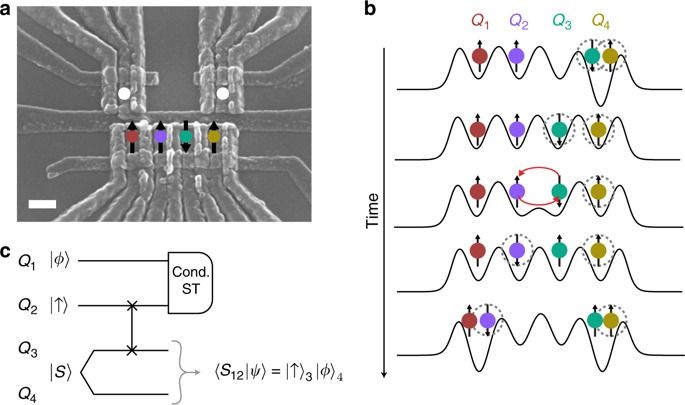
It is one of the most astonishing results of physics: when a complex system is left alone, it will return to its initial state with almost perfect precision. Gas particles, for example, chaotically swirling around in a container, will return almost exactly to their starting positions after some time. This “Poincaré Recurrence Theorem” is the foundation of modern chaos theory. For decades, scientists have investigated how this theorem can be applied to the world of quantum physics. Now, researchers at TU Wien (Vienna) have successfully demonstrated a kind of “Poincaré recurrence” in a multi-particle quantum system. The results have been published in the journal Science.
An Old Question, Revisited
At the end of the 19th century, the French scientist Henri Poincaré studied systems which cannot be fully analysed with perfect precision — for example solar systems consisting of many planets and asteroids, or gas particles, which keep bumping into each other. His surprising result: every state which is physically possible will be occupied by the system at some point — at least to a very good degree of approximation. If we just wait long enough, at some point all planets will form a straight line, just by coincidence. The gas particles in a box will create interesting patterns, or go back to the state in which they were when the experiment started.