A software engineer tells BBC’s Panorama about installing the system in police stations in Xinjiang.
Category: robotics/AI – Page 1,687
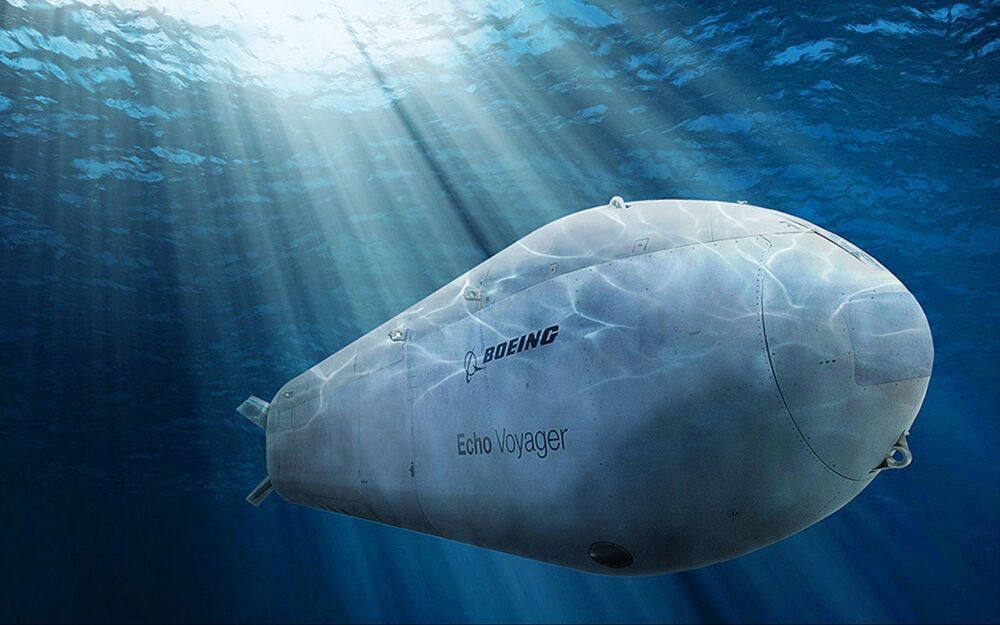
The 50-ton Voyager was developed by Boeing’s PhantomWorks division, which is devoted to advanced new technologies, succeeding a series of smaller Echo Seeker and Echo Ranger UUVs. The 15.5-meter long Echo Voyager has a range of nearly 7500 miles. It has also deployed at sea up to three months in a test, and theoretically could last as long as six months.
Supposedly, Voyager also can dive as deep as 3350 meters—while few military submarines are (officially) certified for dives below 500 meters.
And it isn’t the only robot submarine in the works.
Here’s What You Need to Know: The U.S. Navy has an ambitious vision for future warfare.
At a military parade celebrating its 70th anniversary, the People’s Republic of China unveiled, amongst many other exotic weapons, two HSU-001 submarines—the world’s first large diameter autonomous submarines to enter military service.
Mars Research | Artificial Muscle
Posted in bioprinting, cyborgs, Elon Musk, robotics/AI, space
😃
✅ Instagram: https://www.instagram.com/pro_robots.
You’re on the PRO Robotics channel and in this issue of High Tech News. The latest news from Mars, the first flight of Elon Musk’s starship around the Earth, artificial muscles, a desktop bioprinter and why IBM teaches artificial intelligence to code? All the most interesting technology news in one issue!
Watch the video to the end and write in the comments which news interested you most.
Time Codes:
0:00 In this video.
0:22 News from Mars.
2:08 A system that recognizes the capitals presented in the brain with 94% accuracy.
2:47 SpaceX has scheduled a test orbital flight of Starship.
3:28 Japanese billionaire, Yusaku Maezawa to go to ISS in December.
3:55 Voyager 1
4:27 OSIRIS-REx probe.
4:50 China has launched “Tianhe” basic module into space.
