Water molecules that are close enough to “see’’ each other but far enough apart to be gas-like can undergo a quantum phase transition, a finding of relevance for making future water-based quantum devices.



The new algorithm could render mainstream encryption powerless within years.
Chinese researchers claim to have introduced a new code-breaking algorithm that, if successful, could render mainstream encryption powerless within years rather than decades.
The team, led by Professor Long Guilu of Tsinghua University, proclaimed that a modest quantum computer constructed with currently available technology could run their algorithm, South China Morning Post (SCMP) reported on Wednesday.
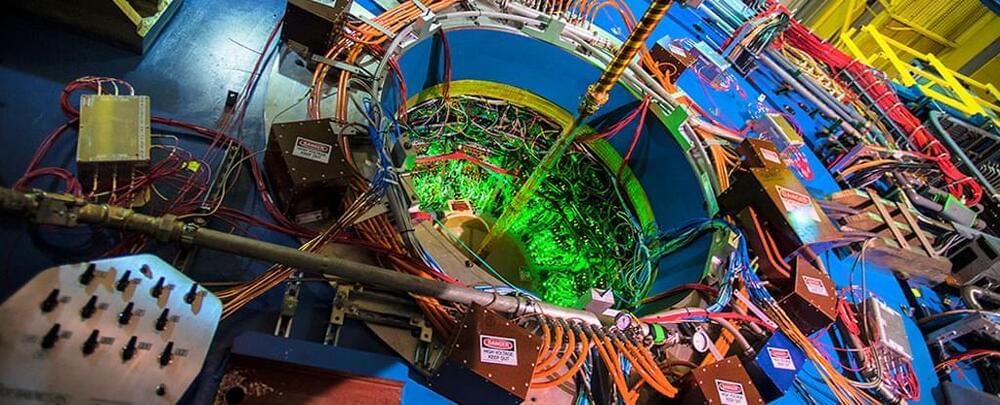

Silently churning away at the heart of every atom in the Universe is a swirling wind of particles that physics yearns to understand.
No probe, no microscope, and no X-ray machine can hope to make sense of the chaotic blur of quantum cogs whirring inside an atom, leaving physicists to theorize the best they can based on the debris of high-speed collisions inside particle colliders.
Researchers now have a new tool that is already providing them with a small glimpse into the protons and neutrons that form the nuclei of atoms, one based on the entanglement of particles produced as gold atoms brush past each other at speed.
The world of the very, very small is a wonderland of strangeness. Molecules, atoms, and their constituent particles did not readily reveal their secrets to the scientists that wrestled with the physics of atoms in the early 20th century. Drama, frustration, anger, puzzlement, and nervous breakdowns abounded, and it is hard for us now, a full century later, to understand what was at stake. What happened was a continuous process of worldview demolition. You might have to give up believing everything you thought to be true about something. In the case of the quantum physics pioneers, that meant changing their understanding about the rules that dictate how matter behaves.
In 1913, Bohr devised a model for the atom that looked somewhat like a solar system in miniature. Electrons moved around the atomic nucleus in circular orbits. Bohr added a few twists to his model — twists that gave them a set of weird and mysterious properties. The twists were necessary for Bohr’s model to have explanatory power — that is, for it to be able to describe the results of experimental measurements. For example, electrons’ orbits were fixed like railroad tracks around the nucleus. The electron could not be in between orbits, otherwise it could fall into the nucleus. Once it got to the lowest rung in the orbital ladder, an electron stayed there unless it jumped to a higher orbit.
Clarity about why this happened started to come with de Broglie’s idea that electrons can be seen both as particles and waves. This wave-particle duality of light and matter was startling, and Heisenberg’s uncertainty principle gave it precision. The more precisely you localize the particle, the less precisely you know how fast it moves. Heisenberg had his own theory of quantum mechanics, a complex device to compute the possible outcomes of experiments. It was beautiful but extremely hard to calculate things with.
Long before we had quantum computers, classical computers, or even calculus, an ancient Greek philosopher known as Zeno of Elea used thought experiments to probe apparent paradoxes. Zeno imagined an arrow flying through the air. At each instant of time, he reasoned, the arrow is stationary. If the arrow’s trajectory is entirely composed of stationary instants, how can the arrow ever move through space? Motion is impossible!
Zeno’s ancient arrow paradox has since evolved into a quantum thought experiment, “the quantum Zeno effect,” whereby we can freeze the state of quantum systems by continuously observing them. In the latest installment of our Quantum Paradoxes content series, I explain the quantum Zeno effect, and show how we can test it out using Qiskit on quantum computers. Read on to find out how this counterintuitive quantum freezing works, and how to create your own quantum freezer game — which even works with entangled qubits! All the code you need is in this Jupyter Notebook, and you’ll also find a detailed explanation in our latest Quantum Paradoxes video.
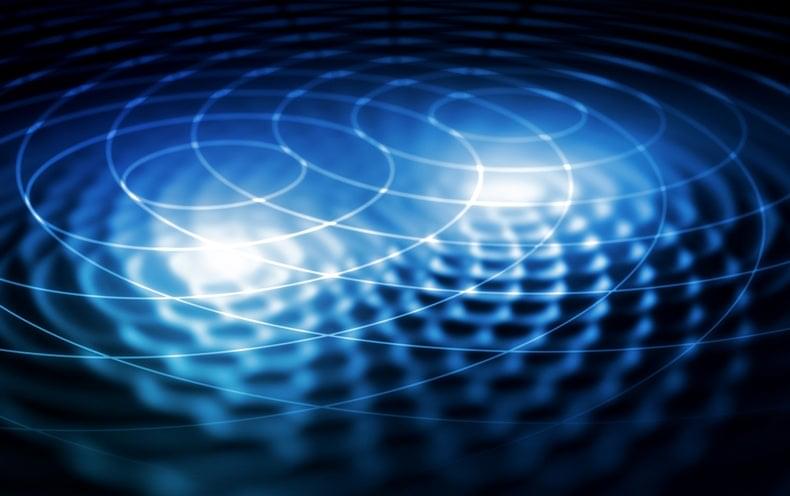

