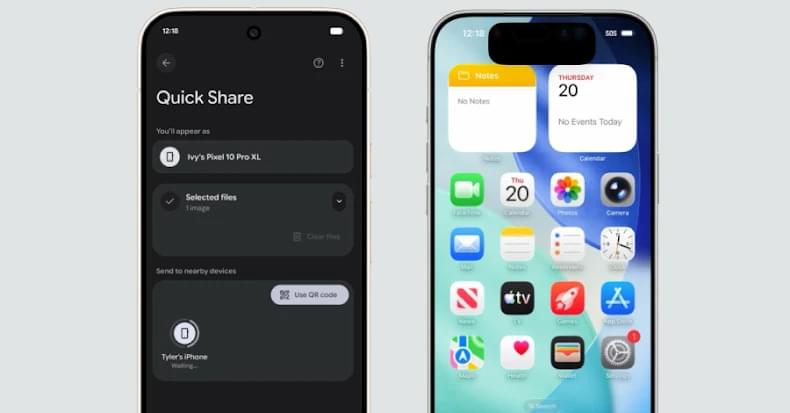
Google expands Quick Share with AirDrop support, boosts Android security, and blocks 115M fraud attempts in India.


Patterns of smartphone use and their impact on mental health are being extensively studied due to the growing dependence of the device in people’s lives.
A recent study tracked late-night smartphone usage in 79 adults with recent suicidal thoughts for 28 days. People using phones late between 11 p.m. and 1 a.m. showed a higher risk of suicidal thoughts the next day, whereas those who actively used the keyboard beyond midnight hours showed a lower risk.
The findings are published in JAMA Network Open.


IronSource Expands Samsung Partnership, Launching on Samsung Mobile Devices in MENA https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20221103005106/en/iro…es-in-MENA
Across West Asia and North Africa (WANA), growing concerns about digital surveillance have placed Israeli cybersecurity firms and their software under intense scrutiny. Among the most alarming cases is AppCloud, a pre-installed application on Samsung’s A and M series smartphones.
The bloatware cannot be uninstalled easily because it runs on the device’s operating system. Uninstalling it requires root access (the highest level of control in a computer system) of the phone to remove the AppCloud package. Its privacy policy is nowhere to be found online and opting out is not always available.
But the real concern lies in who owns AppCloud. When investigating further, we discovered that AppCloud’s privacy policy can be traced back to the controversial Israeli-founded company ironSource (now owned by the American company Unity). ironSource is notorious for its questionable practices regarding user consent and data privacy.
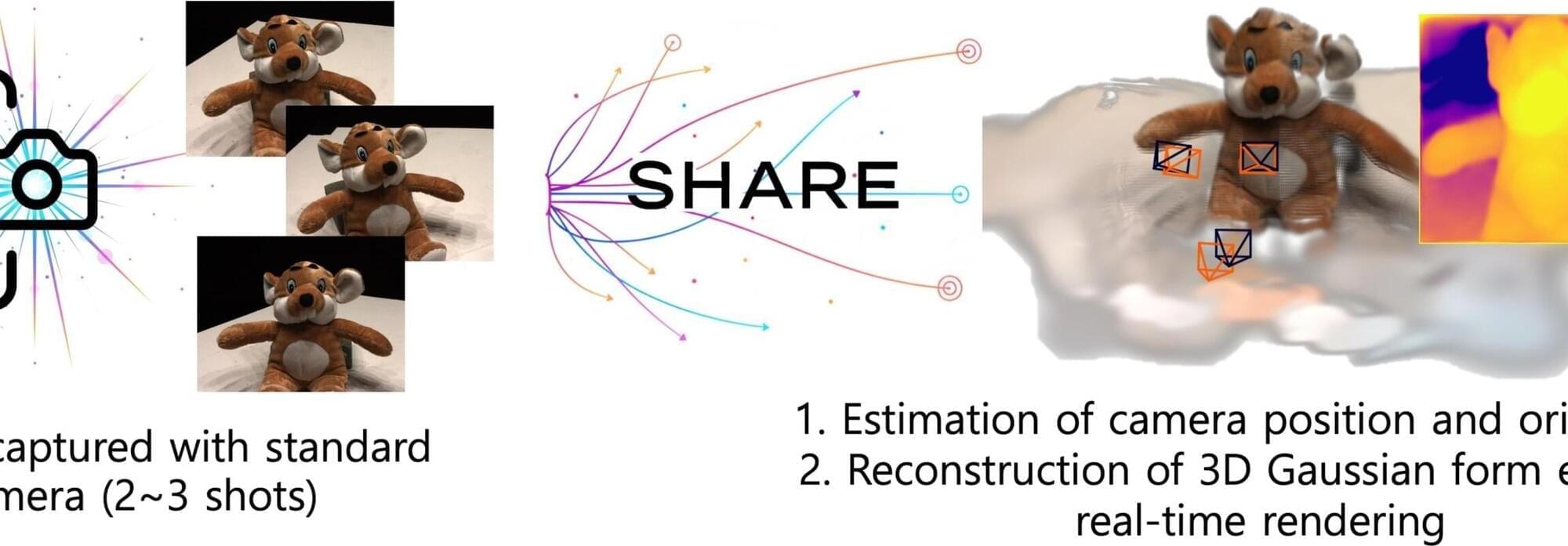
Existing 3D scene reconstructions require a cumbersome process of precisely measuring physical spaces with LiDAR or 3D scanners, or correcting thousands of photos along with camera pose information. A research team at KAIST has overcome these limitations and introduced a technology enabling the reconstruction of 3D—from tabletop objects to outdoor scenes—with just two to three ordinary photographs.
