The new JMG Clips channel for sleep!
My Patreon Page:
https://www.patreon.com/johnmichaelgodier.
My Event Horizon Channel:
The new JMG Clips channel for sleep!
My Patreon Page:
https://www.patreon.com/johnmichaelgodier.
My Event Horizon Channel:
Artificial intelligence (AI) systems are computational models that can learn to identify patterns in data, make accurate predictions or generate content (e.g., texts, images, videos or sound recordings). These models can reliably complete various tasks and are now also used to carry out research rooted in different fields.
Over the past few decades, some AI models have proved promising for the early diagnosis and study of specific diseases or neuropsychiatric conditions. For instance, by analyzing large amounts of brain scans collected using a noninvasive technique known as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), AI could uncover patterns associated with tumors, strokes and neurodegenerative diseases, which could help to diagnose these conditions.
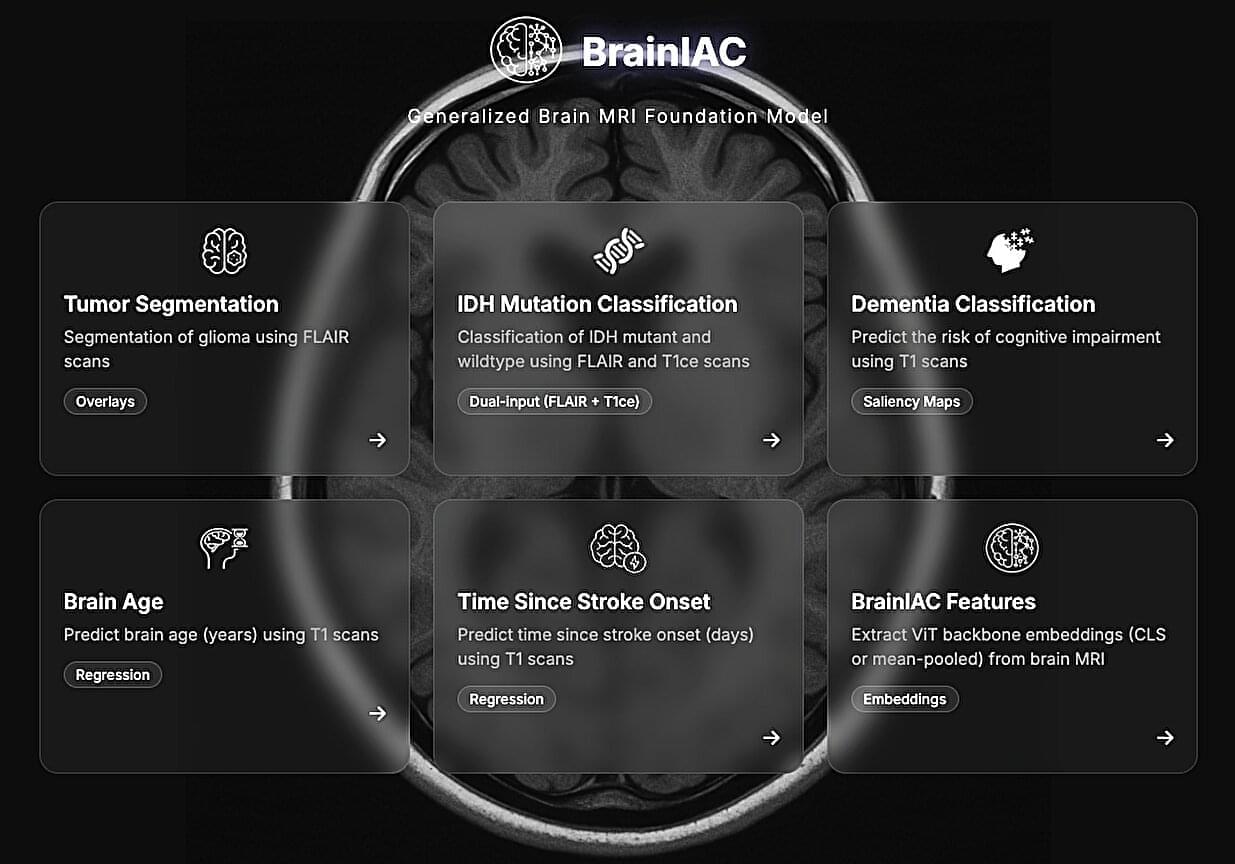
Researchers at Mass General Brigham, Harvard Medical School and other institutes recently developed Brain Imaging Adaptive Core (BrainIAC), a large AI system pre-trained on a vast pool of MRI data that could be adapted to tackle different tasks. This foundation model, presented in a paper published in Nature Neuroscience, was found to outperform many models that were trained to complete specific medical or neuroscience-related tasks.