In a first, physicists have now found interference between two dissimilar subatomic particles. Researchers made the observation at the Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC), a colossal particle accelerator at Long Island’s Brookhaven National Laboratory. The finding broadens the way we understand entanglement and offers new opportunities to use it to study the subatomic world.
“With this new technique, we are able to measure the size and shape of the nucleus to about a tenth of a femtometer, a tenth of the size of an individual proton,” says James Daniel Brandenburg, a physicist at the Ohio State University and a member of RHIC’s STAR experiment, where the new phenomenon was seen. That’s 10 to 100 times more precise than previous measurements of high-energy atomic nuclei.
RHIC is designed to collide heavy ions, such as the nuclei of gold atoms. In this case, though, researchers were interested in near misses, not collisions. As the gold nuclei zing at near light speed through the collider, they create an electromagnetic field that generates photons. When two gold nuclei come close to one another but don’t collide, the photons may ping off the neighboring nuclei. These near misses used to be considered background noise, says STAR collaborator Raghav Kunnawalkam Elayavalli, a physicist at Vanderbilt University. But looking at the close-call events “opened up a whole new field of physics that initially was not accessible,” Kunnawalkam Elayavalli says.
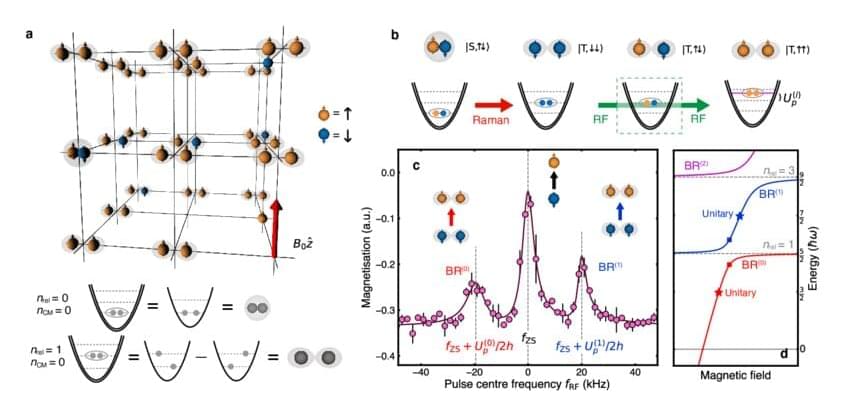
“Suppose you knew everything there was to know about a water molecule—the chemical formula, the bond angle, etc.,” says Joseph Thywissen, a professor in the Department of Physics and a member of the Centre for Quantum Information & Quantum Control at the University of Toronto.
“You might know everything about the molecule, but still not know there are waves on the ocean, much less how to surf them,” he says. “That’s because when you put a bunch of molecules together, they behave in a way you probably cannot anticipate.”
Thywissen is describing the concept in physics known as emergence: the relationship between the behavior and characteristics of individual particles and large numbers of those particles. He and his collaborators have taken a first step in understanding this transition from “one-to-many” particles by studying not one, not many, but two isolated, interacting particles, in this case potassium atoms.
Quantum computing expert and software engineer Anastasia Marchenkova discusses what’s next in quantum computing.

A breakthrough in quantum research – the first detection of excitons (electrically neutral quasiparticles) in a topological insulator has been achieved by an international team of scientists collaborating within the Würzburg-Dresden Cluster of Excellence ct.qmat. This discovery paves the way for a new generation of light-driven computer chips and quantum technologies. It was enabled thanks to smart material design in Würzburg, the birthplace of topological insulators. The findings have been published in the journal Nature Communications.
<em>Nature Communications</em> is a peer-reviewed, open-access, multidisciplinary, scientific journal published by Nature Portfolio. It covers the natural sciences, including physics, biology, chemistry, medicine, and earth sciences. It began publishing in 2010 and has editorial offices in London, Berlin, New York City, and Shanghai.