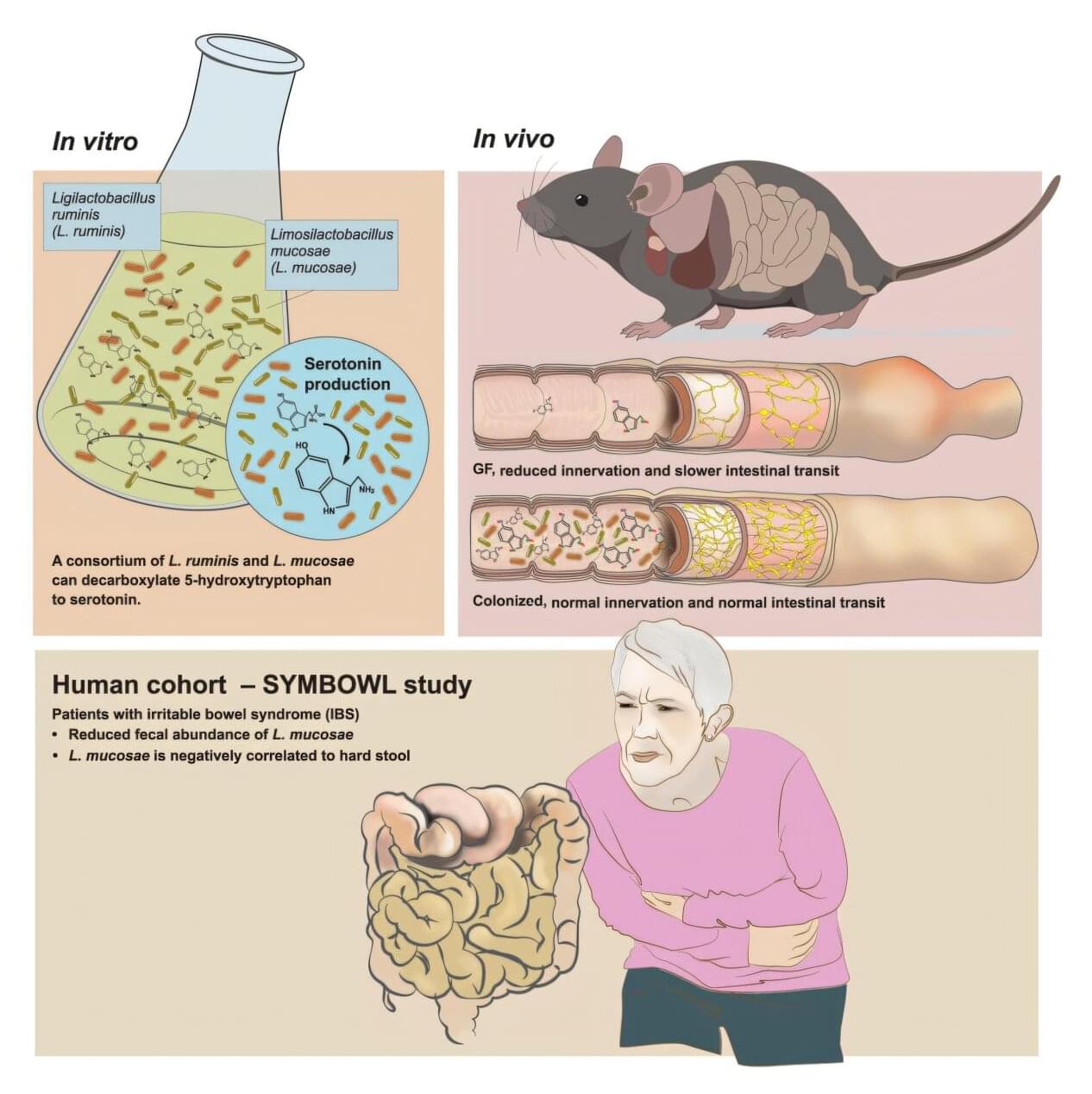
Research from the University of Gothenburg, Sweden, clarifies the complex interaction between gut bacteria and irritable bowel syndrome (IBS). Experiments demonstrate that gut bacteria can produce the important substance serotonin. The finding may lead to future treatments.
IBS is a common gastrointestinal disorder, more common in women, with symptoms such as abdominal pain, constipation or diarrhea. The cause of the disease is not clear, but the intestinal environment, including the gut microbiota and serotonin, appear to be important factors.
Serotonin is best known as a neurotransmitter in the brain, but over 90% of the body’s serotonin is produced in the gut, where it controls bowel movements via the enteric nervous system, sometimes called the “gut–brain.”