5:25 Successful tests of the Module “Nauka“
6:00 IBM creates datasets to teach artificial intelligence programming.
6:45 Elon Musk promises to open access to FSD’s autopilot on a subscription basis in June.
7:08 Honda and AutoX report first 100 days of fully autonomous AutoX robot cabs.
7:25 Baidu.
7:41 Robot to untangle hair.
8:10 SoftBank sold Boston Dynamics, but continues to fund robot startups.
8:35 Boston University developers have created a robotic gripper capable of picking up even a single grain of sand.
9:06 U.S. Air Force unveils robot for washing F-16 Viper aircraft.
9:35 E Ink.
10:07 Artificial muscle fibers.
10:40 Gravity Industries jetpacks.
#prorobots #robots #robot #future technologies #robotics.
An iPhone app that estimates biological aging discovered that life expectancy has the capacity to be almost double the current norm.
GEYLANG, Singapore — Have you made any plans for the 22nd century yet? A new study finds you might want to think about it because it’s possible for humans to live to see their 150th birthday!
Scientists in Singapore have developed an iPhone app that accurately estimates biological aging. It discovered that life expectancy has the capacity to be almost double the current norm. The findings are based on blood samples from hundreds of thousands of people in the United States and United Kingdom.
The instrument, called DOSI, uses artificial intelligence to work out body resilience, the ability to recover from injury or disease. DOSI, which stands for dynamic organism state indicator, takes into account age, illnesses, and lifestyles to make its estimates.
Our oceans are filled with tiny pieces of plastic. These tiny devices can break them down.
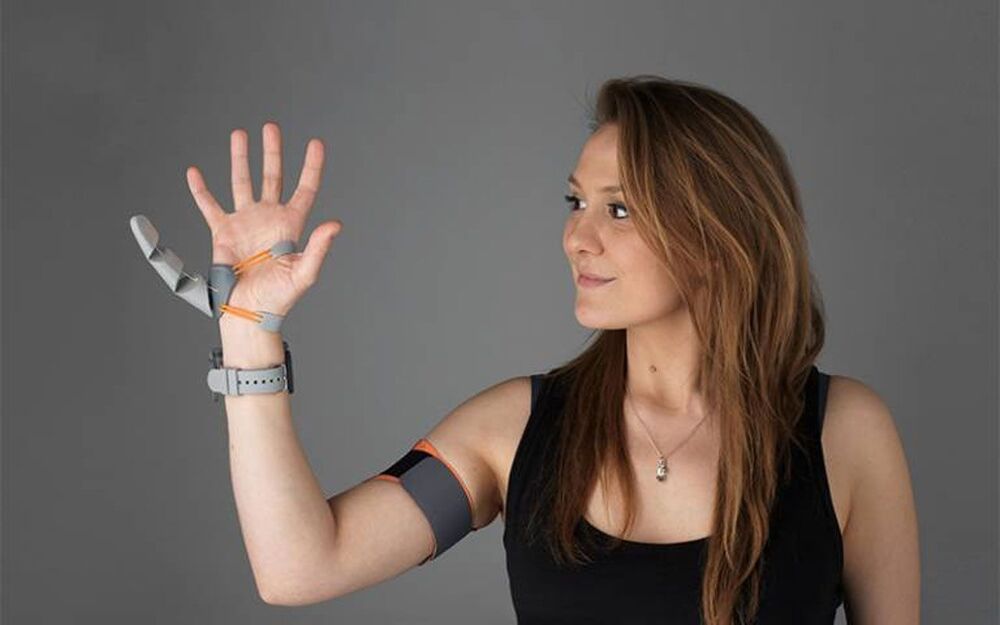
UCL researchers have created a strange robotic “third thumb” that attaches to the hand and adds a large extra digit on the opposite side of the hand from the thumb. Researchers found that using the robotic thumb can impact how the hand is represented in the brain. For the research, scientists trained people to use an extra robotic thumb and found they could effectively carry out dexterous tasks such as building a tower of blocks using a single hand with two thumbs.
