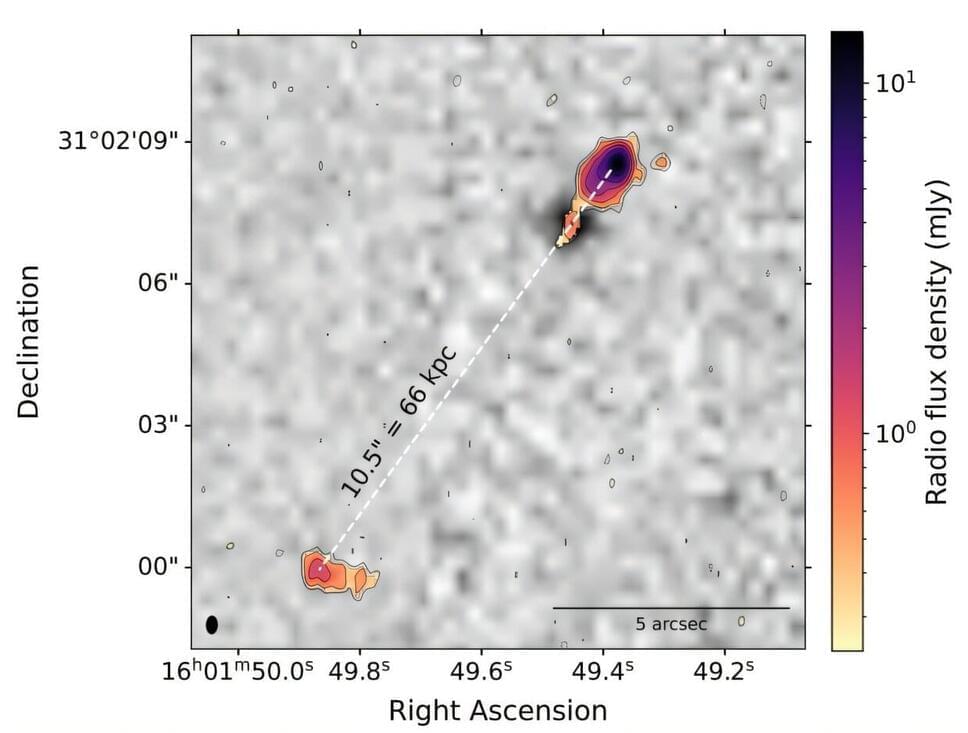
The newly found ORC, designated ORC J0219–0505, was discovered in data from the MIGHTEE survey conducted by the MeerKAT radio telescope located in the Meerkat National Park in the Northern Cape of South Africa. The 371,600 light-year-wide ORC seems to be associated with the elliptical galaxy WISEA J021912.43–050501.8. It has features that seem to set it apart from other ORCs, including the fact that it appears fainter and that details of its structure reveal it leans to one side.
“Odd Radio Circles: Circles of radio emission found around distant galaxies that we still don’t understand,” lead researcher and Western Sydney University astronomer Ray Norris told Space.com. “It’s a completely unexpected discovery, not predicted by the physics we already know, and therefore revealing a gap in our knowledge.
So we hope these will tell us something new about how galaxies form and interact.