The results, posted to the arXiv preprint server, suggest a new paradigm in which spaces captured by camera can be immediately transformed into virtual environments.
The research team led by Professor Sung-Eui Yoon from the School of Computing developed the new technology called SHARE (Shape-Ray Estimation), which can reconstruct high-quality 3D scenes using only ordinary images, without precise camera pose information.

Google is backpedaling on its decision to introduce new identity verification rules for all developers, stating that it will also introduce accounts for limited app distribution and will allow users to install apps from unverified devs.
As announced in August, Google was planning to introduce what it called “Developer Verification” starting in 2026 to block malware spreading via sideloaded apps sourced from outside the official Google Play app store.
The new rules require that all apps must originate from developers with verified identities to be installed on certified Android devices; otherwise, their installation will be blocked.
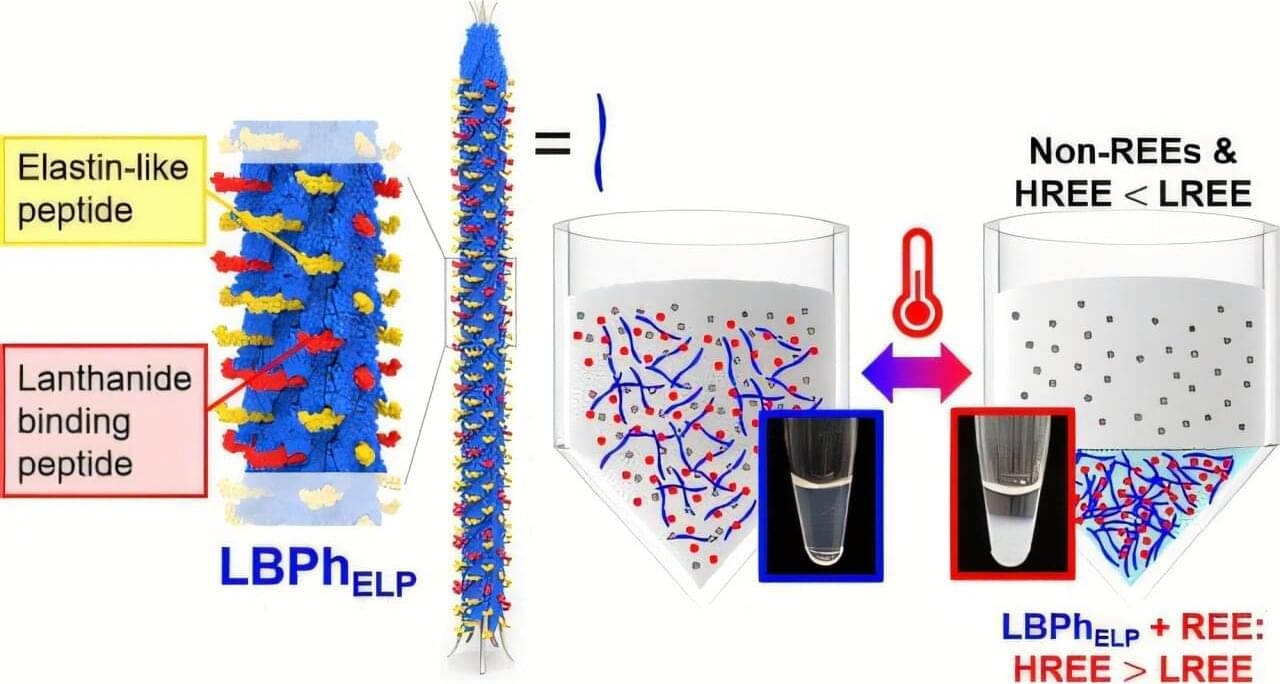
Today’s high-tech electronics and green energy technologies would not function without rare earth elements (REEs). These 17 metals possess unique properties essential to creating items like the phosphors that illuminate our mobile phone displays and the powerful magnets used in electric vehicles and wind turbines. But extracting these substances from raw materials is a dirty process that relies on toxic chemicals and leaves behind polluted waste.
Now, a team of UC Berkeley-led researchers may have solved this problem—thanks to a tiny virus.
