A surprising property of how resonant photons interact with an absorbing medium has been uncovered by physicists in Canada. They say they have found that even photons passing straight through the medium energize atoms within it, causing atoms to spend nearly as much time in their excited states as those that have absorbed photons. They see their result as a challenge to theorists trying to describe how light interacts with matter quantum mechanically.
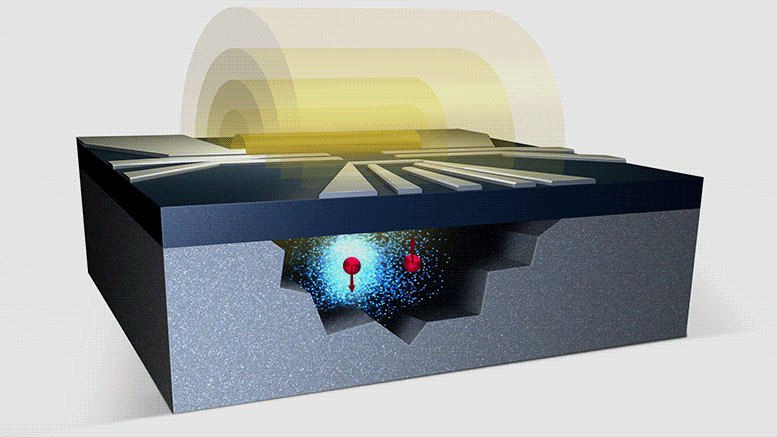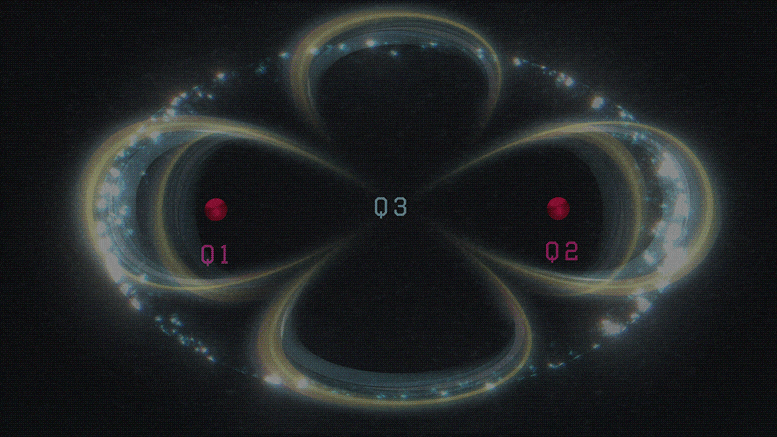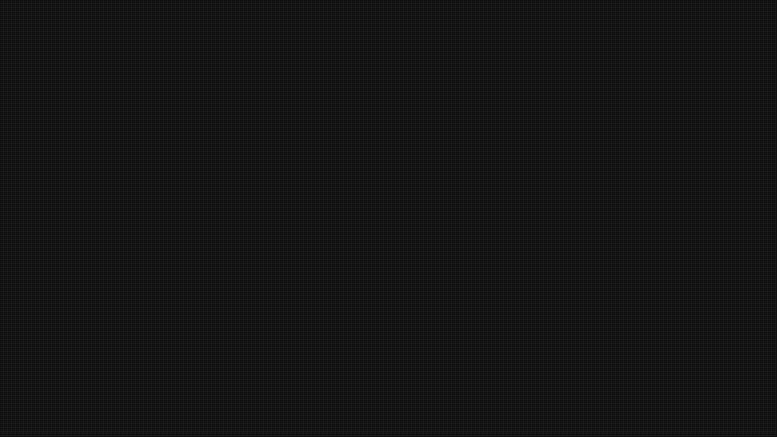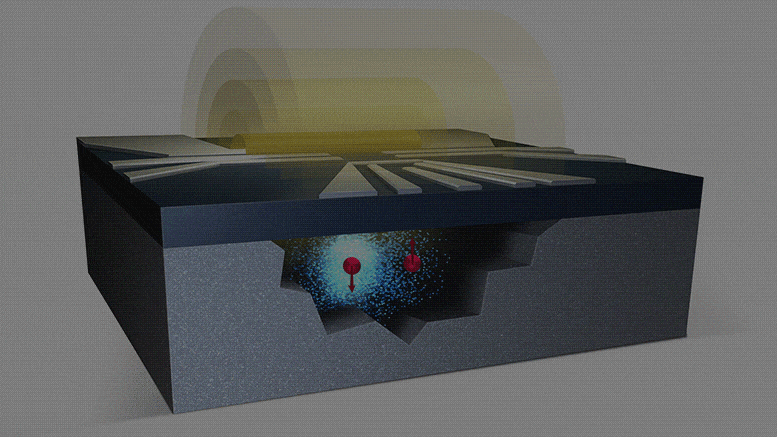
Aephraim Steinberg and colleagues at the University of Toronto made the discovery while investigating what happens to a beam of photons passing through a cloud of atoms when the photons’ frequency is equal to that of one of the atomic transitions. Intuitively, they say, it would be expected that those photons exciting atoms within the cloud would be absorbed and then at best re-emitted in a random direction. As such, the flux of photons coming from excited atoms that are detected in the forward direction would be miniscule.
Indeed, they point out, this idea that only absorbed, or “lost”, photons contribute to the excitation springs naturally from theory that tells us the total time atoms spend in the excited state is directly proportional to the number of photons that are lost.