A physics paper proposes neither you nor the world around you are real.
Category: physics – Page 256
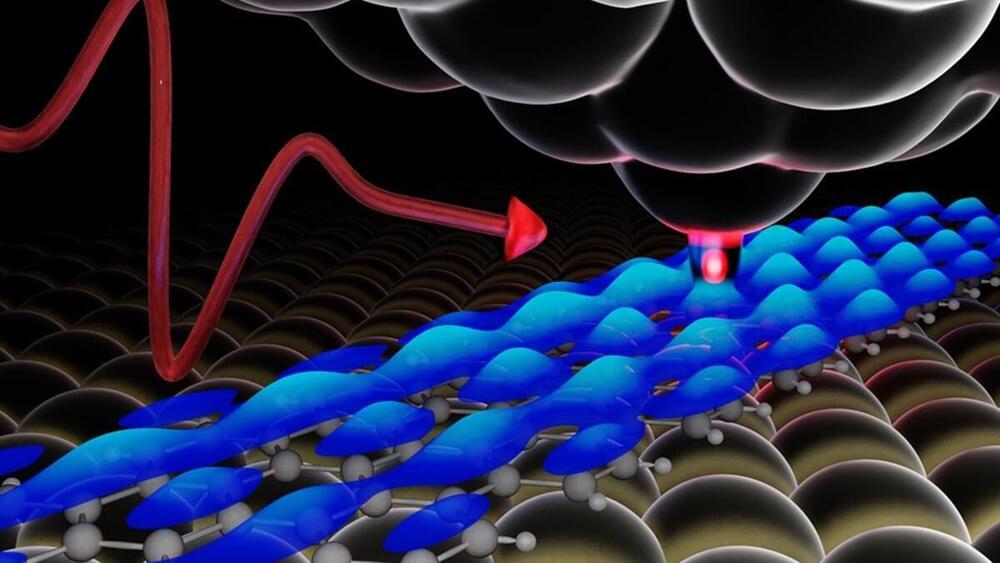
Lightwave-driven scanning tunneling spectroscopy of atomically precise graphene nanoribbons
When physicist Tyler Cocker joined Michigan State University in 2018, he had a clear goal: build a powerful microscope that would be the first of its kind in the United States.
Having accomplished that, it was time to put the microscope to work.
“We knew we had to do something useful,” said Cocker, Jerry Cowen Endowed Chair in Experimental Physics in the College of Natural Science’s Department of Physics and Astronomy. “We’ve got the nicest microscope in the country. We should use this to our advantage.”

Blowing Up the Universe: BICEP3 Tightens the Bounds on Cosmic Inflation
A new analysis of the South Pole-based telescope’s cosmic microwave background observations has all but ruled out several popular models of inflation.
Physicists looking for signs of primordial gravitational waves by sifting through the earliest light in the cosmos – the cosmic microwave background (CMB) – have reported their findings: still nothing.
But far from being a dud, the latest results from the BICEP3 experiment at the South Pole have tightened the bounds on models of cosmic inflation, a process that in theory explains several perplexing features of our universe and which should have produced gravitational waves shortly after the universe began.
4 of Physics’ (Other) Greatest Mysteries
Physicists are interested in the big questions like “Where did we come from?” and “What is all this stuff?”. But the answers to some of these questions, just lead to more questions.
Hosted by: Michael Aranda.
SciShow is on TikTok! Check us out at https://www.tiktok.com/@scishow.
———
Support SciShow by becoming a patron on Patreon: https://www.patreon.com/scishow.
———
Huge thanks go to the following Patreon supporters for helping us keep SciShow free for everyone forever:
Alisa Sherbow, Silas Emrys, Chris Peters, Adam Brainard, Dr. Melvin Sanicas, Melida Williams, Jeremy Mysliwiec, charles george, Tom Mosner, Christopher R Boucher, Alex Hackman, Piya Shedden, GrowingViolet, Nazara, Matt Curls, Ash, Eric Jensen, Jason A Saslow, Kevin Bealer, Sam Lutfi, James Knight, Christoph Schwanke, Bryan Cloer, Jeffrey Mckishen.
———
Looking for SciShow elsewhere on the internet?
SciShow Tangents Podcast: http://www.scishowtangents.org.
Facebook: http://www.facebook.com/scishow.
Twitter: http://www.twitter.com/scishow.
Instagram: http://instagram.com/thescishow.
———
https://www.space.com/25075-cosmic-inflation-universe-expans…aphic.html.
Why we need inflation: https://www.space.com/42202-why-we-need-cosmic-inflation.html.
https://www.space.com/42261-how-did-inflation-happen-anyway.html.
Inflation review: https://arxiv.org/pdf/hep-ph/0304257.pdf.
Evidence for inflation https://www.forbes.com/sites/startswithabang/2019/05/11/ask-…d0a2891d07
GW detection: https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1475-7516/2021/01/012
Penrose cyclic cosmology: https://aip.scitation.org/doi/abs/10.1063/1.4727997?journalCode=apc.
