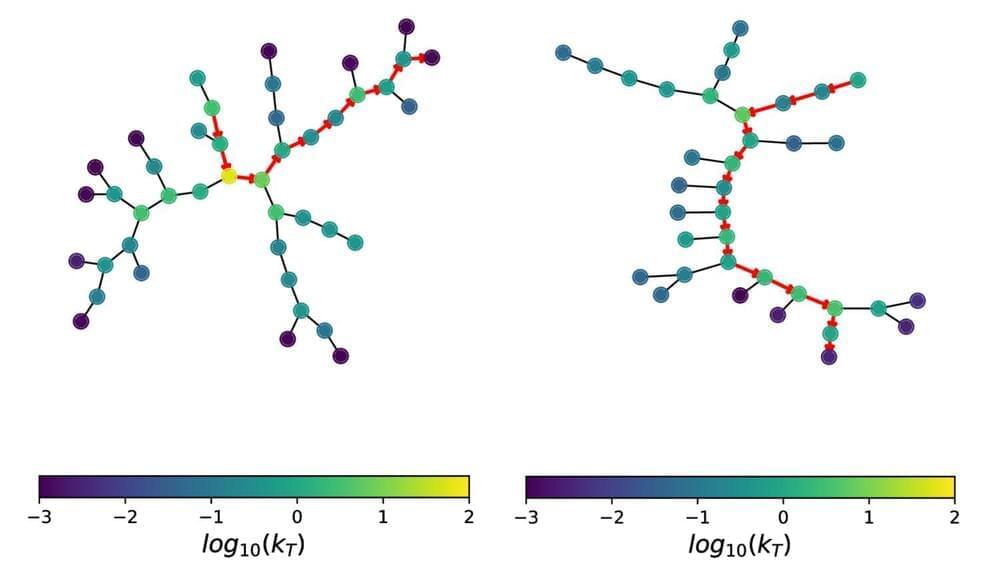
What happens when – instead of recording a single particle track or energy deposit in your detector – you see a complex collection of many particles, with many tracks, that leaves a large amount of energy in your calorimeters? Then congratulations: you’ve recorded a “jet”! Jets are the complicated experimental signatures left behind by showers of strongly-interacting quarks and gluons. By studying the internal energy flow of a jet – also known as the “jet substructure” – physicists can learn about the kind of particle that created it. For instance, several hypothesised new particles could decay into heavy Standard Model particles at extremely high (or “boosted”) energies. These particles could then decay into multiple quarks, leaving behind “boosted”, multi-pronged jets in the ATLAS experiment. Physicists use “taggers” to distinguish these jets from background jets created by single quarks and gluons. The type of quarks produced in the jet can also give extra information about the original particle. For example, Higgs bosons and top quarks often decay to b-quarks – seen in ATLAS as “b-jets” – which can be distinguished from other kinds of jets using the long lifetime of the B-hadron. The complexity of jets naturally lends itself to Artificial Intelligence (AI) algorithms, which are able to efficiently distil large amounts of information into accurate decisions. AI algorithms have been a regular part of ATLAS data analysis for several years, with ATLAS physicists continuously pushing these tools to new limits. This week, ATLAS physicists presented four exciting new results about jet tagging using AI algorithms at the BOOST 2023 conference held at Lawrence Berkeley National Lab (USA). Figure 1: The graphs showing the full declustering shower development and the primary Lund jet plane in red are shown in (left) for a jet originating from a W-boson and in (right) for a jet originating from a light-quark. (Image: ATLAS Collaboration/CERN) Artificial intelligence is revolutionising how ATLAS researchers identify – or ‘tag’ – what types of particles create jets in the experiment. Two results showcased new ATLAS taggers used for identifying jets coming from a boosted W-boson decay as opposed to background jets originating from light quarks and gluons. Typically, AI algorithms are trained on “high-level” jet substructure information recorded by the ATLAS inner detector and calorimeters – such as the jet mass, energy correlation ratios and jet splitting scales. These new studies instead use “low-level” information from these same detectors – such as the direct kinematic properties of a jet’s constituents or the novel two-dimensional parameterisation of radiation within a jet (known as the “Lund Jet plane”), built from the jet’s constituents and using graphs based on the particle-shower development (see Figure 1). These new taggers made it possible to separate the shape of signal and background far more effectively than any high-level taggers could do alone (see Figure 2). In particular, the Lund Jet plane-based tagger outperforms the other methods, by using the same input to the AI networks but in a different format inspired by the physics of the jet shower development. A similar evolution was followed for the development of a new boosted Higgs tagger, which identifies jets originating from boosted Higgs bosons decaying hadronically to two b-quarks or c-quarks. It also uses low-level information – in this case, tracks reconstructed from the inner detector associated with the single jet containing the Higgs boson decays. This new tagger is the most performant tagger to date, and represents a factor of 1.6 to 2.5 improvement, at a 50% boosted Higgs signal efficiency, over the previous version of the tagger, which used high-level information from the jet and b/c-quark decays as input for a neural network (see Figure 3). Figure 2: Signal efficiency as a function of the background rejection for the different W-boson taggers: one is based on the Lund jet plane, while the others use unordered sets of particles or graphs with additional structure. (Image: ATLAS Collaboration/CERN) Figure 3: Top and multijet rejections as a function of the H→bb signal efficiency. Performance of the new boosted Higgs tagger is compared to the previous taggers using high-level information from the jet b-quark decays. (Image: ATLAS Collaboration/CERN) Finally, ATLAS researchers presented two new taggers that aim to differentiate between jets originating from quarks and those originating from gluons. One tagger looked at the charged-particle constituent multiplicity of the jets being tagged, while the other combined several jet kinematic and jet substructure variables using a Boosted Decision Tree. Physicists compared the performance of these quark/gluon taggers; Figure 4 shows the rejection of gluon jets as a function of quark selection efficiency in simulation. Several studies of Standard-Model processes – including vector boson fusion – and new physics searches with quark-rich signals could greatly benefit from these taggers. However, in order for them to be used in analyses, additional corrections on the signal efficiency and background rejection need to be applied to bring the performance of the taggers in data and simulation to be the same. Researchers measured both the efficiency and rejection rates in Run-2 data for these taggers, and found good agreement between the measured data and predictions; therefore, only small corrections are needed. The excellent performance of these new jet taggers does not come without questions. Crucially, how can researchers interpret what the machine-learning models learned? And why do more complex architectures show a stronger dependence on the modelling of simulated physics processes used for the training, as shown in the two W-tagging studies? Challenges aside, these taggers set an outstanding baseline for analysing LHC Run-3 data. Given the current strides being made in machine learning, its continued application to particle physics will hopefully increase the understanding of jets and revolutionise the ATLAS physics programme in the years to come. Figure 4: Signal efficiency as a function of the background rejection for different quark taggers. The use of machine learning (BDT) results in an improved performance. (Image: ATLAS Collaboration/CERN) Learn more Tagging boosted W bosons with the Lund jet plane in ATLAS (ATL-PHYS-PUB-2023–017) Constituent-based W-boson tagging with the ATLAS detector (ATL-PHYS-PUB-2023–020) Transformer Neural Networks for Identifying Boosted Higgs Bosons decaying into bb and cc in ATLAS (ATL-PHYS-PUB-2023–021) Performance and calibration of quark/gluon-jet taggers using 140 fb−1 of proton–proton collisions at 13 TeV with the ATLAS detector (JETM-2020–02) Comparison of ML algorithms for boosted W boson tagging (JETM-2023–003) Summary of new ATLAS results from BOOST 2023, ATLAS News, 31 July 2023.