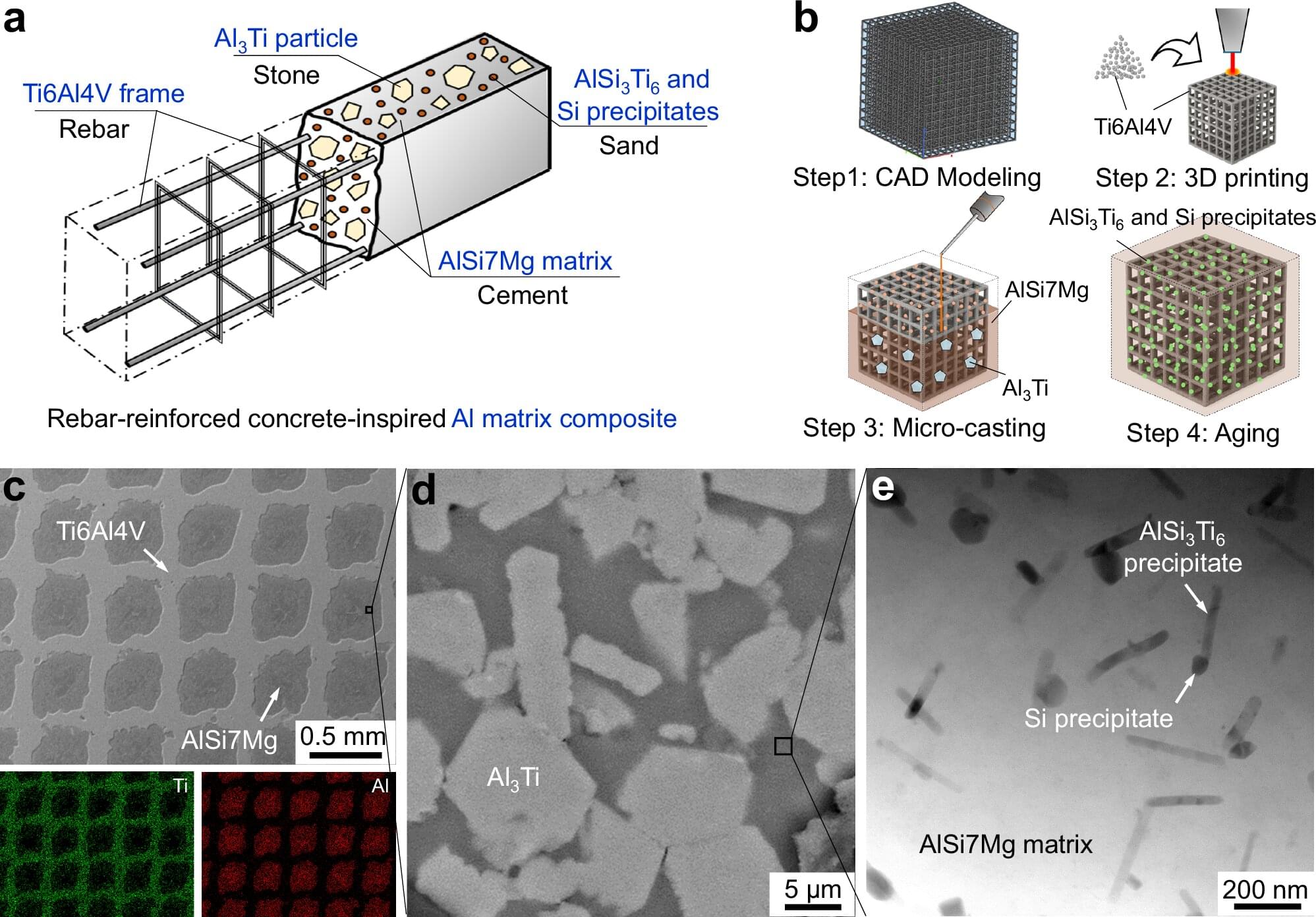
A research team from NIMS, Tohoku University and AIST has developed a new technique for controlling the nanostructures and magnetic domain structures of iron-based soft amorphous ribbons, achieving more than a 50% reduction in core loss compared with the initial amorphous material.
The developed material exhibits particularly high performance in the high-frequency range of several tens of kilohertz—required for next-generation, high-frequency transformers and EV drive power supply circuits. This breakthrough is expected to contribute to the advancement of these technologies, development of more energy-efficient electric machines and progress toward carbon neutrality.
The research is published in Nature Communications.