New evidence for cyclic universe claimed by Roger Penrose and colleagues
Fine-tuning:
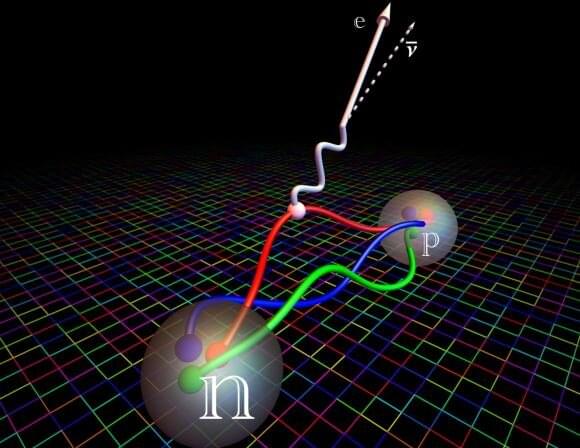
Understanding the early universe depends on estimating the lifespan of neutrons
When we look into the night sky, we see the universe as it once was. We know that in the past, the universe was once warmer and denser than it is now. When we look deep enough into the sky, we see the microwave remnant of the big bang known as the cosmic microwave background. That marks the limit of what we can see. It marks the extent of the observable universe from our vantage point.
The cosmic background we observe comes from a time when the universe was already about 380,000 years old. We can’t directly observe what happened before that. Much of the earlier period is fairly well understood given what we know about physics, but the earliest moments of the big bang remain a bit of a mystery. According to the standard model, the earliest moments of the universe were so hot and dense that even the fundamental forces of the universe acted differently than they do now. To better understand the big bang, we need to better understand these forces.
One of the more difficult forces to understand is the weak force. Unlike more familiar forces such as gravity and electromagnetism, the weak is mostly seen through its effect of radioactive decay. So we can study the weak force by measuring the rate at which things decay. But there’s a problem when it comes to neutrons.
How to See Black Holes + Kugelblitz Challenge Answer | Space Time | PBS Digital Studios
Viewers like you help make PBS (Thank you 😃). Support your local PBS Member Station here: https://to.pbs.org/DonateSPACE
Find out how scientists are mapping the black holes throughout the Milky Way and beyond as well as the answer to the Escape the Kugelblitz Challenge Question. Were you able to save humanity?
Get your own Space Time tshirt at http://bit.ly/1QlzoBi.
Tweet at us! @pbsspacetime.
Facebook: facebook.com/pbsspacetime.
Email us! pbsspacetime [at] gmail [dot] com.
Comment on Reddit: http://www.reddit.com/r/pbsspacetime.
Help translate our videos! https://www.youtube.com/timedtext_cs_panel?tab=2&c=UC7_gcs09iThXybpVgjHZ_7g.
Quasars, X-ray Binaries and Supermassive voids at the center of our galaxies … black holes take many forms. In this episode Matt tells us what these different types of black holes are and how scientists are using VLBI, Very Long Baseline Interferometry, to map the different black holes throughout the known universe.
Resolving Microlensing Events with Triggered VLBI
Should We Build a Dyson Sphere? | Space Time | PBS Digital Studios
To check out any of the lectures available from Great Courses Plus go to http://ow.ly/Y8lm303oKJe.
SXSW Panel Picker Sign-up: https://panelpicker.sxsw.com/vote/68148
Get your own Space Time tshirt at http://bit.ly/1QlzoBi.
Tweet at us! @pbsspacetime.
Facebook: facebook.com/pbsspacetime.
Email us! pbsspacetime [at] gmail [dot] com.
Comment on Reddit: http://www.reddit.com/r/pbsspacetime.
Support us on Patreon! http://www.patreon.com/pbsspacetime.
Help translate our videos! https://www.youtube.com/timedtext_cs_panel?tab=2&c=UC7_gcs09iThXybpVgjHZ_7g.
The Kepler telescope recently noticed a strange partial eclipse that some have speculated could be a Dyson Sphere. Are Dyson Sphere’s possible? Are they practical? What other alternatives to futuristic energy capture do we have to choose from? Why not a kugelblitz — a swarm of black hole powered engines?
Previous Episode.
Joscha Bach — Reconciling consciousness with physicalism
Speaking at the 6th International FQXi Conference, “Mind Matters: Intelligence and Agency in the Physical World.”
The Foundational Questions Institute (FQXi) catalyzes, supports, and disseminates research on questions at the foundations of physics and cosmology, particularly new frontiers and innovative ideas integral to a deep understanding of reality but unlikely to be supported by conventional funding sources.
Please join us at www.fqxi.org!

The technology we (or aliens) need for long-distance interstellar travel
Solutions to the problems of interstellar travel
Given the insane scale of interstellar distances, how might we extrapolate from the physics we do understand to envisioning possible ways that aliens (or us in the future) could cross the cosmic void? There are a few possible solutions to the problem of interstellar travel.
