almost every time people go online, whether they are searching for content, watching a video, or shopping for a product. Not only do these technologies increase the efficiency and accuracy of consumption but, in the online ecosystem, service providers innovate upon and monetize behavioral data that is captured either directly from a user’s device, a website visit or by third parties.
Advertisers are increasingly dependent on this data and the algorithms that adtech and martech employ to understand where their ads should be placed, which ads consumers are likely to engage with, which audiences are most likely to convert, and which publisher should get credit for conversions.
Additionally, the collection and better utilization of data helps publishers generate revenue, minimize data risks and costs, and provide relevant consumer-preference-based audiences for brands.
Fundamental Research On Ethical & Trustworthy Artificial Intelligence, For Health, Environment, And A Sustainable Future — Dr. Patrick van der Smagt, Ph.D., Director, ArtificiaI Intelligence Research, Volkswagen.
Dr. Patrick van der Smagt is Director of ArtificiaI Intelligence Research, Volkswagen AG, and Head of Argmax. AI (https://argmax.ai/), the Volkswagen Group Machine Learning Research Lab, in Munich, focusing on a range of research domains, including probabilistic deep learning for time series modelling, optimal control, reinforcement learning robotics, and quantum machine learning.
Dr. van der Smagt is also a research professor in the Computer Science faculty at Eötvös Loránd University in Budapest.
Dr. van der Smagt previously directed a lab as professor for machine learning and biomimetic robotics at the Technical University of Munich while leading the machine learning group at the research institute fortiss, and before that, founded and headed the Assistive Robotics and Bionics Lab at DLR, the German Aerospace Center.
Besides publishing numerous papers and patents on machine learning, robotics, and motor control, Dr. van der Smagt has won a number of awards, including the 2013 Helmholtz-Association Erwin Schrödinger Award, the 2014 King-Sun Fu Memorial Award, the 2013 Harvard Medical School/MGH Martin Research Prize, the 2018 Webit Best Implementation of AI Award, and best-paper awards at various machine learning and robotics conferences and journals.