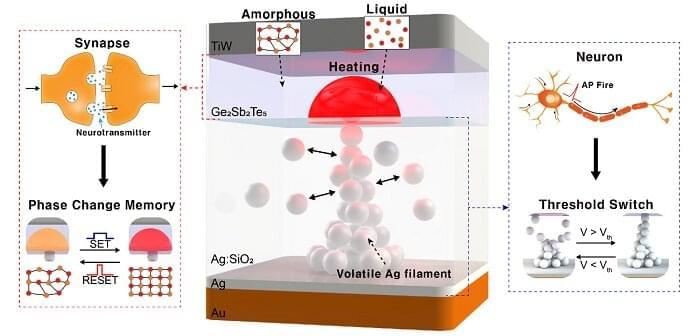
Researchers have reported a nano-sized neuromorphic memory device that emulates neurons and synapses simultaneously in a unit cell, another step toward completing the goal of neuromorphic computing designed to rigorously mimic the human brain with semiconductor devices.
Neuromorphic computing aims to realize artificial intelligence (AI) by mimicking the mechanisms of neurons and synapses that make up the human brain. Inspired by the cognitive functions of the human brain that current computers cannot provide, neuromorphic devices have been widely investigated. However, current Complementary Metal-Oxide Semiconductor (CMOS)-based neuromorphic circuits simply connect artificial neurons and synapses without synergistic interactions, and the concomitant implementation of neurons and synapses still remains a challenge. To address these issues, a research team led by Professor Keon Jae Lee from the Department of Materials Science and Engineering implemented the biological working mechanisms of humans by introducing the neuron-synapse interactions in a single memory cell, rather than the conventional approach of electrically connecting artificial neuronal and synaptic devices.
Similar to commercial graphics cards, the artificial synaptic devices previously studied often used to accelerate parallel computations, which shows clear differences from the operational mechanisms of the human brain. The research team implemented the synergistic interactions between neurons and synapses in the neuromorphic memory device, emulating the mechanisms of the biological neural network. In addition, the developed neuromorphic device can replace complex CMOS neuron circuits with a single device, providing high scalability and cost efficiency.