As reported in Nano Letters, the researchers genetically engineered a harmless virus to act like a “smart sponge” that grabs rare earth metals from water, and, with a gentle change in temperature and acidity (pH), releases them for collection. Their unusual, groundbreaking approach could lead to a “clean” biological alternative to traditional extraction methods for REEs and other critical elements.
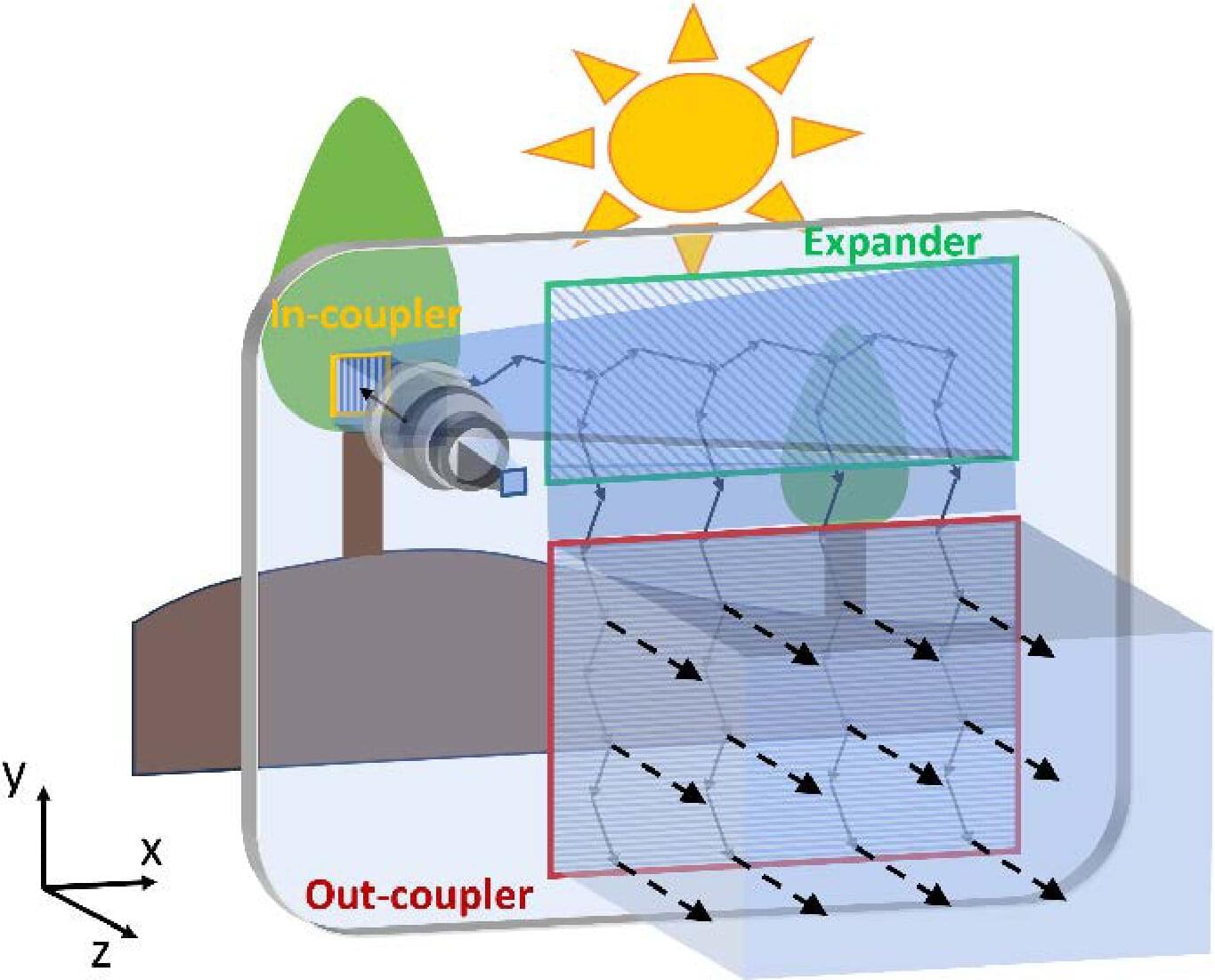
Researchers have designed and demonstrated a new optical component that could significantly enhance the brightness and image quality of augmented reality (AR) glasses. The advance brings AR glasses a step closer to becoming as commonplace and useful as today’s smartphones.
“Many of today’s AR headsets are bulky and have a short battery life with displays that are dim and hard to see, especially outdoors,” said research team leader Nick Vamivakas from the University of Rochester. “By creating a much more efficient input port for the display, our work could help make AR glasses much brighter and more power-efficient, moving them from being a niche gadget to something as light and comfortable as a regular pair of eyeglasses.”
In an article published in the journal Optical Materials Express, the researchers describe how they replaced a single waveguide in-coupler—the input port where the image enters the glass—with one featuring three specialized zones, each made of a metasurface material, to achieve improved performance.
