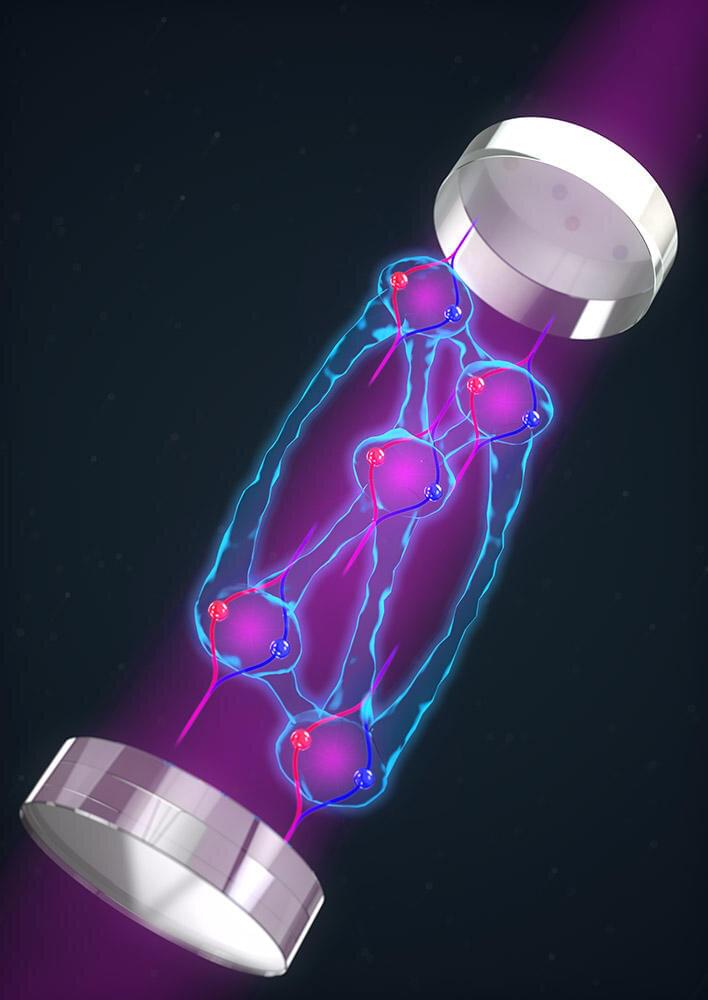
Just in time for Halloween’s spooky season, a quantum sensor now has double the spookiness by combining entanglement between atoms and delocalization of atoms.
Future quantum sensors will be able to provide more precise navigation, explore for needed natural resources, more precisely determine fundamental constants, look more precisely for dark matter, or maybe someday discover gravitational waves thanks to a team of researchers led by Fellow James K. Thompson from the Joint Institute for Laboratory Astrophysics (JILA) and the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST).
Thompson and his team have for the first time successfully combined two of the “spookiest” features of quantum mechanics: entanglement between atoms and delocalization of atoms. By doubling down on these “spooky” features, better quantum sensors can be made.
Full Story:
Metamorworks/iStock.
What are these ‘spooky’ features?