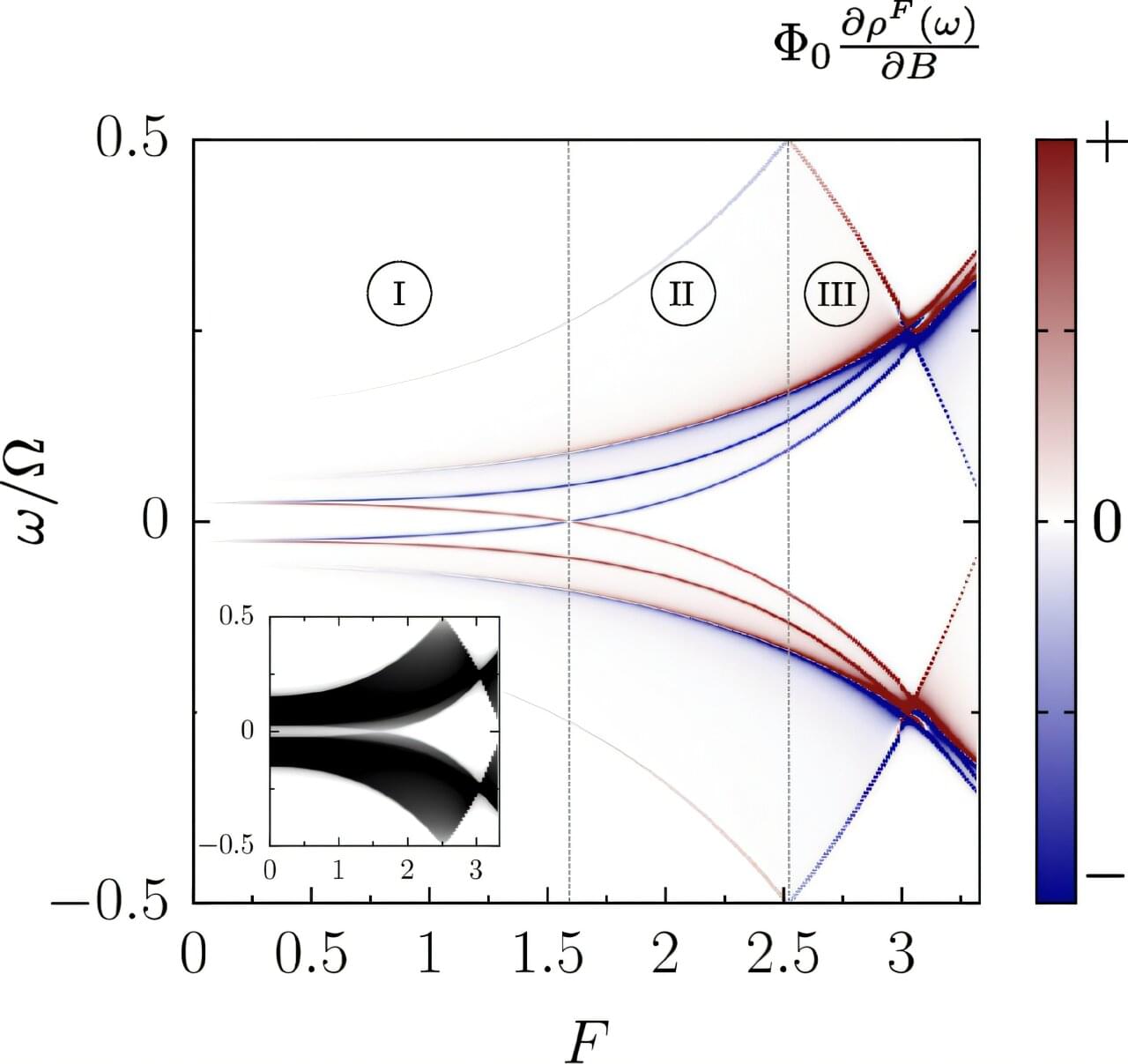
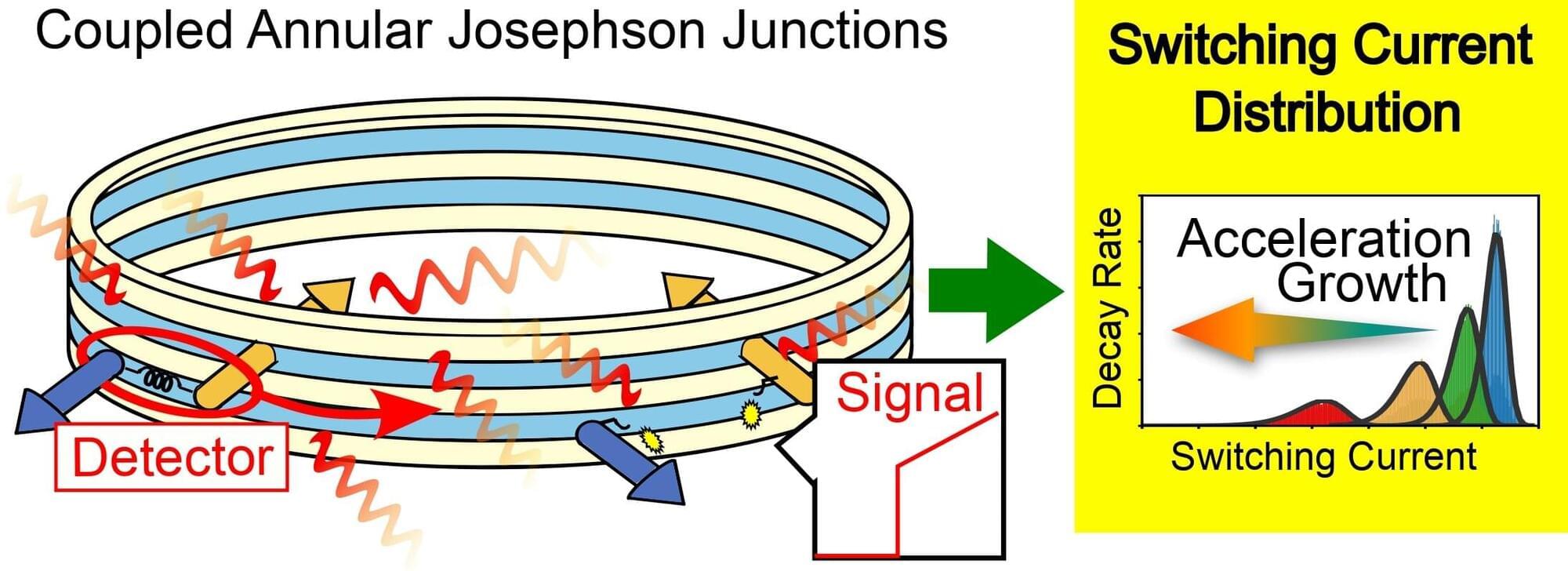
A British startup has installed New York City’s first quantum computer at a data center in Manhattan.
Oxford Quantum Circuits has placed the system at a data center run by Digital Realty Trust in the Google building in Chelsea, billing the technology to customers of the site as a means of running artificial intelligence programs faster and more efficiently. Oxford Quantum Chief Executive Officer Gerald Mullally said he expects his firm to spend tens of millions of dollars over three to five years, in part to buy Nvidia Corp. chips to integrate into it. He declined to provide the exact costs of the computer.