A new study scanned 22,484 pornography sites and found them riddled with trackers from major technology companies.



Early this morning, I was asked this question at Quora. It’s a pretty basic request of network administrators, including parents, schools and anyone who administers a public, sensitive or legally exposed WiFi hot spot.
Is there a quick and easy way to view, log, or otherwise monitor the web sites visited by people on your home or office network?
Yes. It’s free and and it is pretty easy to do.
It gets a bit trickier, if the individual on your network is using a VPN service that they have configured on their device.[1] A VPN does not stop you from logging their browsing, but all of their activity will point to the VPN address instead of the site that they are actually visiting. In that case, there is another way to monitor their activity. See note #1, below.
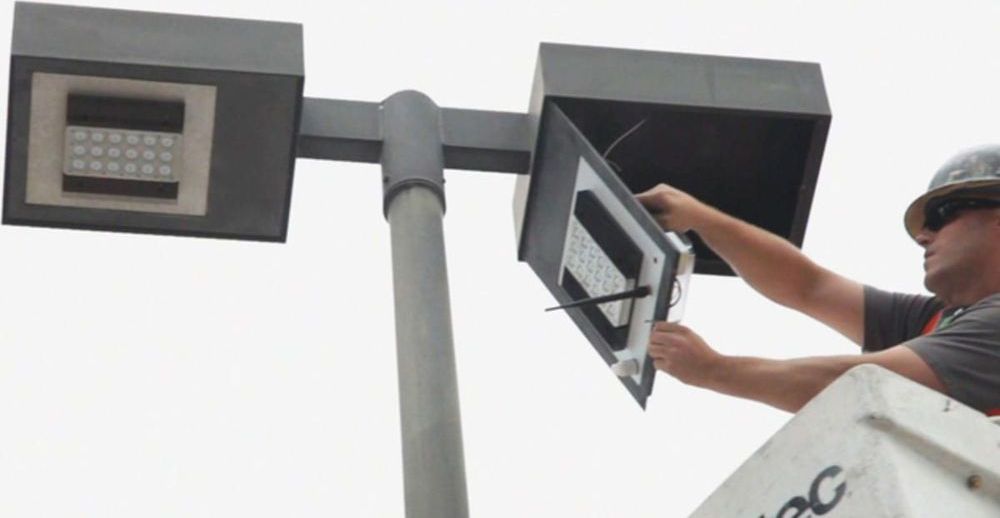

While more people and places are switching to energy-saving LED light bulbs, a California company has found a way to turn them into smart networks that can collect and feed data. However, the new technological opportunities are also raising privacy concerns, reports CBS News’ Bill Whitaker.
For example, should you find yourself in terminal “B” at Newark airport, look up. Those aren’t just new lights. They’re smart lights — a sophisticated array of LED fixtures with built-in sensors and cameras connected over a wireless network. They monitor security and the flow of foot traffic.
“Newark’s primarily interested in energy saving,” said Hugh Martin, president of Sensity, the Silicon Valley company that developed the smart lights at Newark and also a parking garage in San Jose.
Biometrics is defined as the measurement of life signs. One of the main aims of current security research is to acquire biometric data of sufficient detail and reliability for verification or identification of individuals.
A newly developed electric-field sensing technology with unprecedented sensitivity and noise immunity can passively acquire physiological signals in an electrically noisy environment.
Robert Prance

Transistors are now the size of atoms.
Scary but real.
The NSA is working on a computer system that can predict what people are thinking.
“Think of 2001: A Space Odyssey and the most memorable character, HAL 9000, having a conversation with David. We are essentially building this system. We are building HAL. The system can answer the question, ‘What does X think about Y?’”

Spotlight: FBI Pushes Forward with Massive Biometric Database Despite Privacy Risks.
The Electronic Privacy Information Center (EPIC) focuses public attention on emerging civil liberties, privacy, First Amendment issues and works to promote the Public Voice in decisions concerning the future of the Internet.
Biology Biometrics Chemistry/Toxicology Environmental Fire & Explosives Firearms & Toolmarks Questioned Documents
Technology/Digital Evidence Trace Evidence Other
Forensic databases — biology name sub

