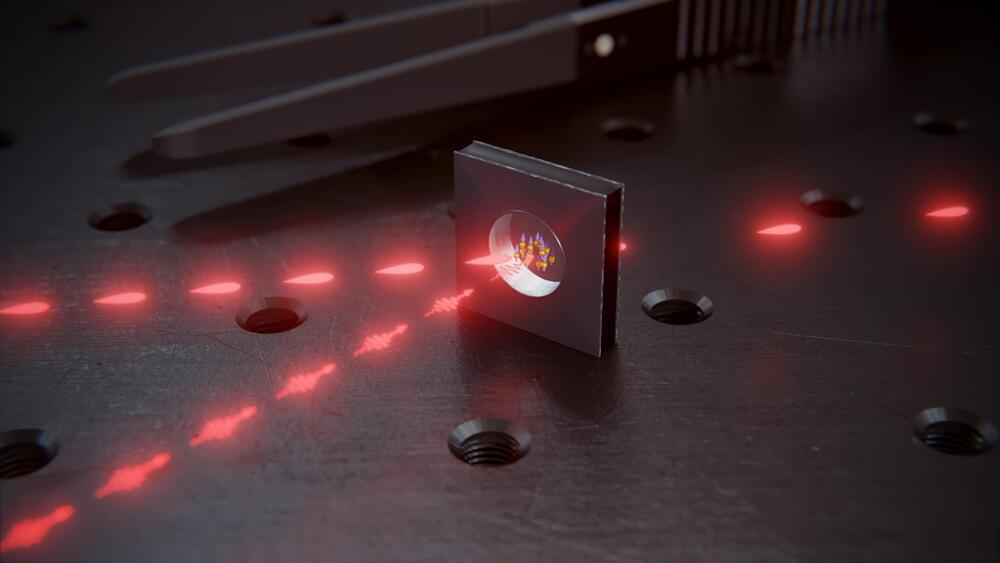
Light pulses can be stored and retrieved in the glass cell, which is filled with rubidium atoms and is only a few millimeters in size.
Light particles are particularly suited to transmitting quantum information.
Researchers at the University of Basel have built a quantum memory element based on atoms in a tiny glass cell. In the future, such quantum memories could be mass-produced on a wafer.
It is hard to imagine our lives without networks such as the internet or mobile phone networks. In the future, similar networks are planned for quantum technologies that will enable the tap-proof transmission of messages using quantum cryptography and make it possible to connect quantum computers to each other.
Like their conventional counterparts, such quantum networks require memory elements in which information can be temporarily stored and routed as needed. A team of researchers at the University of Basel led by Professor Philipp Treutlein has now developed such a memory element, which can be micro-fabricated and is, therefore, suitable for mass production. Their results were published in Physical Review Letters.