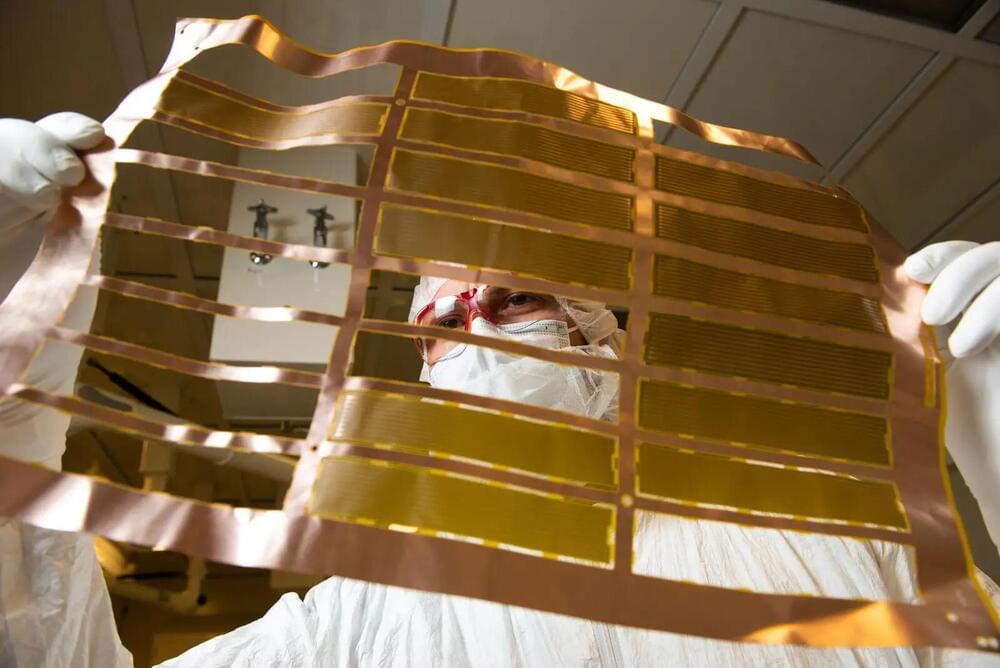
Chinese researchers are working on ways to develop their own semiconductor lithography process to compete with ASML.
Researchers at Tsinghua University are working to bring microchip production to China to bypass US sanctions, reports the South China Morning Post.
Using a new method called steady-state microbunching (SSMB), the team believes this new technique could be employed to mass produce high-quality microchips and reduce China’s dependence on lithography systems from the likes of industry giants like Advanced Semiconductor Materials Lithography (ASML).