Have you ever wondered what makes you intelligent? How are you able to see, hear, think, read, sing, solve problems, and perform any number of intelligent tasks?
Your brain learns a model of the world, and this model recreates the structure of everything you know. Everything you do and experience is based on this model. Intelligence is the ability to create this model of the world.
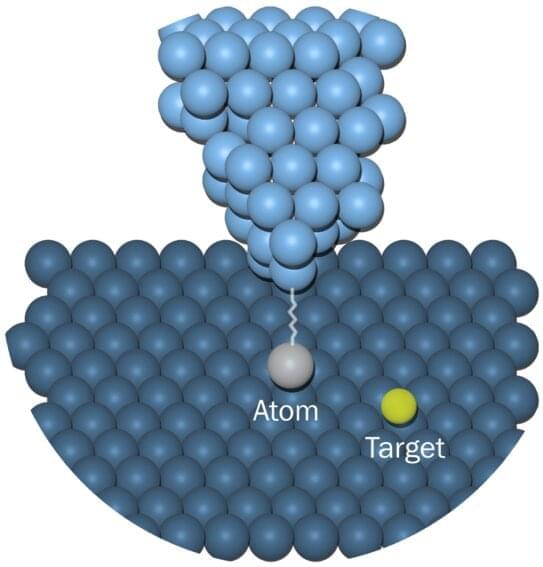
But how can a bunch of cells in your brain create a model of the world and everything in it? The Thousand Brains Theory provides an answer. Not only that, but it also provides a blueprint for how to build truly intelligent machines.
Visit https://numenta.com/ for more information.
Produced by Mind’s Eye Creative Studio: https://www.mec.co.za/
- — - -
Numenta is leading the new era of machine intelligence. Our deep experience in theoretical neuroscience research has led to tremendous discoveries on how the brain works. We have developed a framework called the Thousand Brains Theory of Intelligence that will be fundamental to advancing the state of artificial intelligence and machine learning. By applying this theory to existing deep learning systems, we are addressing today’s bottlenecks while enabling tomorrow’s applications.