Researchers said that participants trained to use the extra thumb increasingly felt like it was part of their body. Initially, the Third Thumb was part of a project seeking to reframe the way people view prosthetics from replacing a lost function to becoming an extension of the human body. UCL Professor Tamar Makin says body augmentation is a growing field aimed at extending the physical abilities of humans.
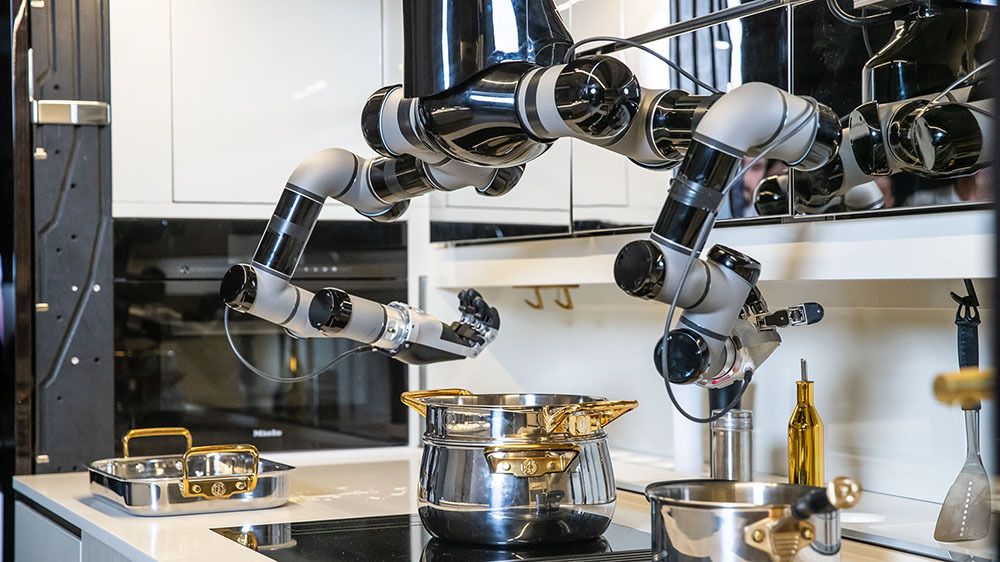
Anyone who spends a lot of time in the kitchen knows that there’s at least one gadget out there for every single step in the cooking process. But there has never been an appliance that could handle them all. Until now, that is.
Later this year, London-based robotics company Moley will begin selling the first robot chef, according to the Financial Times. The company claims the ceiling-mounted device, called the Moley Robotics Kitchen, will be able to cook over 5000 recipes and even clean up after itself when it’s done.
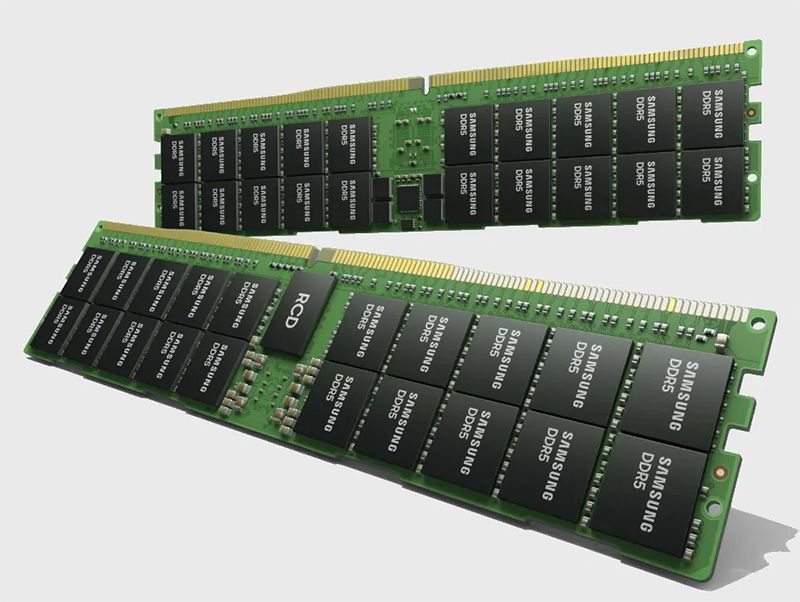
2 sticks of RAM giving you 1TB of memory will be the norm soon.
