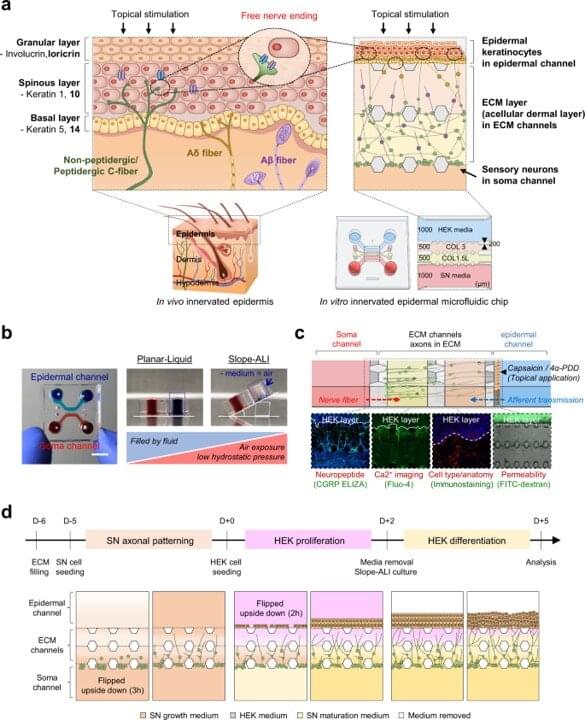
University of California, San Diego study suggests new way to personalize mental health care.
Major depressive disorder affects 16.1 million adults in the United States and costs $210 billion annually. While the primary symptoms of depression are psychological, scientists and doctors have come to understand that depression is a complex disease with physical effects throughout the body. For example, measuring markers of cellular metabolism has become an important approach to studying mental illnesses and developing new ways to diagnose, treat, and prevent them.
Study links cellular metabolism with depression.