When it comes to health, some of our animal neighbors have extraordinary advantages. Ostriches, for example, are highly resistant to viruses, while sharks rarely develop cancer. And species like naked mole rats and bowhead whales live for astonishingly long periods of time, decades and centuries, respectively.
Researchers are now starting to understand why another species—the golden spiny mouse—seems to be unhindered by the negative health effects that typically accompany aging.
Reporting in Science Advances, researchers at Yale School of Medicine (YSM) have begun to uncover how this wild mouse, native to rocky deserts in the Middle East, resists physical, cognitive, and immunological decline while living six to seven times longer than other wild mice.
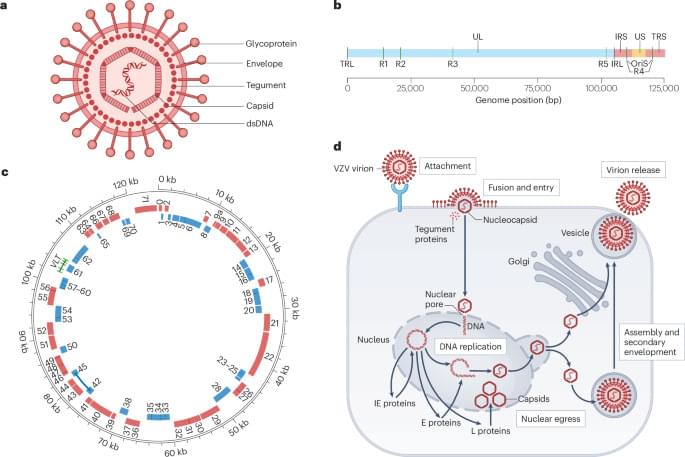
Varicella zoster virus (VZV) infection causes varicella and herpes zoster and, rarely, severe central nervous system (CNS) complications, including encephalitis. Ogunjimi et al. review the evidence linking herpes zoster with stroke and dementia, summarize innate and adaptive immune responses to VZV-related CNS disease, and debate the consequences of vaccination.
Unlike treatments that focus on removing plaques that have already formed, levetiracetam works differently. It blocks the production of toxic amyloid beta peptides in the first place.
In this video we look into one of the developing areas of computing: wetware. Most specifically neuromorphic computing, a science which uses actual neurons on chips.
We talk to Cortical labs, the company that developed the pong-playing dish brain, and professor Thomas Hartung to understand what the benefits of this technology are.
🚀 Discover deep-dive engineering stories and breakthrough technologies on Interesting Engineering:
/ @interestingengineeringie.
🪖 Explore military innovation and defense technology on Military Mechanics:
/ @militarymechanicsie.
🔔 Subscribe to IE Brief for daily updates on the discoveries, technologies, and global developments shaping our world:
/ @ienews-brief.
🔬 Complex tech, simply explained. Discover how the world works with IE Explains: / @ie-explains

An early-life anxious temperament (AT) is a risk factor for the development of anxiety, depression, and comorbid substance abuse. We validated a nonhuman primate model of early-life AT and identified the dorsal amygdala as a core component of AT’s neural circuit. Here, we combine RNA sequencing, viral-vector gene manipulation, functional brain imaging, and behavioral phenotyping to uncover AT’s molecular substrates.
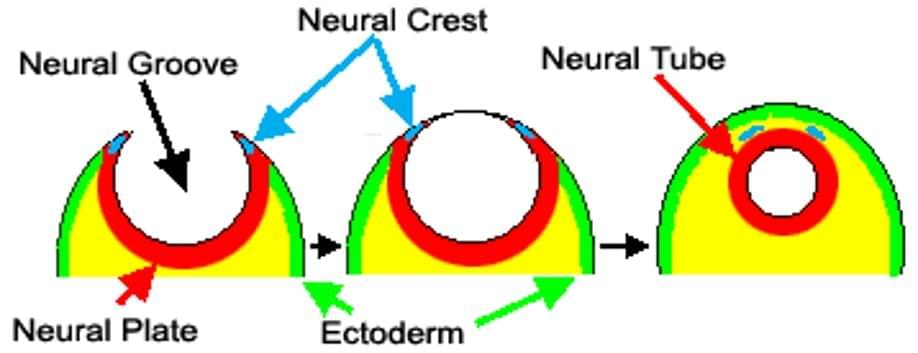
Neural development is the complex, lifelong process of forming and refining the nervous system, beginning with embryonic neurulation (neural tube formation) and continuing through maturation and remodeling.
The brain starts forming weeks after conception, with development continuing through childhood and adolescence.
Signaling molecules like Sonic hedgehog (SHH) and TGF-beta regulate this process.
Brain architecture is shaped by experiences and environmental factors.
Disruptions can cause neural tube defects like spina bifida.
Fore more information, click on the link below: https://sciencemission.com/Neural-Development
Sciencenewshighlights ScienceMission

A Dartmouth study challenges the conventional view that the amygdala—the two-sided structure deep in the brain involved in emotion, learning, and decision making—is simply the brain’s primitive “fear center,” reflexively driving us to avoid the things we fear, from high places and tight spaces to spiders and large crowds. The researchers report in Nature Communications that the amygdala is far more complex, acting as a sophisticated arbiter to help the brain choose between competing strategies for learning and decision-making.
“Historically, the amygdala has been studied from the perspective of fear learning, and it has been generalized to reward learning,” says Jae Hyung Woo, a Ph.D. candidate in the psychological and brain sciences and the study’s first author. “Our main hypothesis was that it must have other functions given its extensive connections to the rest of the brain.”