While consumers today typically use computers with 8GB or 16GB of DDR4 RAM inside, Samsung is pushing ahead with the next generation of memory modules. Its latest stick of RAM is a 512GB DDR5 module running at 7200Mbps.
The new module will be used in servers performing “the most extreme compute-hungry, high-bandwidth workloads.” That means supercomputers, artificial intelligence, and machine learning. It was made possible thanks to advanced HKMG technology, which Samsung adopted back in 2018 for its GDDR6 memory. Basically, HKMG replaces the insulator layer in DRAM structures. The high dielectric material contained in the layer reduces current leakage and therefore allows higher performance. At the same time, Samsung managed to reduce power usage in the new module by 13%.
“Samsung is the only semiconductor company with logic and memory capabilities and the expertise to incorporate HKMG cutting-edge logic technology into memory product development,” said Young-Soo Sohn, Vice President of the DRAM Memory Planning/Enabling Group at Samsung Electronics. “By bringing this type of process innovation to DRAM manufacturing, we are able to offer our customers high-performance, yet energy-efficient memory solutions to power the computers needed for medical research, financial markets, autonomous driving, smart cities and beyond.”
O,.o! Awesome: 3
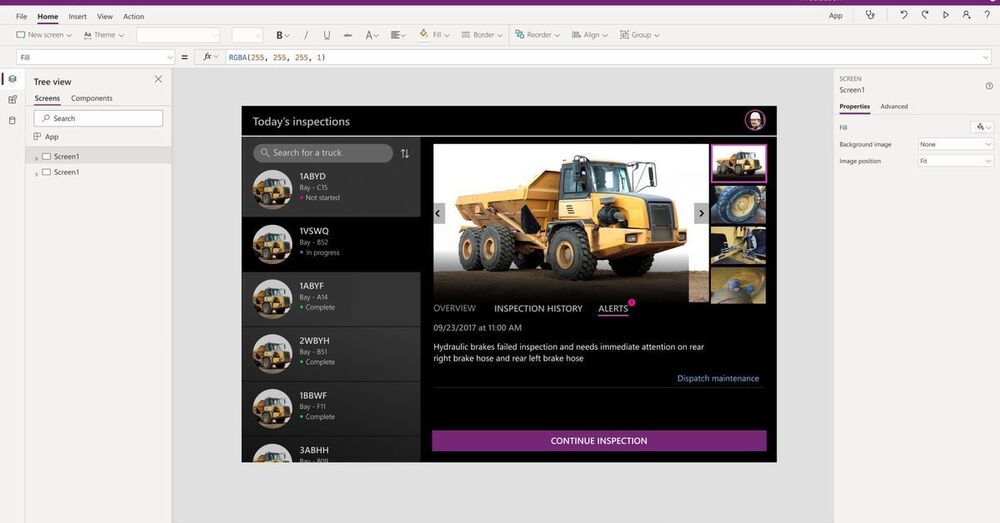
Microsoft has announced an update for its PowerApps software that uses GPT-3 to turn natural speech into code. The tool only works with the company’s simple Power Fx coding language, but it shows the potential of machine learning to transform programming.
