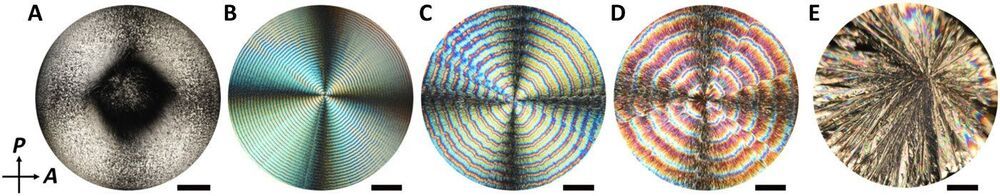
Chemical organization in reaction-diffusion systems offer a strategy to generate materials with ordered morphologies and architecture. Periodic structures can be formed using molecules or nanoparticles. An emerging frontier in materials science aims to combine nanoparticles and molecules. In a new report on Science Advances, Amanda J. Ackroyd and a team of scientists in chemistry, physics and nanomaterials in Canada, Hungary and the U.S. noted how solvent evaporation from a suspension of cellulose nanocrystals (CNCs) and L-(+)-tartaric acid [abbreviated L-(+)-TA] caused the phase separation of precipitation to result in the rhythmic alteration of CNC-rich, L-(+)-TA rings. The CNC-rich regions maintained a cholesteric structure, while the L-(+)-TA-rich bands formed via radially elongated bundles to expand the knowledge of self-organizing reaction-diffusion systems and offer a strategy to design self-organizing materials.
Chemical organization
The process of self-organization and self-assembly occurs universally in non-equilibrium systems of living matter, geochemical environments, materials science and in industry. Existing experiments that lead to periodic structures can be divided into two groups including the classical Liesegang-type experiments and chemical organization via periodic precipitation to generate materials with ordered morphologies and structural hierarchy. In this work, Ackroyd et al. developed a strategy for solvent evaporation to phase separate an aqueous solution of tartaric acid/cellulose nanocrystals [L-(+)-TA/CNC or TA/CNC] for its subsequent precipitation to result in a rhythmic alternation of CNC-rich or CNC-depleted ring-type regions. The team developed a kinetic model which agreed with the experimental results quantitatively. The work expands the range of self-organizing reaction-diffusion systems to pave the way for periodically structured functional materials.