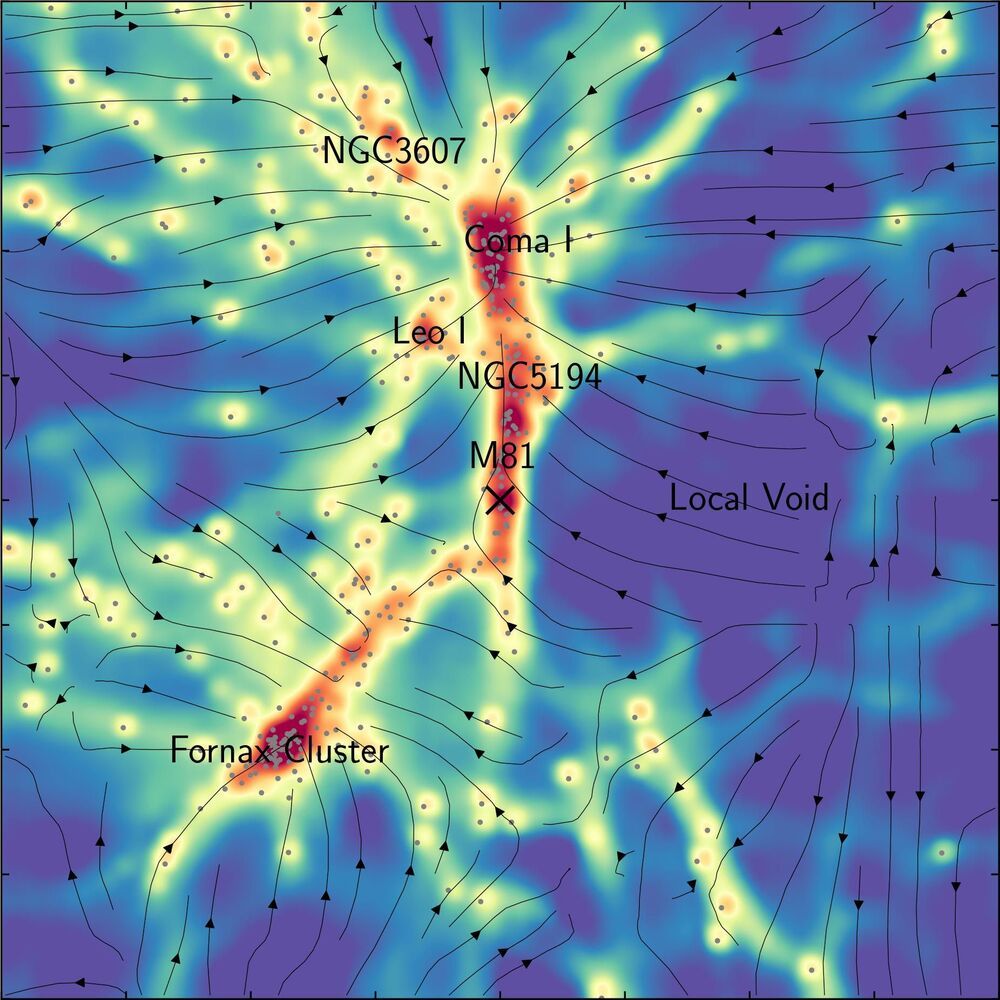
A new map of dark matter in the local universe reveals several previously undiscovered filamentary structures connecting galaxies. The map, developed using machine learning by an international team including a Penn State astrophysicist, could enable studies about the nature of dark matter as well as about the history and future of our local universe.
Dark matter is an elusive substance that makes up 80% of the universe. It also provides the skeleton for what cosmologists call the cosmic web, the large-scale structure of the universe that, due to its gravitational influence, dictates the motion of galaxies and other cosmic material. However, the distribution of local dark matter is currently unknown because it cannot be measured directly. Researchers must instead infer its distribution based on its gravitational influence on other objects in the universe, like galaxies.
“Ironically, it’s easier to study the distribution of dark matter much further away because it reflects the very distant past, which is much less complex,” said Donghui Jeong, associate professor of astronomy and astrophysics at Penn State and a corresponding author of the study. “Over time, as the large-scale structure of the universe has grown, the complexity of the universe has increased, so it is inherently harder to make measurements about dark matter locally.”